Elon Musk has donated millions to the Future of Life Institute, and now the organization is putting that money to use by funding research into keeping artificial intelligence “robust and…


Elon Musk has donated millions to the Future of Life Institute, and now the organization is putting that money to use by funding research into keeping artificial intelligence “robust and…

Which just goes to show that you should never buy ANY form of robotics or AI software from a company that has any of the following words in it’s name: Sky, Net, Skynet, Cyberdine, and or Extermination. wink

“It has taken time for neural networks, initially conceived 50 years ago, to become accepted parts of information technology applications. After a flurry of interest in the 1990s, supported in part by the development of highly specialized integrated circuits designed to overcome their poor performance on conventional computers, neural networks were outperformed by other algorithms, such as support vector machines in image processing and Gaussian models in speech recognition.” Read more

“The first marketable, personal computers in the late 70s came about after almost 40 years of research and development, which created the technology at public expense. One of the peculiarities, if you’d like, of our system of innovation and development is that it’s radically anti-capitalist in many ways…People who paid taxes in the 50s and 60s may not have known it, but they were creating what was ultimately marketed by Apple. But they don’t get any of the profit. I think that’s a social pathology and the same carries over into space.” Read more

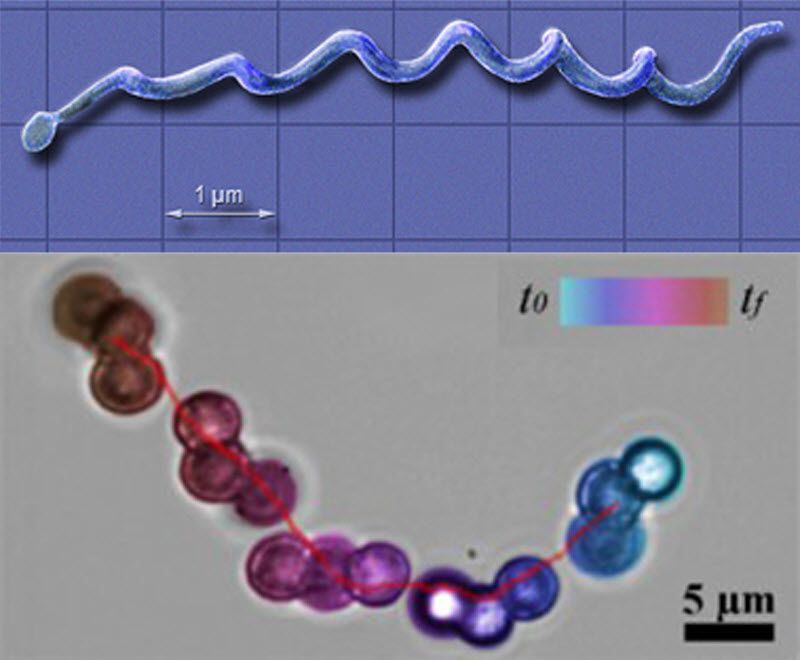
Drexel’s microswimmer robots (bottom) are modeled, in form and motion, after spiral-shaped Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria (top), which cause Lyme Disease (credit: Drexel University)

Lately, media around the web has been bracing for robots — not time-traveling robots per se, but robot workers. Specifically, the increased sophistication of artificial intelligence and improved engineering of robotics has spurred a growing concern about what people are going to do when all the regular jobs are done by robots.
A variety of solutions have been proposed to this potential technological unemployment (we even had an entire Future of Work series dealing with this topic in March), many of which suggest that there will still be things that humans can do that robots can’t, but what are they? Read more
A slew of articles are claiming that an “exasperated” artificial intelligence snapped at its programmer during a conversation about morality and ethics. Sadly, it’s another example of the media overselling the capabilities of simple chatbots.
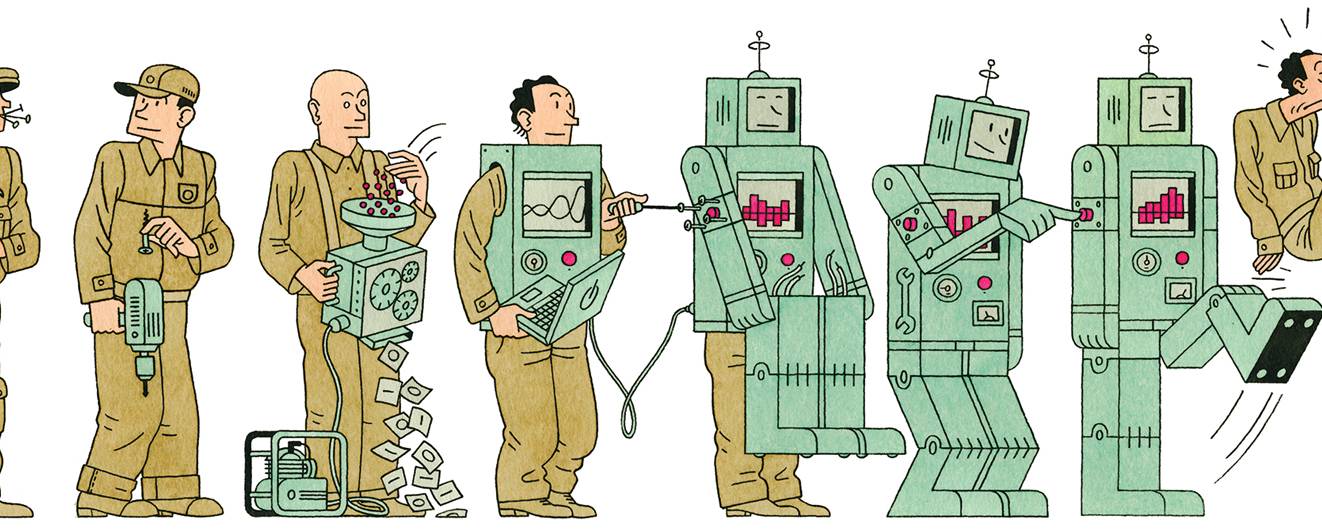
“These are long-term trends that began decades ago, says David Autor, an MIT economist who has studied ‘job polarization’—the disappearance of middle-skill jobs even as demand increases for low-paying manual work on the one hand and highly skilled work on the other. This ‘hollowing out’ of the middle of the workforce, he says, ‘has been going on for a while.’ Nevertheless, the recession of 2007–2009 may have sped up the destruction of many relatively well-paid jobs requiring repetitive tasks that can be automated.”