A team of researchers from University of Toronto Engineering has discovered hidden multi-dimensional side channels in existing quantum communication protocols.
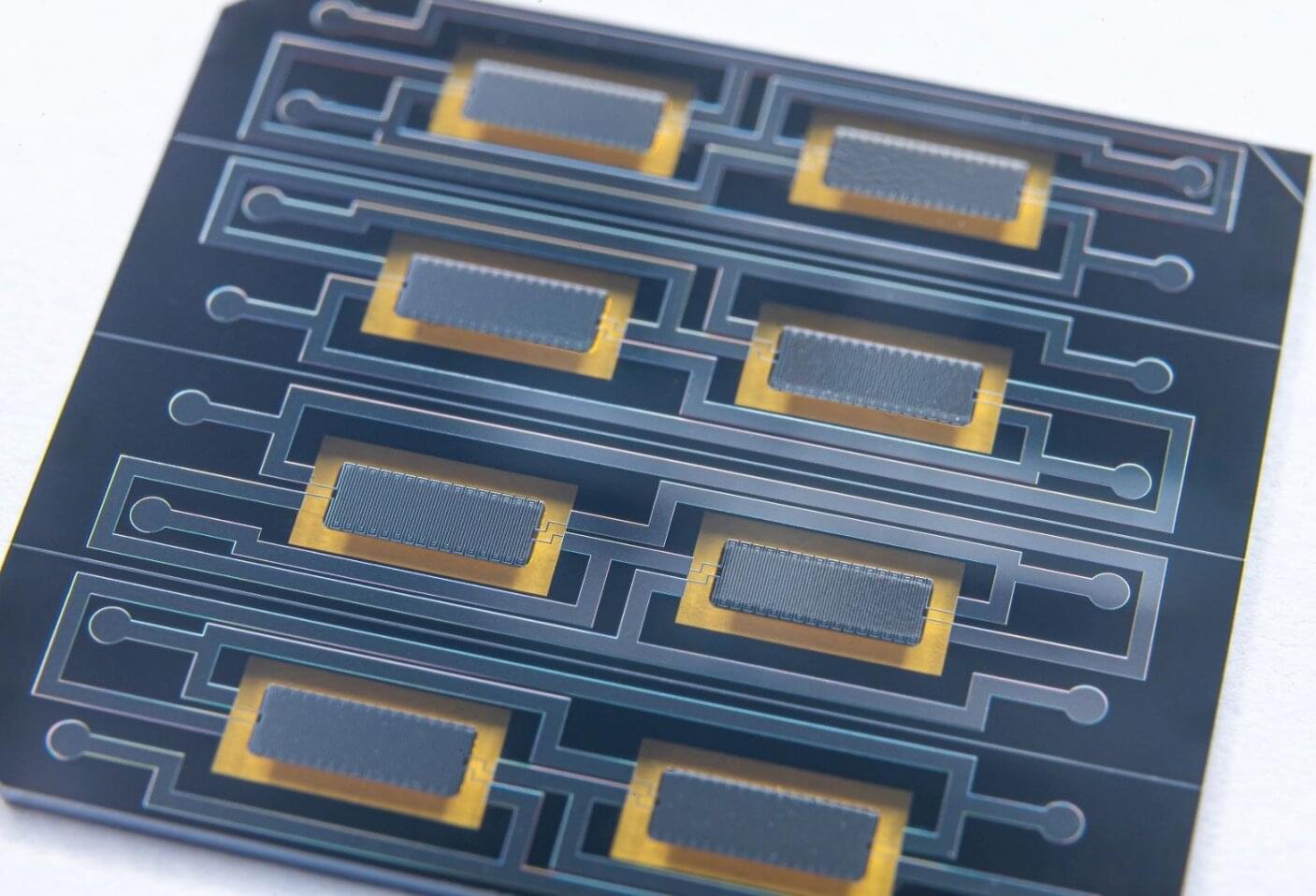
The new side channels arise in quantum sources, which are the devices that generate the quantum particles —typically photons—used to send secure messages. The finding could have important implications for quantum security.
“What makes quantum communication more secure than classical communication is that it makes use of a property of quantum mechanics known as conjugate states,” says Ph.D. student Amita Gnanapandithan, lead author on a paper published in Physical Review Letters.