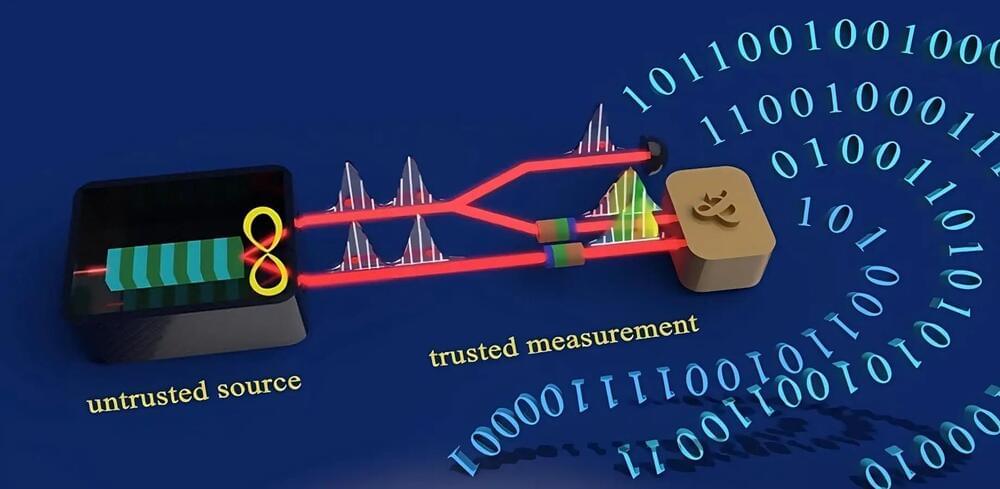
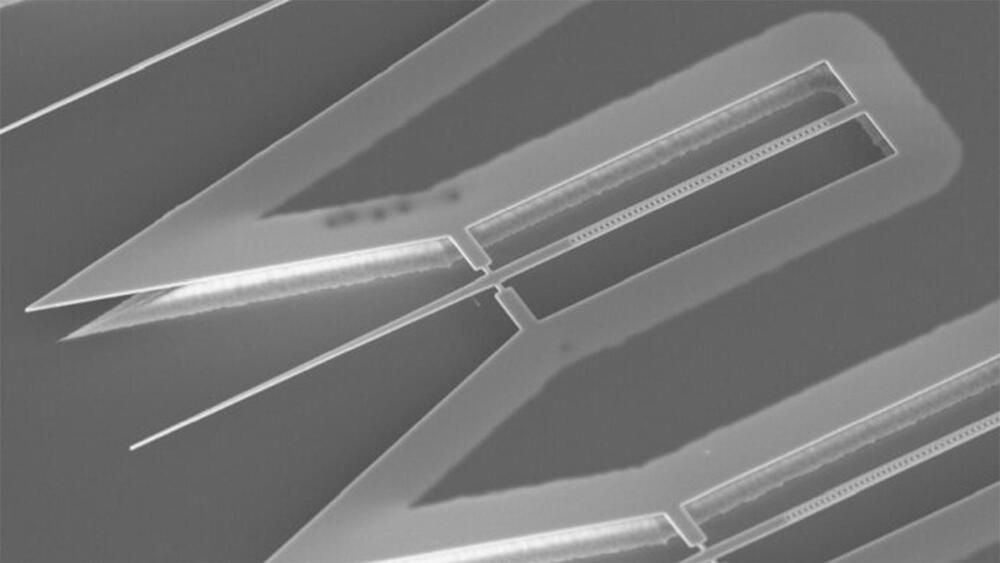
Quantum information (QI) processing may be the next game changer in the evolution of technology, by providing unprecedented computational capabilities, security and detection sensitivities. Qubits, the basic hardware element for quantum information, are the building block for quantum computers and quantum information processing, but there is still much debate on which types of qubits are actually the best.
Research and development in this field is growing at astonishing paces to see which system or platform outruns the other. To mention a few, platforms as diverse as superconducting Josephson junctions, trapped ions, topological qubits, ultra-cold neutral atoms, or even diamond vacancies constitute the zoo of possibilities to make qubits.
So far, only a handful of qubit platforms have been demonstrated to have the potential for quantum computing, marking the checklist of high-fidelity controlled gates, easy qubit-qubit coupling, and good isolation from the environment, which means sufficiently long-lived coherence.