What would it be?
Category: space – Page 1,034
Nonprofit Wants to Map Lunar Heritage Sites Using Blockchain
Yellowstone National Park, The Dolomites, Auschwitz Birkenau, The Great Wall … Apollo 11’s Tranquility Base?
For All Moonkind and TODAQ Financial have teamed up to map heritage sites on the Moon—using blockchain.
“Unlike similar sites on Earth that are protected under the UNESCO World Heritage Convention, sites on the Moon which bear witness to unparalleled technological accomplishments are not protected or even recognized by international law,” Michelle Hanlon, space lawyer and co-founder of For All Moonkind, said in a statement.
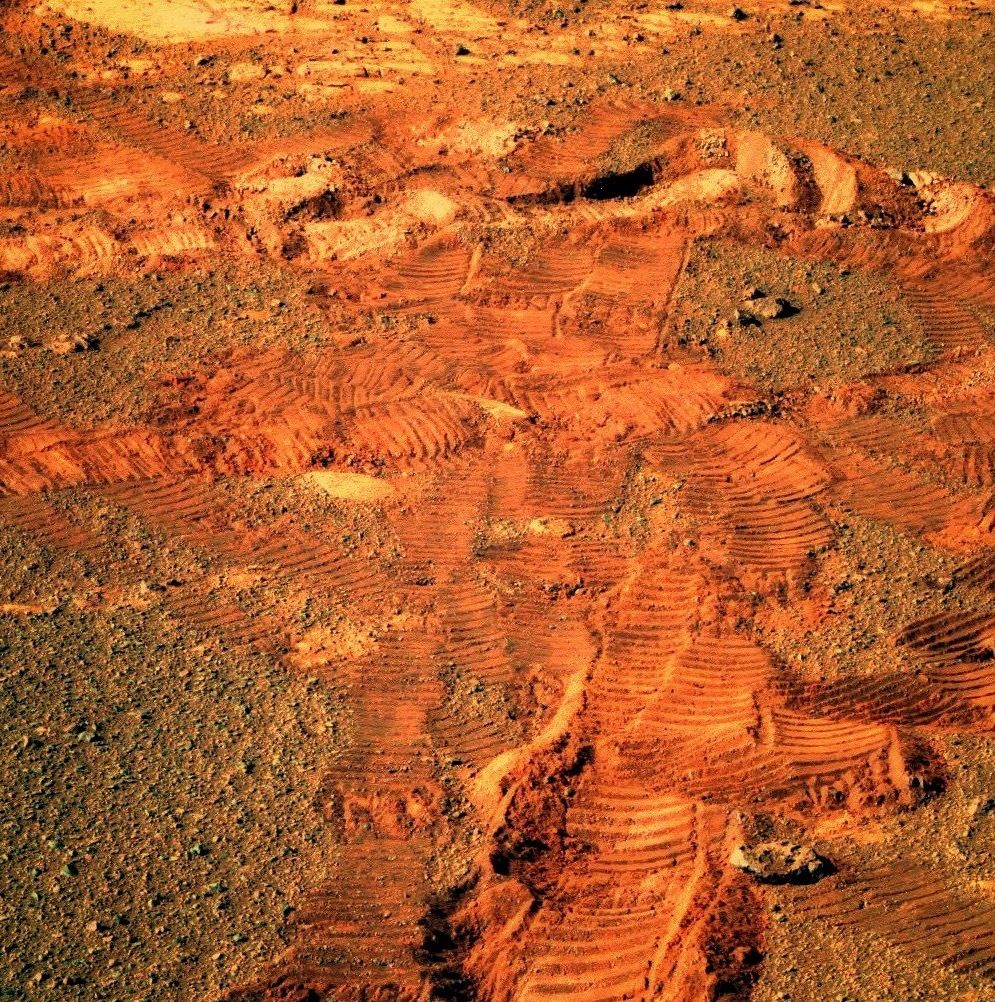

The Mars Exploration Rovers Update: Opportunity Makes Tracks on Magical Mystery Tour of Different Rocks
Update from a space robot rolling around Mars!
Sols 5073–5102
Opportunity continued exploring the south trough of Perseverance in May, still looking for evidence that explains just how this one-of-a-kind valley meandering through Endeavour Crater’s rim formed, and, along the way, helped the Mars Exploration Rover (MER) mission chalk up yet another first, linking with three relay orbiters in one Martian day or sol to send a pipeline of data home.
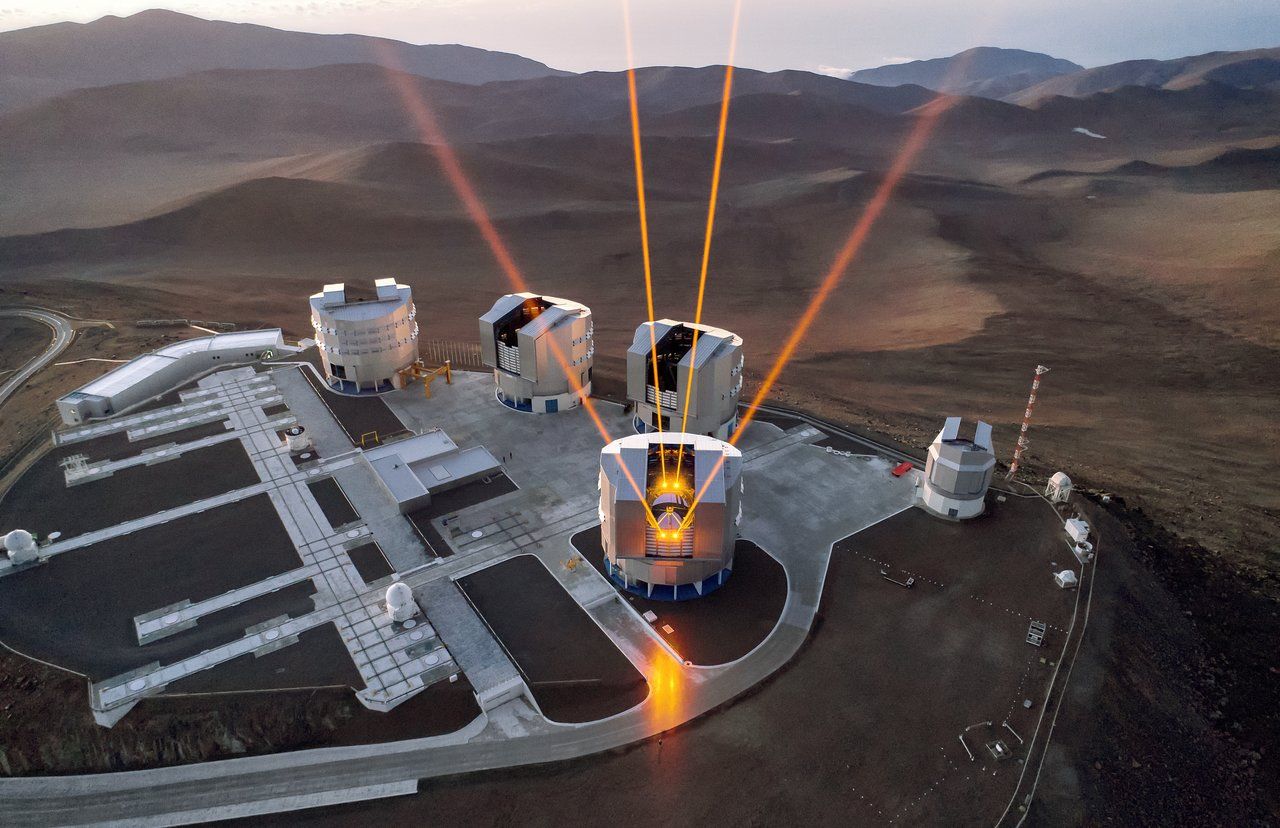


Advancing astronomy one laser at a time
ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) at Paranal Observatory, Chile, is the world’s most advanced optical instrument. The VLT uses state-of-the-art technology to provide the sharpest possible images, including adaptive optics with the laser guide stars shown in this image. The VLT uses these lasers to measure the turbulence in the Earth’s atmosphere, and responds by changing the shape of a mirror to counteract the negative effects of this turbulence.
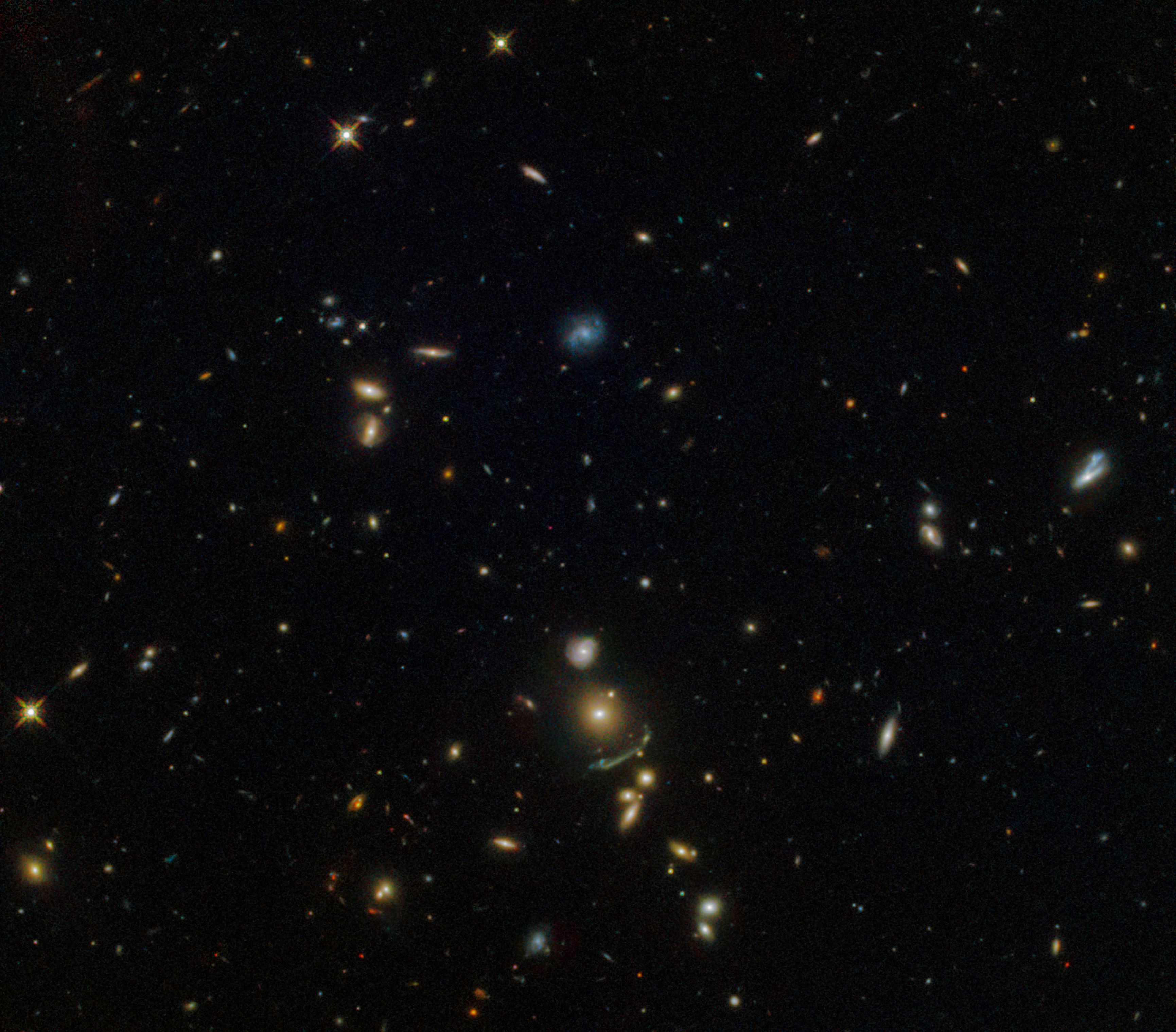

Hubble Spots a Green Cosmic Arc
This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image shows a cluster of hundreds of galaxies located about 7.5 billion light-years from Earth. The brightest galaxy within this cluster, named SDSS J1156+1911, is visible in the lower middle of the frame. It was discovered by the Sloan Giant Arcs Survey, which studied data maps covering huge parts of the sky from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. The survey found more than 70 galaxies that look to be significantly affected by a cosmic phenomenon known as gravitational lensing.
Gravitational lensing is one of the predictions of Albert Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity. The mass contained within a galaxy is so immense that it can actually warp and bend the very fabric of its surroundings (known as space-time), forcing light to travel along curved paths. As a result, the image of a more distant galaxy appears distorted and amplified to an observer, as the light from it has been bent around the intervening galaxy. This effect can be very useful in astronomy, allowing astronomers to see galaxies that are either obscured or too distant to be otherwise detected by our current instruments.
Galaxy clusters are giant structures containing hundreds to thousands of galaxies, some with masses over one million billion times the mass of the Sun! SDSS J1156+1911 is only roughly 600 billion times the mass of the Sun, making it less massive than the average galaxy. However, it is massive enough to produce the fuzzy, greenish streak seen just below the brightest galaxy — the lensed image of a more distant galaxy.
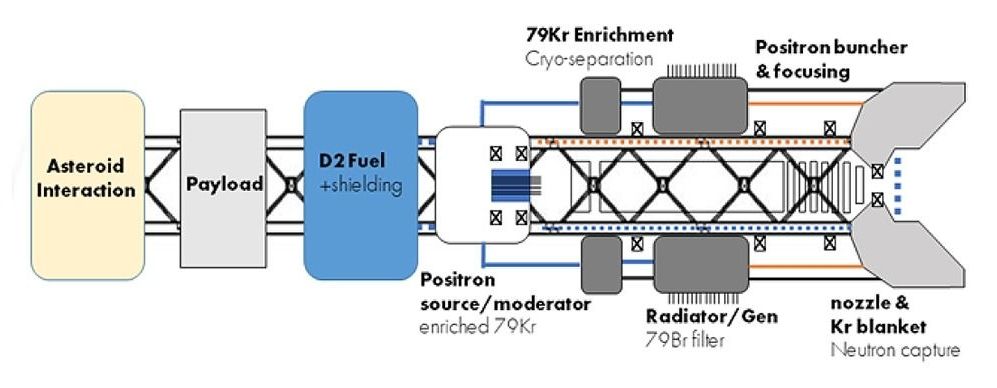
Radioisotope Positron Propulsion
Ryan Weed Positron Dynamics.
Current state of the art in-space propulsion systems based on chemical or ion propellants fail to meet requirements of 21st century space missions. Antimatter is a candidate mechanism for a propulsion system that could transport humans and/or robotic systems with drastically reduced transit times, providing quicker scientific results, increasing the payload mass to allow more capable instruments and larger crews, and reducing the overall mission cost. Unfortunately, previous propulsion concepts relied on unrealistic amounts of trapped antimatter — orders of magnitude away from any near-term capability. The goal of this effort is to determine the feasibility of a (TRL 1–2) radioisotope positron catalyzed fusion propulsion concept that does not rely on trapped antimatter. Such a transformative technology inspires and drives further innovation within the aerospace community and can be applied to a relevant mission — the bulk retrieval of an entire asteroid into translunar space — a mission of great scientific and commercial interest (e.g. asteroid mining). The idea of harnessing resources from asteroids goes back more than a century to Tsiolkovsky. Fundamentally, for asteroid mining to become financially viable, the cost of the retrieval spacecraft must be less than the value gained from the asteroid. Therefore, developing technology (e.g. efficient propulsion systems) that decreases the mass and complexity of the retrieval spacecraft must be a priority.
Editor: Loura Hall

Testing deflection
In 2022, NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) collides with the smaller body of the Didymos binary asteroid system in an attempt to measurably shift its orbit.
ESA’s Hera mission, now under study, will examine the aftermath of this impact to help determine whether humans can deflect threatening asteroids.
Hera will also demonstrate the ability to operate at close proximity around a low-gravity asteroid with some on-board autonomy similar in scope to a self-driving car, going on to deploy Europe’s first deep-space CubeSats, and potentially also a micro-lander, to test out a new multi-point intersatellite link technology.
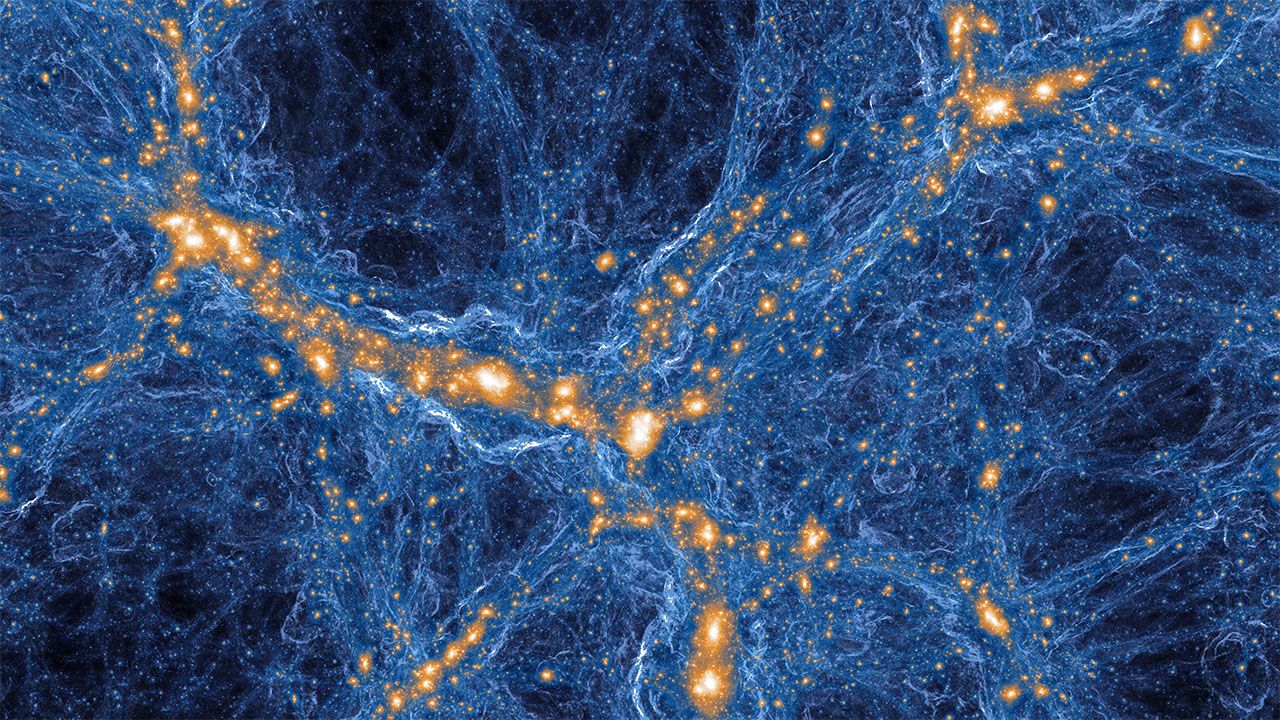
Galaxy simulations are at last matching reality—and producing surprising insights into cosmic evolution
In general, modelers attack the problem by breaking it into billions of bits, either by dividing space into a 3D grid of subvolumes or by parceling the mass of dark and ordinary matter into swarms of particles. The simulation then tracks the interactions among those elements while ticking through cosmic time in, say, million-year steps. The computations strain even the most powerful supercomputers. BlueTides, for example, runs on Blue Waters—a supercomputer at the University of Illinois in Urbana that can perform 13 quadrillion calculations per second. Merely loading the model consumes 90% of the computer’s available memory, Feng says.
For years such simulations produced galaxies that were too gassy, massive, and blobby. But computer power has increased, and, more important, models of the radiation-matter feedback have improved. Now, hydrodynamic simulations have begun to produce the right number of galaxies of the right masses and shapes—spiral disks, squat ellipticals, spherical dwarfs, and oddball irregulars—says Volker Springel, a cosmologist at the Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies in Germany who worked on Millennium and leads the Illustris simulation. “Until recently, the simulation field struggled to make spiral galaxies,” he says. “It’s only in the last 5 years that we’ve shown that you can make them.”
The models now show that, like people, galaxies tend to go through distinct life stages, Hopkins says. When young, a galaxy roils with activity, as one merger after another stretches and contorts it, inducing spurts of star formation. After a few billion years, the galaxy tends to settle into a relatively placid and stable middle age. Later, it can even slip into senescence as it loses its gas and the ability make stars—a transition our Milky Way appears to be making now, Hopkins says. But the wild and violent turns of adolescence make the particular path of any galaxy hard to predict, he says.

China invites international researchers to do science on its future space station
By the end of 2022, China hopes to have its biggest space station yet orbiting around Earth, and the country’s space agency wants other nations to use it. China is inviting all members of the United Nations to submit applications to fly experiments on board the future habitat, dubbed the China Space Station. It’s a major step toward international cooperation for China and its space program, which has mostly relied on domestic hardware and capabilities in the past.
“The China Space Station belongs not only to China, but also to the world,” Shi Zhongjun, China’s ambassador to the UN, said in a statement about the initiative. As a guide for the decision, Zhongjun cited the 50-year-old Outer Space Treaty, which maintains that the exploration of space should be peaceful and benefit all countries.