Circa 2021
Mycelium is very light in weight, it naturally floats on water, it can withstand the cold of space where we don’t have to worry about cold welding, and we can add in fine strains of metal material which is used to transmit almost any type of signal. As you can see, there are numerous reasons why mycelium is quite suitable for our satellites in space, on land, and in the air on its way to space.
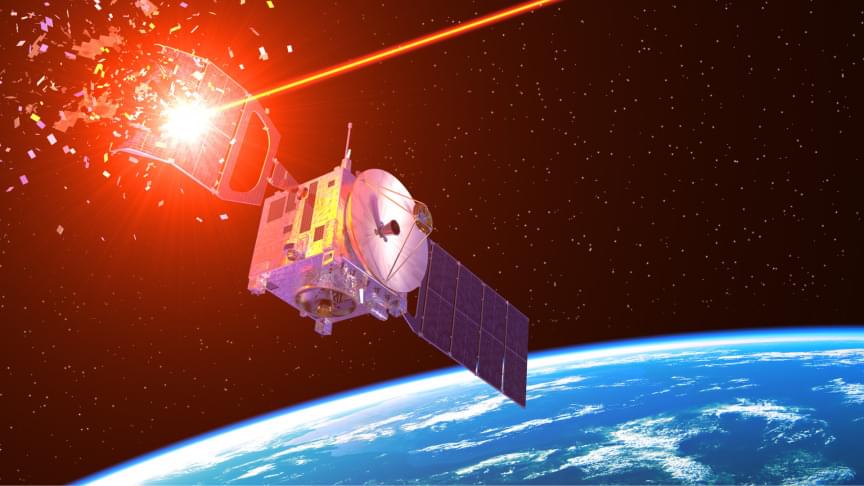
Of course, there’s also the all-important issue of space debris, which is projected to become a severe hazard to satellites and spacecraft in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) in the coming years.
According to the SDO, more than 560 break-ups, explosions, collisions, or anomalous events that resulted in fragmentation have taken place since the launch of the first artificial satellite in 1957 (Sputnik 1). With the proliferation of small satellites and the mega-constellations that are (or soon will be) deployed, the risk of collision rises considerably.