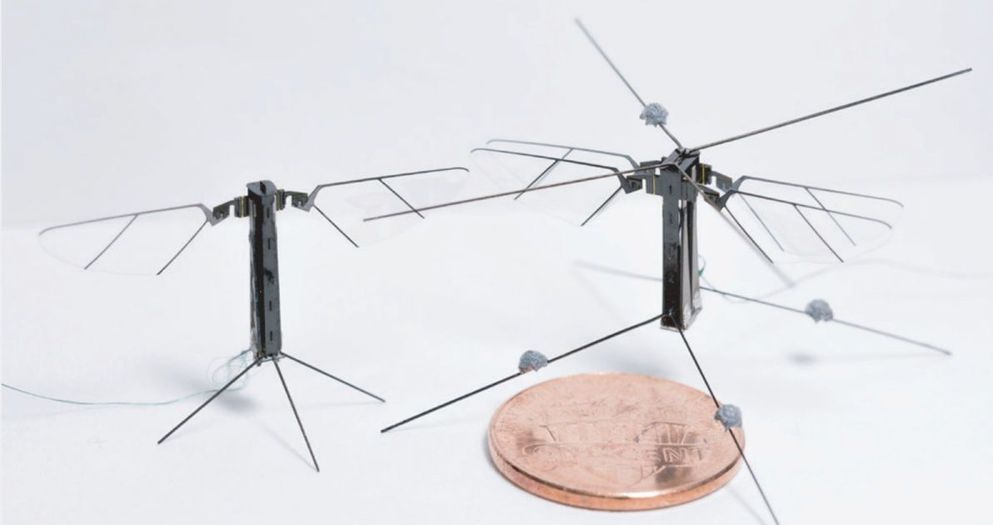
The new technology could be used for the development of effective and time-sensitive search-and-rescue robots.
Category: robotics/AI – Page 2,368
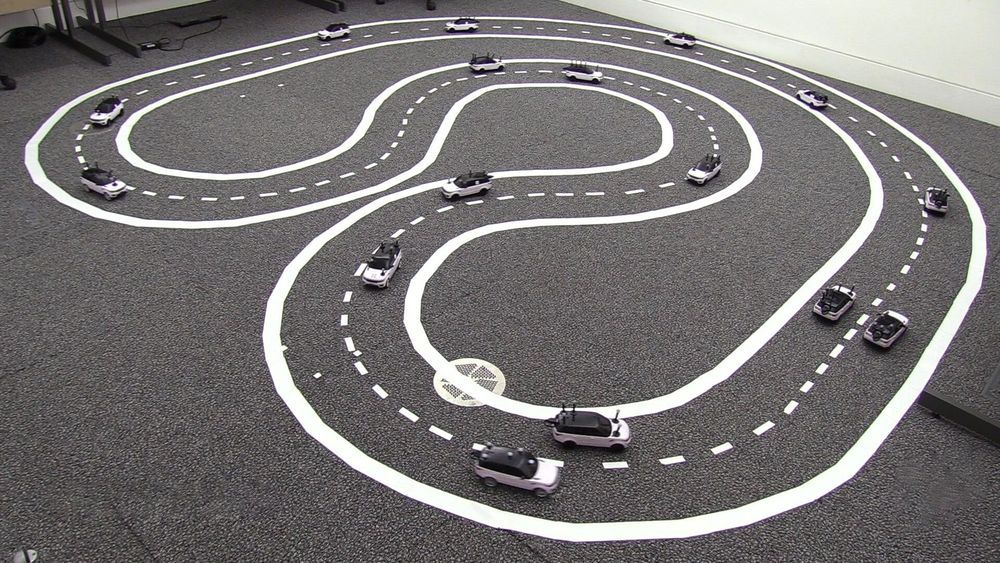

Driverless cars working together can speed up traffic
A fleet of driverless cars working together to keep traffic moving smoothly can improve overall traffic flow by at least 35 percent, researchers have shown.
The researchers, from the University of Cambridge, programmed a small fleet of miniature robotic cars to drive on a multi-lane track and observed how the traffic flow changed when one of the cars stopped.
When the cars were not driving cooperatively, any cars behind the stopped car had to stop or slow down and wait for a gap in the traffic, as would typically happen on a real road. A queue quickly formed behind the stopped car and overall traffic flow was slowed.

Why CRISPR Technology is the Key to Innovation in AI
CRISPR technology is a simple yet powerful tool for editing genomes. It allows researchers to easily alter DNA sequences and modify gene function.
It has many potential applications include correcting genetic defects, treating and preventing the spread of diseases and improving crops. By delivering the CRISPR enzyme Cas9 nuclease coupled with synthetic guide RNA (gRNA) into a cell, the cell’s genome can be cut at a desired location, that allows existing genes to be removed or add new ones.
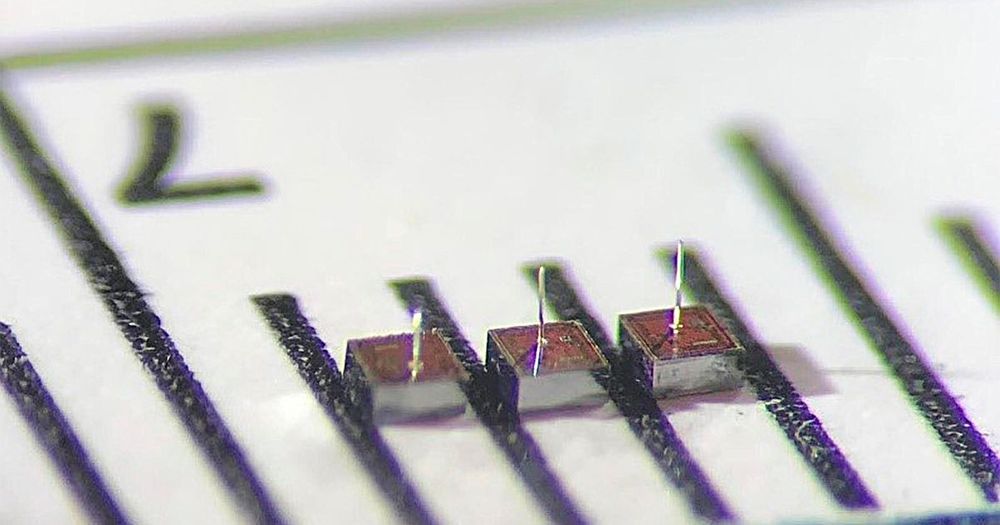
Wireless Network Brings Dust-Sized Brain Implants a Step Closer
Brain-computer interfaces have managed some amazing feats: allowing paralyzed people to type words and move a robot using only their minds, to name two examples. Brown University neuroengineering professor Arto Nurmikko has had a hand in some of those developments, but even he says the technology is at only a rudimentary stage—the equivalent of the computer understanding the brain’s intention to bend a single finger.
“We’re trying to go from the bending-of-the-finger paradigm to tying shoe laces and even to the concert pianist level. That requires lots more spatial and temporal resolution from an electronic brain interface,” Nurmikko says. His team is hoping that kind of resolution will come along with the transition from a single, hard wired neural implant to a thousand or more speck-size neural implants that wirelessly communicate with computers outside the brain. At the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, engineers from Brown University, Qualcomm, and the University of California San Diego presented the final part of a communications scheme for these implants. It allows bidirectional communication between the implants and an external device with an uplink rate of 10 megabits per second and a downlink rate of 1 Mb/s.
“We believe that we are the first group to realize wireless power transfer and megabits per second communications” in a neural implant, says Wing Ching (Vincent) Leung, technical director at the Qualcomm Institute Circuits Lab at UC San Diego.
How AI will liberate doctors from keyboards and basements
In hospitals, where many people are treated for life-threatening illnesses, having quality time with your doctor can be the difference between life and death.
However, physicians are often busy, seeing dozens of patients each day. So, then, how can we get more time with them? A.I., says physician and author Eric Topol. In this video, he explains how machine intelligence can free up doctors’ time while they go through their rounds.
Peter Voss Pioneer in Artificial Intelligence
Peter voss is a serial entrepreneur, engineer, inventor and a pioneer in artificial intelligence.
Peter started out in electronics engineering but quickly moved into software. After developing a comprehensive ERP software package, Peter took his first software company from a zero to 400-person IPO in seven years.
Fueled by the fragile nature of software, Peter embarked on a 20-year journey to study intelligence (how it develops in humans, how to measure it, and current AI efforts), and to replicate it in software. His research culminated in the creation of a natural language intelligence engine that can think, learn, and reason — and adapt to and grow with the user. He even coined the term ‘AGI’(Artificial General Intelligence) with fellow luminaries in the space.
Peter founded SmartAction.ai in 2009, which developed the first AGI-based call center automation technology. Now, in his latest venture, Aigo.ai, he is taking that technology a step further with the commercialization of the second generation of his ‘Conversational AI’ technology with a bold mission of providing hyper-intelligent hyper-personal assistants for everyone.
In addition to being an entrepreneur, engineer, inventor, and AI pioneer, Peter often writes and presents on various philosophical topics including rational ethics, free will, and artificial minds; and is deeply involved with futurism and radical life-extension.
Church of Perpetual Life, a science-based church is open to people of all faiths & belief systems. We are non-denominational & non-judgmental and a central gathering place of Transhumans. What unites us is our common faith, belief, and desire in Unlimited Life Spans.

Quest for Immortality
Besides biological immortality, there is also the possibility of digital immortality. The Human Connectome Project launched in 2010 aimed at mapping the entire human brain and to build its “network map” (connectome) to connect its structure to function and behaviour. Once the neural structure of the brain is completely deciphered, the mind can be uploaded into a computer that could control a robot that replicates a human in every respect.
The quest for eternal life is as old as humanity itself. “Grant us liberation from death for the sake of immortality, as the cucumber is severed from its bondage to the creeper”, runs one of the ancient Hindu prayers in the Mahamrityunjay, or the “great death-conquering” mantra. Death is the ultimate end, mysterious and terrible, against which even the strongest is powerless.
How to conquer death is a question every civilisation has tried to address. Myths have grown around immortal beings like gods in every culture, and of valiant but futile attempts of mortal men to attain immortality. But science may be closer to finding an answer to this ancient quest now more than ever before. In the early history of life, unicellular organisms like prokaryotes, protozoans and algae had ageless bodies and were immortal.
The advent of sexual reproduction boosted our chances of survival manifold. It also brought about ageing and death about a billion years ago. But Nature provides examples of immortality: a bacteria does not die naturally unless killed by an antibiotic or UV ray, strawberry plants clone themselves, and the tiny hydrozoans regenerate themselves to defy ageing and death. Cancer cells are also potentially immortal. But first let us be clear about the concept of immortality, which means defying death in order to live forever. But actually, what is ‘forever’? Around 1900, the average life expectancy in the world was only 31 years.
Hyperdimensional computing theory could lead to AI with memories and reflexes
A team of scientists from the University of Maryland recently came up with a take on the hyperdimensional computing theory that could give robots memories and reflexes. This could break the stalemate we seem to be at with autonomous vehicles and other real-world robots, and lead to more human-like AI models.
The solution
The Maryland team came up with a theoretical method by which hyperdimensional computing – a hypervector-based alternative to computations based on Booleans and numbers – could replace current deep learning methods for processing sensory information.