The Alzheimer’s Hypothesis
Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease was first discovered in 1907 in a 51 year old woman by the German physician A. Alzheimer. One of the first changes noticed was an eruption of jealous feelings towards her husband. It wasn’t long before symptoms of rapid memory impairment were observed. The impairments prevented her from finding her way out of her home, She hid herself, she would drag objects to and fro, and occasionally screamed because she believed people were out to kill her.
When she was institutionalized her gestures would show a complete helplessness. As common in most Alzheimer’s patients, she was disoriented as to time and place. At times she would state that she didn’t understand anything, felt confused, and totally lost. When the doctor came in to see her she would consider it as an official visit and would apologize for not having finished her work. Other times she would be terrified and start to yell that the doctor wanted to operate on her. Other times she would send him away in complete indignation uttering phrases indicating that she was afraid that the doctor wanted to damage her woman’s honor. At times she would become completely delirious , dragging her blankets and to and fro, calling for her husband and daughter, and seeming to experience auditory hallucinations. She would often scream for hours and hours in a horrible voice. Mental regression advanced quite steadily. After four and a half years of illness the patient finally died.
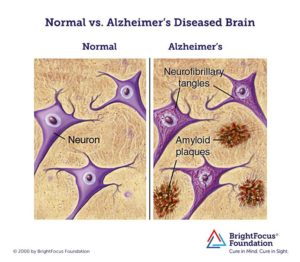
Alzheimer performed a postmortem examination of the woman’s brain. He paid special attention to changes in the “neurofibrils,” fibers in the cytoplasm of a nerve axon — elements of the cytoskeleton that can be stained by a silver solution.
The Bielschowsky silver preparation showed very characteristic changes in the neurofibrils. Looking inside an apparently normal-looking cell, however, one or more single fibers became observably prominent through their striking thickness and specific impregnability. At a more advanced stage many many fibers arranged in parallel showed the same changes. Over time they formed dense bundles and gradually advanced to the surface of the cell. The cell and nucleus would eventually disappear, leaving only a tangled bindle of fibrils where the neuron once was.
Since these fibrils can be readily stained with certain dyes, a chemical transformation of the fibril substance must have taken place. This might be why the fibrils survived the destruction of the cell. The transformation of the fibrils seems to go hand in hand with the storage of an as-of-yet not closely investigated pathological byproduct of neuronal metabolism. Such alterations were found in about one-quarter to one-third of all the neurons in the cerebral cortex. Numerous neurons, especially in the upper cell layers, had completely disappeared.
The number and distribution of neurofibrillary tangles, what are commonly known as the “tombstones” of dead and dying neurons, are correlated with the severity of the symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease.
Phase1
What is the purpose of beta-amyloid?
Alzheimer’s disease causes impairment with memory, thinking, and behavior. Alzheimer’s affects 5.5 million people age 65 and older and approximately 200,000 individuals under the age 65. Alzheimer’s disease is the 5th leading cause of death in the United States. The root cause of Alzheimer’s is still unknown. There are several hypothesis that attempt to explain it. This article focuses on the research being done in a joint effort between a team from Harvard University being led by Rudolf Tanzi and Robert Moir at Boston Massachusetts General Hospital.
Tanzi and Moir investigated the development of Alzheimer’s disease in animals and found the development of amyloid plaques is not unique to humans. 70 percent of vertebrates share certain sequences of particular amino acids in human beta-amyloid. Moir believes because this sequence is shared so widely and has not changed over time that it must be doing something very important. Moir discovered that the antimicrobial peptide LL37 acts as one of the brain’s defenses against microbes alongside beta-amyloid.
In order to test this hypothesis, the team injected the brains of mice that were bred to develop Alzheimer’s plaques comparable to the way humans do with bacteria. Overnight, the mice produced plaques. Tanzi discovered that each plaque had a single bacterium in it. A single bacterium can induce an entire plaque.
25 May 2016
New Scientist
Science Translational Medicine 25 May 2016:
Vol. 8, Issue 340, pp. 340ra72
DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf1059
Amyloid-β peptide protects against microbial infection in mouse and worm models of Alzheimer’s disease
Full Abstract
Phase 2
The Role of Sleep on the Brian’s Filtration System
Lulu Xie and team recently uncovered one of the key functions of sleep. The team compared 2 arousal states in the mouse, sleeping and awake, using state-of-the-art in vivo two-photon imaging. The researchers found that metabolic waste products of neural activity were cleared out of the sleeping brain at a faster rate than during the awake state. Like the accumulation of beta amyloid plaques, sleep is a cross-species phenomenon.
The study by Xie et. al reports that the critical function of metabolic homeostasis is dependant on sleep. The team utilized real-time assessments of tetramethylammonium diffusion and two-photon imaging in live mice. The experiment found a 60 percent increase in the interstitial space in association of natural sleep or anesthesia. This resulted in a noticeable convective exchange of cerebrospinal fluid and interstitial fluid, which are found in the spaces between the blood vessels and surrounding cells.
Thus as a result convective fluxes the rate of β-amyloid clearance during sleep. Hence, the restorative function of sleep may be a consequence of the enhanced removal of potentially neurotoxic waste products that accumulate during our waking hours.
Sleep Drives Metabolite Clearance from the Adult Brain
Science 18 Oct 2013:
Vol. 342, Issue 6156, pp. 373–377
DOI: 10.1126/science.1241224
Full Abstract
In a separate study Ehsan Shokri-Kojori and team published a study on April 9 2018 showing that just 1 night of sleep deprivation builds β-Amyloid within the brain.
PNAS April 24, 2018 115 (17) 4483–4488
Full Abstract

On September 5th of this year The Sleep Research Society came out with a report that collaborates with the data suggesting just how important the role of sleep is to prevent Alzheimer’s disease. The Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging, conducted by Adam P Spira et al showed that those who experienced excessive sleepiness during normal waking hours were nearly three times more likely to have brain deposits of beta amyloid than those who didn’t.
PET scan of a human brain with Alzheimer’s disease
Sleep, zsy152
Published: 05 September 2018
Full Abstract
The accumulated evidence above shows that Beta-Amyloid are part of the brain’s ancient immune system . The evidence also indicates that the buildup of Beta-amyloid plaques occurs when it’s not flushed out. Many researchers, including Rudolf Tanzi and Robert Moir believe that it is the plaques that cause the damage to the brain.
Phase 3
The fIltration System of the Brain
The re-discovery of cellular membranes around the brain known as meningers has a network of lymphatic vessels that drain macromolecules from the CNS (cerebrospinal and interstitial fluids) into the cervical lymph nodes in mice. This lymphatic system was first discovered in 1787 (Mascagni, P. Vasorum lymphaticorum corporis humani historia et ichnographia) and was rediscovered by Da Mesquita et al.
Their research showed that meningeal lymphatics play a central role in brain health and disease by helping to maintaining both cognitive function and proteostasis.
The purpose of the lymphatic system in the body is to drain tissue of interstitial fluid that houses cellular debris and toxic chemicals. A rich protein-fluid called lymph is formed by interstitial fluids which circulates through the lymphatic system before returning to the blood. Lymph is filtered through the lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are responsible for initiating immune responses when foreign particles are detected.
Because the brain does not have its own lymphatic vessels it utilizes the interstitial fluid (ISF) along the walls of blood vessels to transport waste and proteins from the parenchyma to reach the cerebrospinal fluid that circulates through the meninges. The transvascular process is the process in which metabolic waste products, proteins, and other molecules in these fluids are removed from the brain by being transported along the walls of blood vessels, which crosses the blood-brain barrier. To what extent, if any, the meningeal lymphatic vessels were also involved in waste clearance is still unknown.
To verify the critical role of the meningeal lymphatic vessels Da Mesquite et. al injected a drug designed to damage the vessels into one of the three principal openings in the subarachnoid space between the arachnoid and pia mater layers of the meninges surrounding the brain, collectively referred to as the cisterna magna. In order to track the CSF they injected a fluorescent tracer molecule. This provided insight as to where the fluid goes in mice lacking meningeal lymphatic vessels. Da Mesquite et. al noted that the the tracer did not travel deep into the cervical lymph nodes in mice lacking meningeal lymphatic vessels. Injecting high concentrations of a tracer into the CSF can cause the diffusion of a tracer into the brain along blood vessels as shown by previous work — but this too was also reduced. The researchers used different tracers, surgically closing off drainage to the deep cervical lymph nodes; and examined mice with impaired lymphatic vessel development . The authors were able to confirm through these various methods the results by doing so.
The authors also noted that deficits within spatial orientation and memory were a result of meningeal lymphatic destruction.
Another interesting finding by the researchers was a change in gene expression within the hippocampus, a substructure crucial to memory and spatial orientation.
The gene expression resembled those previously observed in neurodegenerative disorders. The accumulated evidence by these experiments suggests collectively that the drainage of brain ISF and CSF by meningeal lymphatics is critical to proper function of cognition within the brain.
These findings present an interesting question: where exactly did the tracers go? One study (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1038/icb.1951.30) suggests that tracers injected into the cisterna magna are transported primarily in the blood and that the lymphatic system is only secondary. To reveal whether the impairment of meningeal lymphatics can lead to a shift in the pathways responsible for controlling brain proteostasis the simultaneous measurements of tracers movements meningeal lymphatics, other lymphatic vessels, (for example the neck) and the blood may give insights into whether there’s an increase in the transvascular removal of waste products across the blood-brain barrier and/or their drainage into the venous system in the meninges.
The next observation by Da Mesquita’s team was a decrease in the diameter and coverage of meningeal lymphatic vessels through induced aging. The researchers also observed a decrease in drainage of tracers from the ISF and CSF into deep cervical lymph nodes. The signaling of the pathway involving vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) and its receptor VEGFR3 promotes lymphatic vessel growth in mice. Likewise when the pathway involving endothelial growth was damaged it caused a loss of meningeal lymphatic vessels. Moreover the authors showed that there was an increase diameter of meningeal lymphatic vessels by providing treatment VEGF-C, improving lymphatic drainage as a result. Consistent with the accumulated research, Da Mesquita et al. showed that the drainage of CSF tracer could be restored into deep cervical lymph nodes by the local delivery of the vegf-c into the cisterna of old mice with a viral vector . This resulted in the restoration of spatial orientation.
The accumulation of amyloid-β protein within the brain, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease, causes age related impairments in the transvascular clearance of waste. The effects of of ablating the meningeal lymphatics in two mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease, in which amyloid-β protein is produced in neurons and secreted into the ISF was investigated by Da Mesquita and team. The results showed that ablation led to the accumulation of amyloid-β protein in the meningenges. The authors also noted to the potential relevance for humans by showing that amyloid-β had accumulated in meningenges of people who had Alzheimer’s disease as well.
When amyloid-β protein deposition in the brain parenchyma first became apparent, Da Mesquita and colleagues discovered that the two mouse models did not exhibit any apparent structural or functional changes in the meningeal lymphatics at the time. Cognitive impairment could not be prevented in either model using viral delivery vegf-c, which points to another disruption in another clearance pathway the early amyloid-β deposition and cognitive impairments in these two models-most likely the transvascular clearance. More than likely an increased burden is placed upon meningeal lymphatic system due to the gradual deterioration of transvascular-clearance routes through aging. Faulty lymphatic drainage of amyloid-β and other proteins from the ISF and CSF may be caused when the capacity of the lymphatic system is reached. This gives strong evidence to suggest that there is a very delicate relationship between meningeal lymphatics and blood vessels in the regulation of proteostasis in the brain.
In order to open new directions for research into cognition, neurodegeneration, and Alzheimer’s disease, the improvement of our understanding of waste clearance pathways from the brain, how the ISF and the CSF drain into the meningeal lymphatics, and how these lymphatic vessels interact with the blood vessels at the blood-brain barrier is vital. The potential of improving clearance with meningeal lymphatics to rebuild brain proteostasis, and may lessen amyloid-β protein deposition have been shown by Da Mesquita et al. to rely upon the local growth of lymphatic vessels. Whether or not the improvement of the impaired function of blood vessels due to aging, and whether enhancing clearance at the blood-brain barrier can improve lymphatic drainage function, remains to be to determined.
Nature 25 July 2018
A lymphatic-waste disposal system implicated in Alzheimer’s Disease
Naturevolume 560, pages185–191 (2018
Functional aspects of meningeal lymphatics in ageing and Alzheimer’s disease
Full Abstract
The accumulated evidence shows that Beta-amyloid may prove to be beneficial in killing off microbes, but also that proper rest is needed to activate the filtration system of the brain to consistently flush out these neurotoxins before they cause impairment or disease . Further research into the prevention of age-related damage to the brain’s lymphatic system may offer clues as to how we can prevent cognitive decline of age-related diseases. Ideally this will be done with protective mechanisms the brain already has in place.
Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease — Volume Pre-press, issue Pre-press, vol. 65, no. 2, pp. 659–682, 2018
Accepted 5 July 2018
Published: 21 August 2018
Postsynaptic Proteome of Non-Demented Individuals with Alzheimer’s Disease Neuropathology
Full Abstract
Further analysis of these key factors could pave the road to ending Alzheimer’s and other age-related diseases.
Nicholi Avery, [email protected]
Adam Alonzi, [email protected]