Microsoft’s October 2024 Patch Tuesday addresses 118 vulnerabilities, two under active exploitation. Apply fixes now.



The digital landscape is constantly changing, and with it, the nature of threats. Social media now plays a crucial role in an organization’s brand and reputation, making it imperative to secure these accounts as part of a comprehensive SaaS security strategy. SSPM social media integrations offer the visibility, control, and protection required to safeguard these essential assets.
Learn how to secure your social accounts now
Found this article interesting? This article is a contributed piece from one of our valued partners. Follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn to read more exclusive content we post.


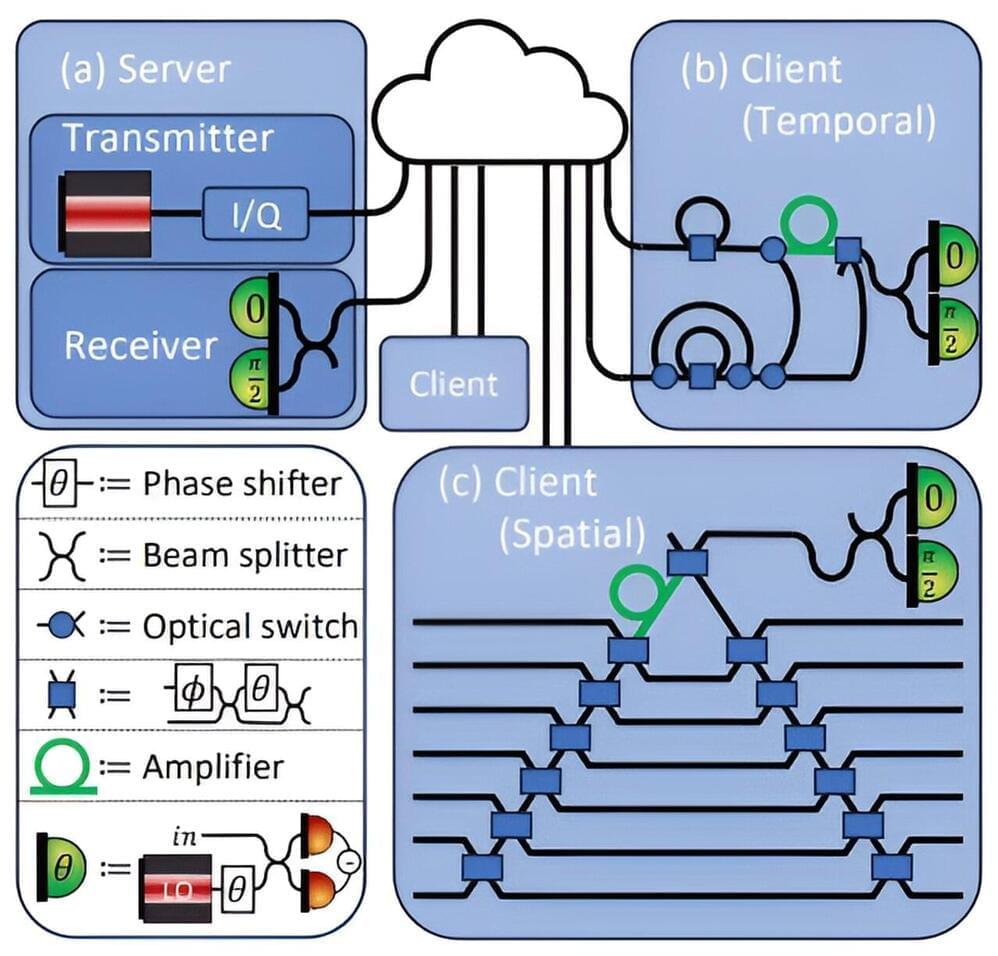
Quantum computers and quantum communication are groundbreaking technologies that enable faster and more secure data processing and transmission compared to traditional computers. In quantum computers, qubits serve as the fundamental units of information, functioning as the quantum mechanical equivalent of bits in classical computing.
Where, for example, laser pulses in a glass fiber transport information from A to B in classical digital communication, quantum mechanics uses individual photons. In principle, this makes it impossible to intercept the transmitted data. Qubits that are optically addressable (can be controlled or read out with light) are suitable for storing the photons’ information and processing it in quantum computers. The qubits can store and process quantum states, and absorb and emit them in the form of photons.
The US government has launched a new supercomputer in Livermore, California.
The Department of Defense (DoD) and National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) this month inaugurated a new supercomputing system dedicated to biological defense at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL).
Specs not shared, but same architecture as upcoming El Capitan system.
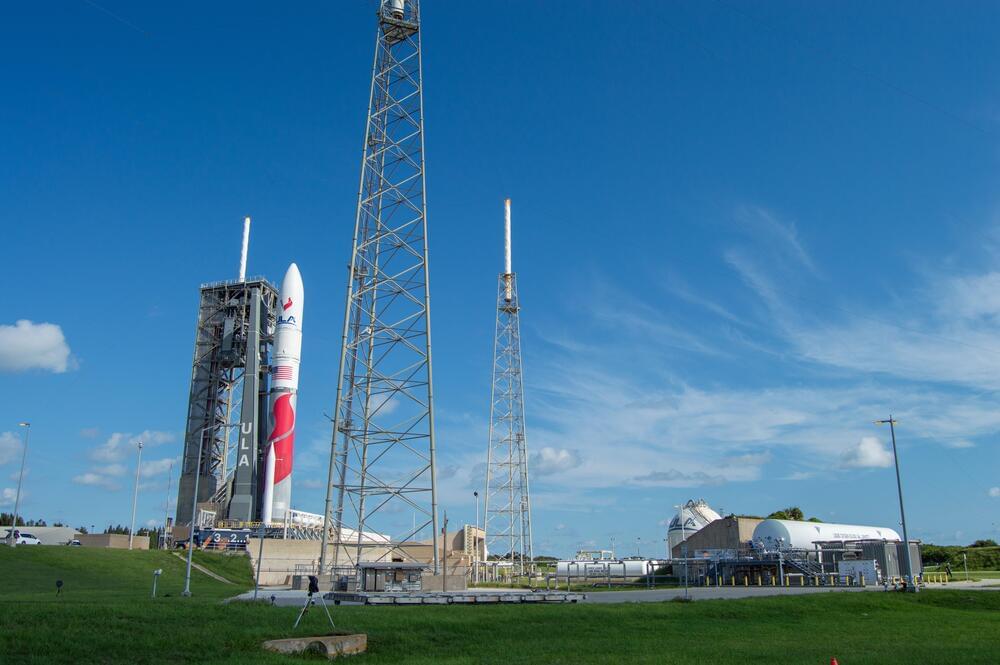




marking a critical milestone in ULA’s path toward certifying the Vulcan Centaur for national security missions with the U.S. Space Force.
The Vulcan VC2S rocket is set to launch the Cert-2 mission from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida, during a launch window on Friday, October 4, 2024, between 6:00 and 9:00 a.m. EDT.
This mission includes an inert payload and key technology demonstrations for the Centaur V upper stage.