Musk has scored bragging rights in the battle of billionaires in space after his SpaceX rockets beat competition from Bezos’s Blue Origin to launch National Security payloads for the U.S. Air Force.
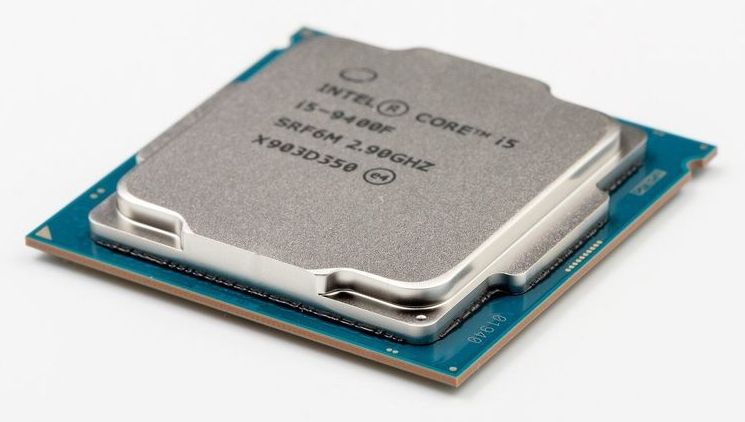



Intel suffered a massive breach Thursday as 20 GB of internal documents were published online.
The confidential documents contain data on the internal designs of chipsets dating back to 2016.
The data were sent by an anonymous source to a Swiss software engineer, Till Kottmann, who specializes in uploading hacked documents. He does so, he has said, to encourage companies to exercise more caution concerning security and “to better find and assess potential issues.” But he admits he is also motivated to release unauthorized documents obtained from hackers “to free information” for all to see.
US chipmaker Intel is investigating a security breach after earlier today 20 GB of internal documents, with some marked “confidential” or “restricted secret,” were uploaded online on file-sharing site MEGA.
The data was published by Till Kottmann, a Swiss software engineer, who said he received the files from an anonymous hacker who claimed to have breached Intel earlier this year.
Kottmann received the Intel leaks because he manages a very popular Telegram channel where he regularly publishes data that accidentally leaked online from major tech companies through misconfigured Git repositories, cloud servers, and online web portals.
Two California companies were selected for DARPA’s Gamma Ray Inspection Technology (GRIT) program and have begun work to develop a transportable, tunable source of gamma rays for a host of national security, industrial, and medical applications.
Lumitron Technologies and RadiaBeam Technologies started work on the GRIT program in April and are exploring novel approaches to achieve high-intensity, tunable, and narrow-bandwidth sources of gamma ray radiation in a compact, transportable form factor.
GRIT aims to provide a source of tunable, pure x-rays and gamma rays from tens of keV (kilo-electron volts) up through three MeV (mega-electron volts). Currently, tunable and narrow bandwidth gamma ray sources only exist at highly specialized user facilities best suited for basic research and are not able to support broad practical applications. Shrinking these photon sources to a transportable system is the major goal and challenge of the GRIT program.

Consumers are ending up increasingly responsive about sharing their data, as data integrity and security has turned into a developing concern. In any case, with the advent of nations teching up with facial recognition, even explorers need to truly begin thinking about what sort of data they could be reluctantly offering to nations, individuals and places.
Facial recognition innovation is a framework that is fit for identifying or confirming an individual from an advanced picture or a video frame. It works by comparing chosen facial highlights and faces inside a database. The technology is utilized in security frameworks and can be compared with different biometrics, for example, fingerprint or iris recognition frameworks. As of late, it has been grabbed and utilized as a business identification and advertising tool. The vast majority have a cell phone camera fit for recognizing features to perform exercises, for example, opening said a cell phone or making payments.
The worldwide market for facial recognition cameras and programming will be worth of an expected $7.8 billion, predicts Markets and Markets. Never again consigned to sci-fi films and books, the technology is being used in various vertical markets, from helping banks recognize clients to empowering governments to look out for criminals. Let’s look at some of the top countries adopting facial recognition technology.
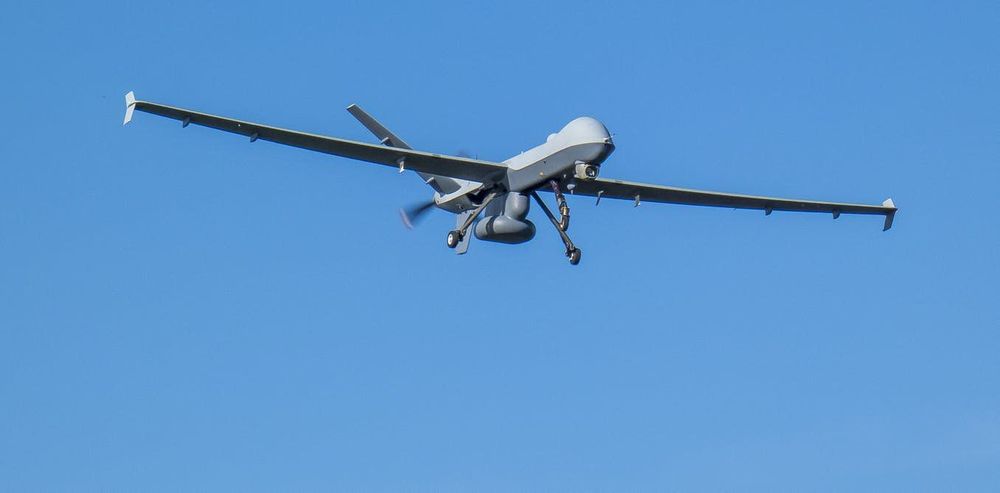

Drones of all sizes are being used by environmental advocates to monitor deforestation, by conservationists to track poachers, and by journalists and activists to document large protests. As a political sociologist who studies social movements and drones, I document a wide range of nonviolent and pro-social drone uses in my new book, “The Good Drone.” I show that these efforts have the potential to democratize surveillance.
But when the Department of Homeland Security redirects large, fixed-wing drones from the U.S.-Mexico border to monitor protests, and when towns experiment with using drones to test people for fevers, it’s time to think about how many eyes are in the sky and how to avoid unwanted aerial surveillance. One way that’s within reach of nearly everyone is learning how to simply disappear from view.

Bitcoin hardware wallet maker Ledger revealed today that its e-commerce database was hacked last month, leaking 1 million emails and some personal documents. No user funds were affected by the breach.
Ledger said the attack targeted only its marketing and e-commerce database, meaning the hackers were unable to access users’ recovery phrases or private keys. All financial information—such as payment information, passwords, and funds—was similarly unaffected. The breach was unrelated to Ledger’s hardware wallets or its Ledger Live security product, the company added.
“Solely contact and order details were involved. This is mostly the email address of approximately [1 million] of our customers. Further to the investigation, we have also been able to establish that a subset of them was also exposed: first and last name, postal address phone number, and product(s) ordered,” said Ledger in its announcement.

Thorcon said it would provide technical support to the ministry’s research and development (R&D) body to develop “a small-scale TMSR reactor under 50 megawatts (MW)”, the company wrote in a statement on Friday, Jul. 24.
“[This will] strengthen national security in the outermost, frontier and least developed regions,” reads the company’s statement.
In a separate statement on Jul. 22, the Defense Ministry said the deal would help it accomplish its 2020–2024 strategic plan but did not mention a planned capacity.
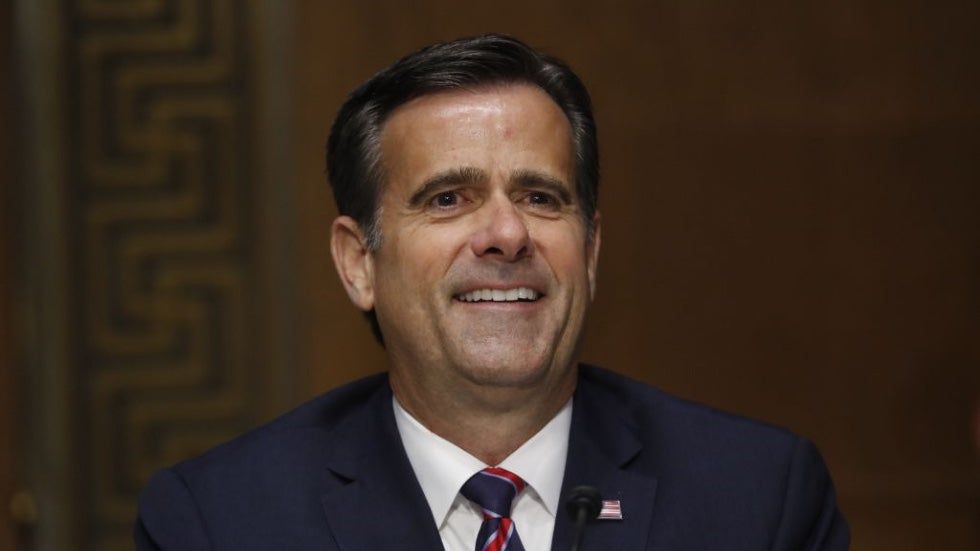

The U.S. intelligence community (IC) on Thursday rolled out an “ethics guide” and framework for how intelligence agencies can responsibly develop and use artificial intelligence (AI) technologies.
Among the key ethical requirements were shoring up security, respecting human dignity through complying with existing civil rights and privacy laws, rooting out bias to ensure AI use is “objective and equitable,” and ensuring human judgement is incorporated into AI development and use.
The IC wrote in the framework, which digs into the details of the ethics guide, that it was intended to ensure that use of AI technologies matches “the Intelligence Community’s unique mission purposes, authorities, and responsibilities for collecting and using data and AI outputs.”

🤔
In October 2019, the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security hosted a pandemic tabletop exercise called Event 201 with partners, the World Economic Forum and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. Recently, the Center for Health Security has received questions about whether that pandemic exercise predicted the current novel coronavirus outbreak in China. To be clear, the Center for Health Security and partners did not make a prediction during our tabletop exercise. For the scenario, we modeled a fictional coronavirus pandemic, but we explicitly stated that it was not a prediction. Instead, the exercise served to highlight preparedness and response challenges that would likely arise in a very severe pandemic. We are not now predicting that the nCoV-2019 outbreak will kill 65 million people. Although our tabletop exercise included a mock novel coronavirus, the inputs we used for modeling the potential impact of that fictional virus are not similar to nCoV-2019.