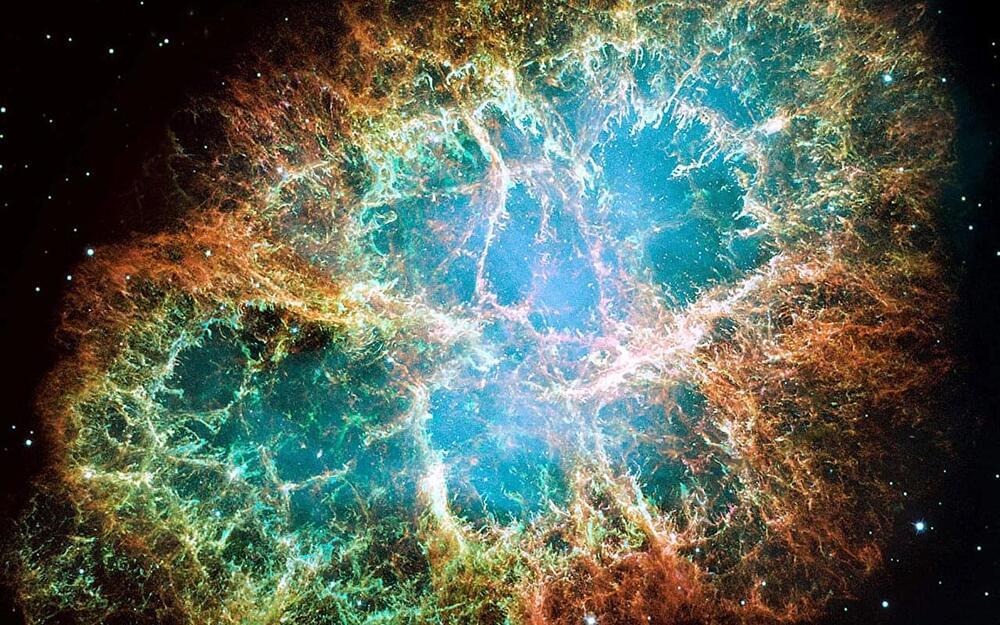
Do you have a telescope? Would you like to see some of the same night sky objects from the ground that Hubble has from space? We invite you to commemorate Hubble’s 35th anniversary by accepting our year-long stargazing challenge. On a clear night, find a safe location with a dark sky away from bright lights, point your telescope skyward, and with the help of star and finder charts, gaze upon some of the same iconic nebulae and galaxies Hubble has observed. How many of them can you find?