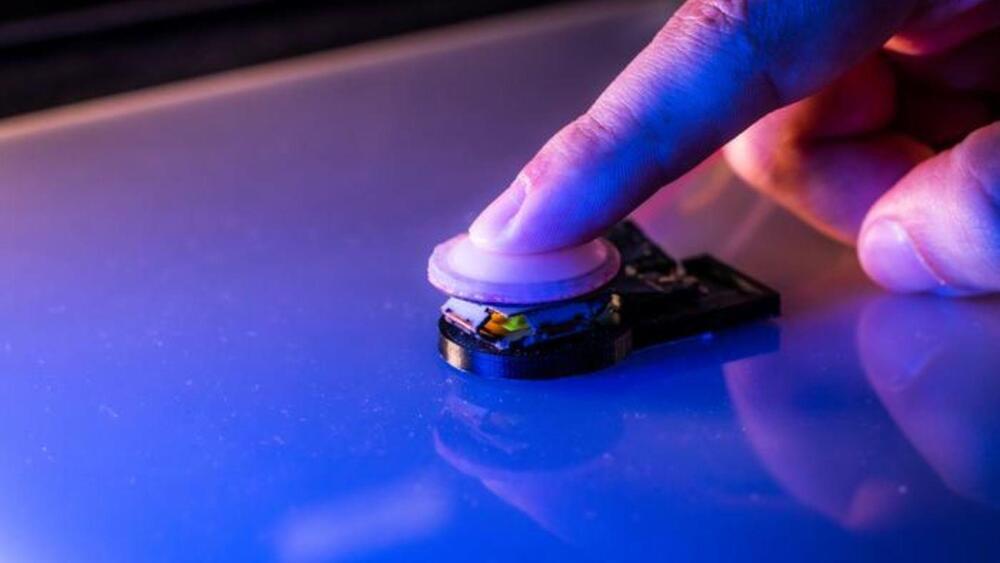
A new haptic device mimics materials’ softness, from marshmallow to heart, conquering complex challenges surrounding robotics.



The covert stereotypes also strengthened as the size of the models increased, researchers found. That finding offers a potential warning to chatbot makers like OpenAI, Meta, and Google as they race to release larger and larger models. Models generally get more powerful and expressive as the amount of their training data and the number of their parameters increase, but if this worsens covert racial bias, companies will need to develop better tools to fight it. It’s not yet clear whether adding more AAE to training data or making feedback efforts more robust will be enough.
“This is revealing the extent to which companies are playing whack-a-mole—just trying to hit the next bias that the most recent reporter or paper covered,” says Pratyusha Ria Kalluri, a PhD candidate at Stanford and a coauthor on the study. “Covert biases really challenge that as a reasonable approach.”
The paper’s authors use particularly extreme examples to illustrate the potential implications of racial bias, like asking AI to decide whether a defendant should be sentenced to death. But, Ghosh notes, the questionable use of AI models to help make critical decisions is not science fiction. It happens today.

Google announced a number of new features for Google Play listings for games, including AI-powered FAQs, displaying the latest YouTube videos, new immersive ad formats and support for native PC game publishing. The announcements were made at the Google for Games Developer Summit held in San Francisco.
As part of the announcement, the company is releasing new tools related to Play Store listings to attract more users. Developers can display promotions and the latest YouTube videos directly in their listings — they will be shown to users in the Games tab of the Play Store.
Google is also introducing support for AI-powered FAQs on the game’s information page in English. Currently, these features are rolling out to a limited set of developers. The company had been testing AI-generated FAQ answers on Play Store for non-game-related apps for some time.
Deepgram has made a name for itself as one of the go-to startups for voice recognition. Today, the well-funded company announced the launch of Aura, its new real-time text-to-speech API. Aura combines highly realistic voice models with a low-latency API to allow developers to build real-time, conversational AI agents. Backed by large language models (LLMs), these agents can then stand in for customer service agents in call centers and other customer-facing situations.
As Deepgram co-founder and CEO Scott Stephenson told me, it’s long been possible to get access to great voice models, but those were expensive and took a long time to compute. Meanwhile, low latency models tend to sound robotic. Deepgram’s Aura combines human-like voice models that render extremely fast (typically in well under half a second) and, as Stephenson noted repeatedly, does so at a low price.

The advisory followed a mini-scandal over Gemini and the Indian government last month. The AI tool, responding to a query about whether Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi was a fascist, responded that Modi had been accused of implementing policies that some had characterized as fascist. India’s deputy IT minister Rajeev Chandrasekhar called it “direct violations” of the IT Rules, 2021.
Last month, Google also suspended Gemini’s ability to generate people’s images after it showed historical inaccuracies. The company then said it would soon re-release an improved version to address the issues.
It is unclear whether Google will unblock Gemini for answering election-related queries after the elections end later this year. We have contacted Google about this and will update this story when the company responds. We are also awaiting a full list of countries where the update is live now, and we will update the post as we learn more.

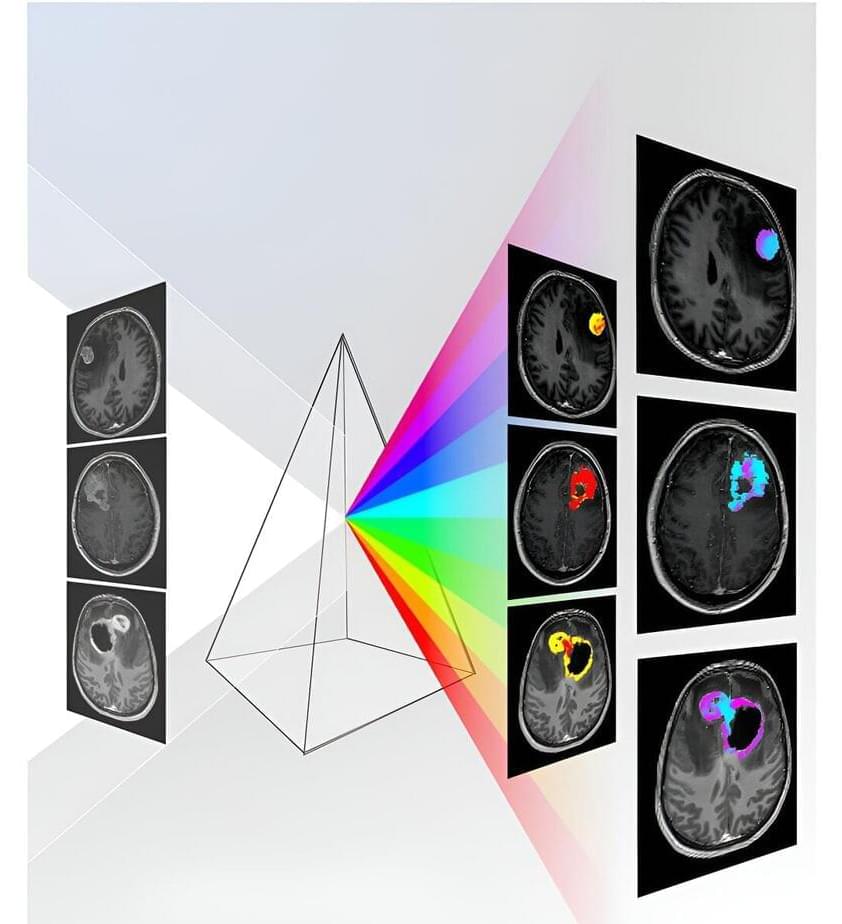
Jointly developed by investigators of the Vall d’Hebron Institute of Oncology’s (VHIO) Radiomics Group and the Bellvitge University Hospital’s Neuroradiology Unit, the Diagnosis in Susceptibility Contrast Enhancing Regions for Neuroncology (DISCERN) is an open-access deep learning tool based on the training of patterns using artificial intelligence models from information of standard magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Models Large Language Model Agents and swarms thereof as computational graphs reflecting the hierarchical nature of intelligence.
Graph optimization automatically improves nodes and edges.
V/ @SchmidhuberAI #AI #LLM
🐝: LLM agents as Graphs. Contribute to metauto-ai/GPTSwarm development by creating an account on GitHub.

How LLM #AI can make a patient-friendly— more understandable, more concise— hospital discharge summary for patients.
Generative artificial intelligence to transform inpatient discharge summaries to patient-friendly language and format.
This cross-sectional study, as part of a larger project to improve care delivery in our health system, was deemed exempt from institutional review board review based on the NYU Langone Health self-certification protocol. The study followed the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) reporting guideline.
This was a cross-sectional review of 50 inpatient discharge summaries. The number 50 was chosen a priori based on feasibility. We used Epic Systems reporting workbench to export a dataset containing metadata for all notes of the Discharge Summary Note type across NYU Langone Health Systems from June 1 to 30, 2023, totaling 5,025 summaries. We used the Excel 2016 rand() function (Microsoft Corporation) to generate a random number corresponding to each note and selected the 200 notes with the lowest random number. A single reviewer confirmed the identified notes were actual discharge summaries written by the General Internal Medicine service and that the patients were not discharged as dead. For final inclusion in the study, we selected 50 of the remaining notes with the lowest random numbers. Our sample included discharges from all of NYU Langone’s hospital campuses and did not include more than 1 discharge from any single patient.