When Jeremy Sell saw the word “poignant” spelled correctly in an essay, the jig was up.
AI is rapidly becoming too sophisticated for even veteran educators’ detective skills, educators and experts say.
Google has released a new Pro model of its latest AI, Gemini, and company sources say it has outperformed GPT-3.5 (the free version of ChatGPT) in widespread testing. According to performance reports, Gemini Ultra exceeds current state-of-the-art results on 30 of the 32 widely-used academic benchmarks used in large language model (LLM) research and development. Google has been accused of lagging behind OpenAI’s ChatGPT, widely regarded as the most popular and powerful in the AI space. Google says Gemini was trained to be multimodal, meaning it can process different types of media such as text, pictures, video, and audio.
Insider also reports that, with a score of 90.0%, Gemini Ultra is the first model to outperform human experts on MMLU (massive multitask language understanding), which uses a combination of 57 subjects such as math, physics, history, law, medicine and ethics for testing both world knowledge and problem-solving abilities.
The Google-based AI comes in three sizes, or stages, for the Gemini platform: Ultra, which is the flagship model, Pro and Nano (designed for mobile devices). According to reports from TechCrunch, the company says it’s making Gemini Pro available to enterprise customers through its Vertex AI program, and for developers in AI Studio, on December 13. Reports indicate that the Pro version can also be accessed via Bard, the company’s chatbot interface.
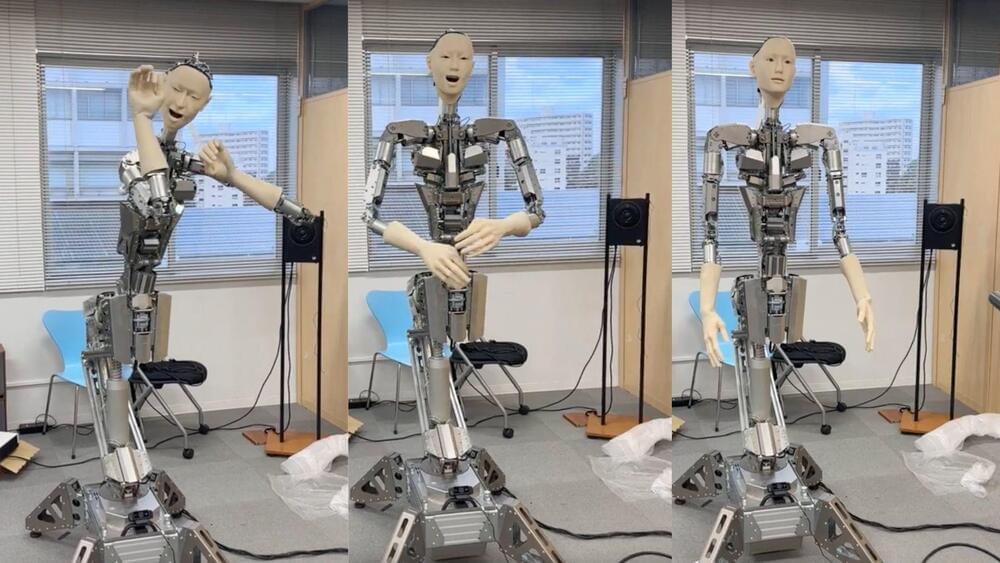



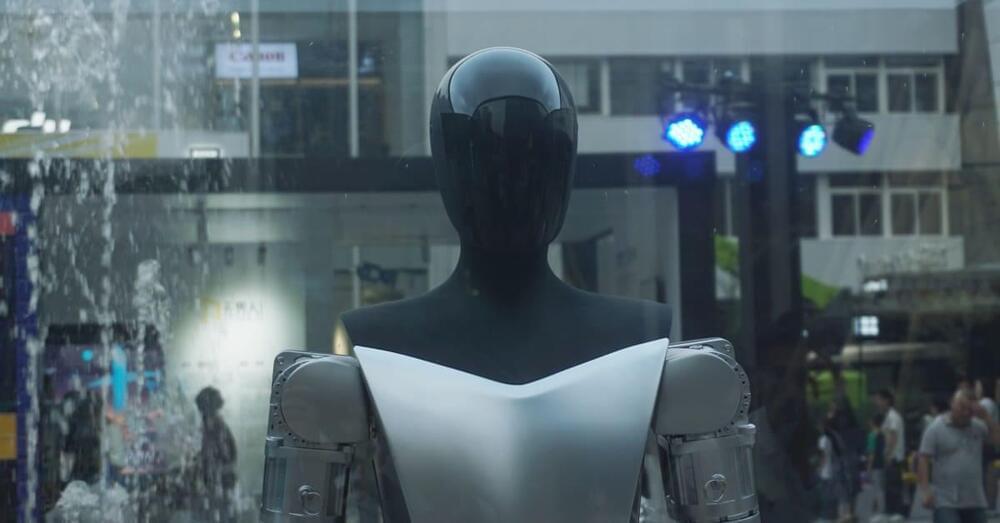
Meet Alter3, a humanoid robot from the University of Tokyo that can strike various poses, from selfies to playing a spooky ghost, thanks to ChatGPT-4 AI.
In a fusion of cutting-edge technology, a highly advanced humanoid robot has been paired with unparalleled capabilities by leveraging artificial intelligence (AI).
Introducing Alter3, a humanoid robot with the ability to generate spontaneous motion through the utilization of a Large Language Model (LLM), namely GPT-4.
Developed by a University of Tokyo team, Alter3 employs Open AI’s latest tool to dynamically assume various poses, from a selfie stance to mimicking a ghost, all without the need for pre-programmed entries in its database.
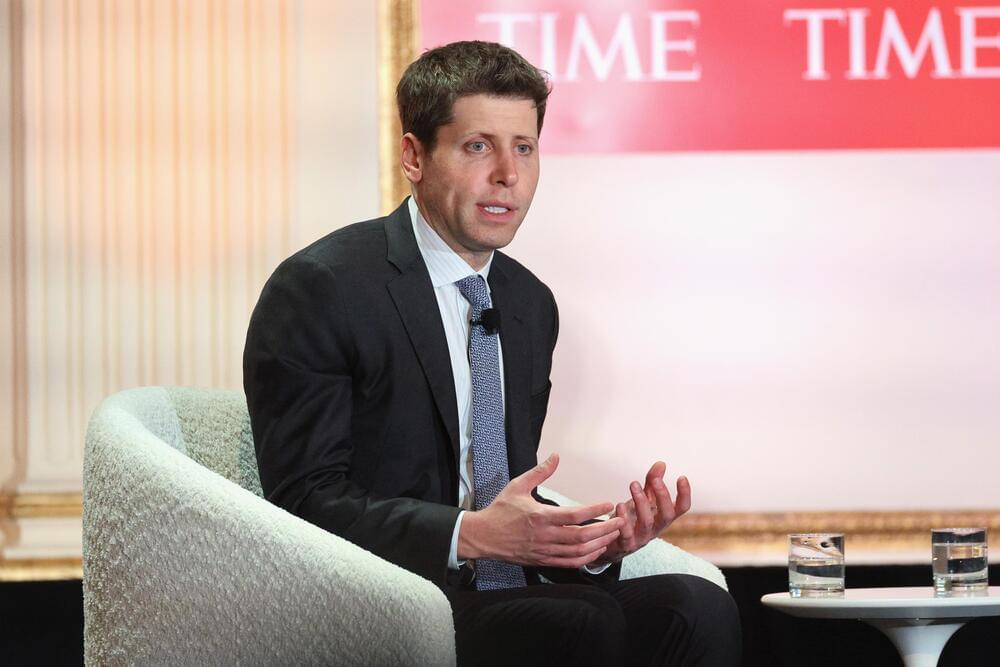

If 2023 was the year artificial intelligence became a household topic of conversation, it’s in many ways because of Sam Altman, CEO of the artificial intelligence research organization OpenAI.
The OpenAI CEO spoke candidly about his November ousting and reinstatement at the company and the risks and rewards AI can bring in the future.
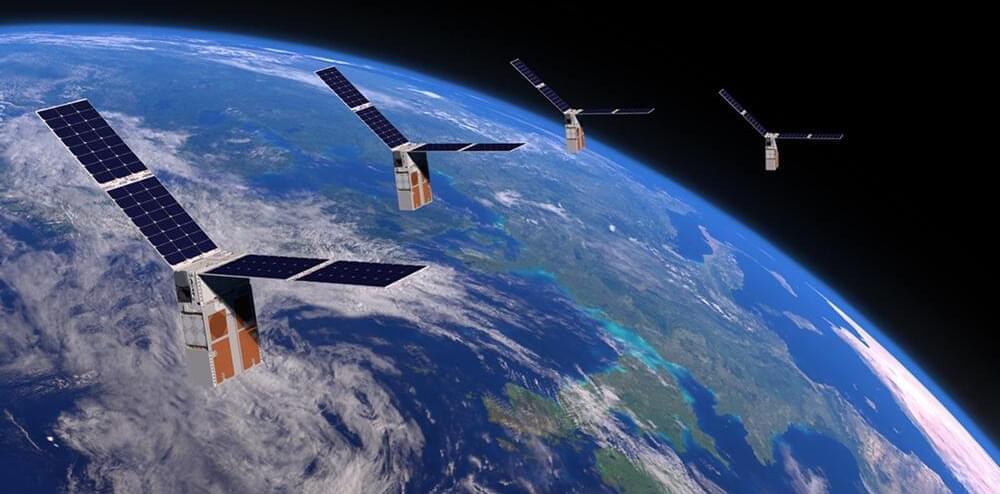


NASA’s Starling mission will test new technologies for autonomous swarm navigation on four CubeSats in low-Earth orbit. Credit: Blue Canyon Technologies/NASA
NASA ’s Starling spacecraft are getting in formation: the mission team has spent the last two months troubleshooting issues and commissioning the four spacecraft, nicknamed Blinky, Pinky, Inky, and Clyde.
Pinky, Inky, and Clyde have successfully completed their propulsion system commissioning and have executed maneuvers to get into their swarm operations configuration, maintaining a range between 50–200 km apart. The three have also successfully demonstrated two-way communications with their crosslink radios in this closer proximity.

Supernovae, which are exploding stars, play a pivotal role in galaxy formation and evolution. However, simulating these phenomena accurately and efficiently has been a significant challenge. For the first time, a team including researchers from the University of Tokyo has utilized deep learning to enhance supernova simulations. This advancement accelerates simulations, crucial for understanding galaxy formation and evolution, as well as the evolution of chemistry that led to life.
When you hear about deep learning, you might think of the latest app that sprung up this week to do something clever with images or generate humanlike text. Deep learning might be responsible for some behind-the-scenes aspects of such things, but it’s also used extensively in different fields of research. Recently, a team at a tech event called a hackathon applied deep learning to weather forecasting. It proved quite effective, and this got doctoral student Keiya Hirashima from the University of Tokyo’s Department of Astronomy thinking.
Researchers at Western Sydney University in Australia have teamed up with tech giants Intel and Dell to build a massive supercomputer intended to simulate neural networks at the scale of the human brain.
They say the computer, dubbed DeepSouth, is capable of emulating networks of spiking neurons at a mind-melting 228 trillion synaptic operations per second, putting it on par with the estimated rate at which the human brain completes operations.
The project was announced at this week’s NeuroEng Workshop hosted by Western Sydney’s International Centre for Neuromorphic Systems (ICNS), a forum for luminaries in the field of computational neuroscience.