During a virtual conference briefing this week, SpaceX founder and CEO Elon Musk provided more details about a new plan that his company has to mitigate the impact of their Starlink satellite constellation on night sky observation. Musk first revealed on Twitter the intent to build a “sun visor” to lower their visibility, but we didn’t know much about how it would work or how it compared to the test dark paint job that SpaceX tried previously.
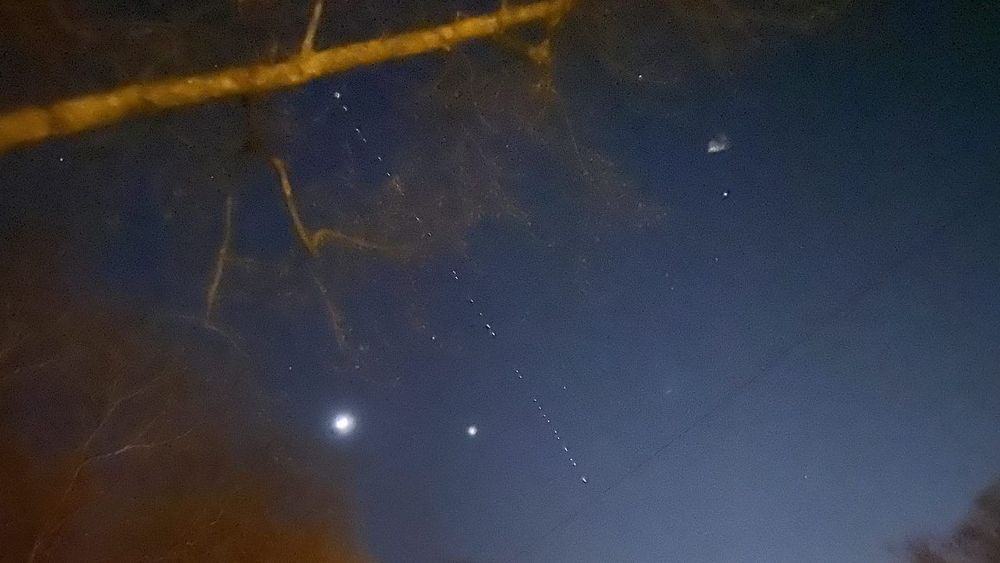
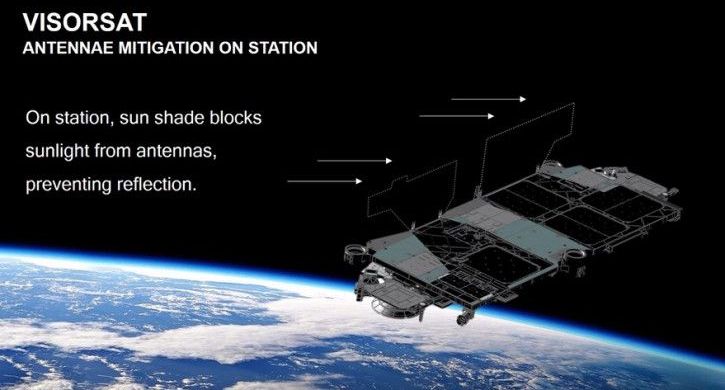
As reported by Space News, SpaceX’s new “VisorSat” approach will essentially use sun visors to block inbound sunlight from hitting the reflective antennas on the spacecraft, stopping them from reflecting said light back to Earth, which is why they appear as bright lights in the night sky.
This new hardware addition to future Starlink satellites will supplement other measures, including making use of a new method for changing the orientation of the satellites as they raise into their target orbits after launch, which is a period during which they’re especially visible. The overall goal, according to Musk, is to “make the satellites invisible to the naked eye within a week, and to minimize the impact on astronomy,” with a specific focus on ensuring that whatever impact the constellation does have doesn’t impeded the ability of scientists and researchers to make new discoveries.