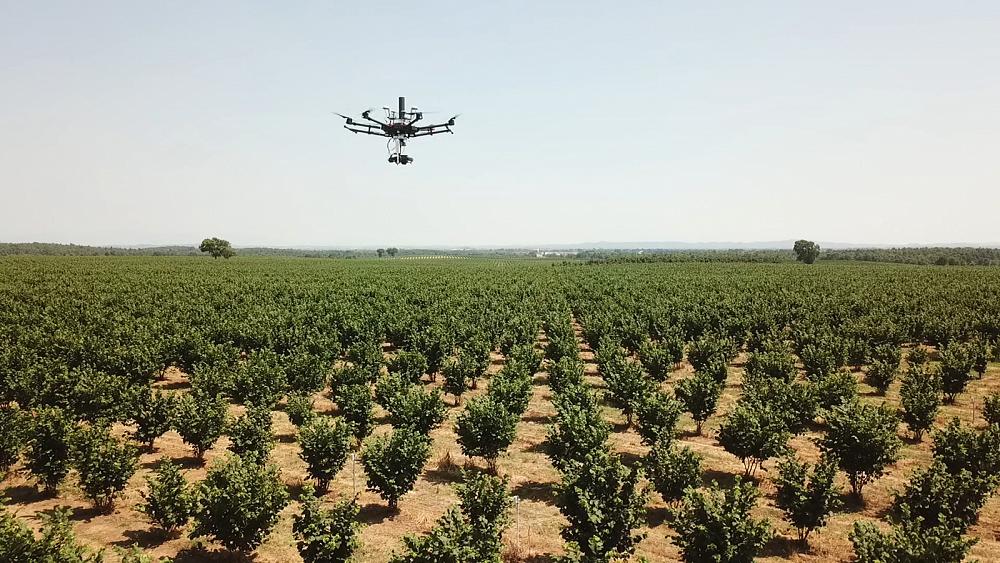
On this week’s episode of Futuris, Euronews visits a hazelnut orchard in Italy to see how the new generation of robots can help farmers and agronomists make agriculture cheaper and more environmentally friendly.



Computer vision is one of the most popular applications of artificial intelligence. Image classification, object detection and object segmentation are some of the use cases of computer vision-based AI. These techniques are used in a variety of consumer and industrial scenarios. From face recognition-based user authentication to inventory tracking in warehouses to vehicle detection on roads, computer vision is becoming an integral part of next-generation applications.
Computer vision uses advanced neural networks and deep learning algorithms such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Single Shot Multibox Detector (SSD) and Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN). Applying these algorithms requires a thorough understanding of neural network architecture, advanced mathematics and image processing techniques. For an average ML developer, CNN remains to be a complex branch of AI.
Apart from the knowledge and understanding of algorithms, CNNs demand high end, expensive infrastructure for training the models, which is out of reach for most of the developers.
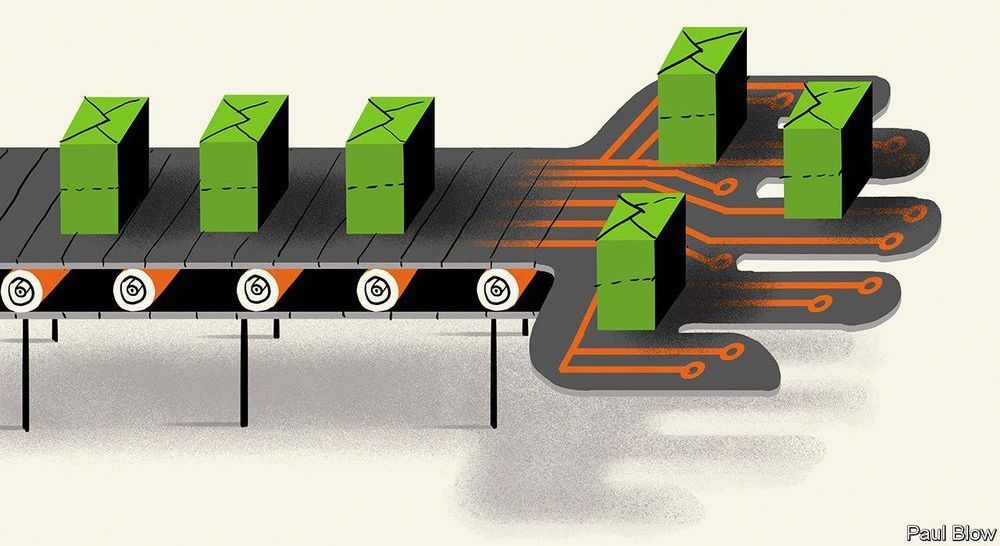
Consultants at Gartner recently calculated that in 2021 “ai augmentation” will create $2.9trn of “business value” and save 6.2bn man-hours globally. A survey by McKinsey last year estimated that ai analytics could add around $13trn, or 16%, to annual global gdp by 2030. Retail and logistics stand to gain most.
Two surprising leaders have emerged from the pack.

During Amazon’s all-hands meeting in March, CEO Jeff Bezos stated that he is fascinated by the emerging trends in the auto industry. Bezos noted that it was this fascination that ultimately played a part in Amazon’s hefty $700 million investment in electric truck startup Rivian Automotive back in February.
“If you think about the auto industry right now, there’s so many things going on with Uber-ization, electrification, the connected car — so it’s a fascinating industry. It’s going to be something very interesting to watch and participate in, and I’m very excited about that whole industry,” Bezos said.
Bezos’ optimism for emerging industries extends beyond the electric car market. Apart from Rivian, Amazon has also invested in self-driving startup Aurora, hinting that the CEO is also looking to capitalize on autonomous driving technology for the e-commerce giant’s operations in the future. If its investment in Aurora pans out, for example, Amazon would likely gain an optimized solution that would allow the company to deliver shipments to its customers using self-driving machines.
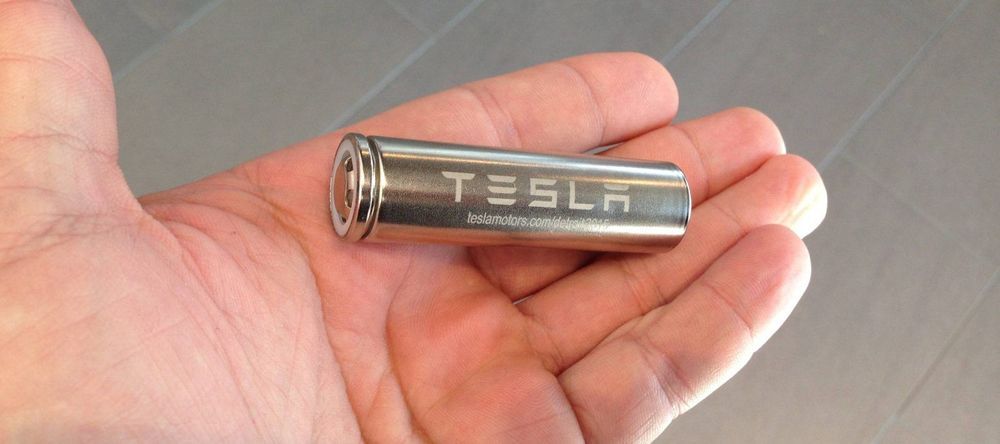

When talking about the economics of Tesla’s future fleet of robotaxis at the Tesla Autonomy Event, Tesla CEO Elon Musk emphasized that the vehicles need to be durable in order for the economics to work:
“The cars currently built are all designed for a million miles of operation. The drive unit is design, tested, and validated for 1 million miles of operation.”
But the CEO admitted that the battery packs are not built to last 1 million miles.
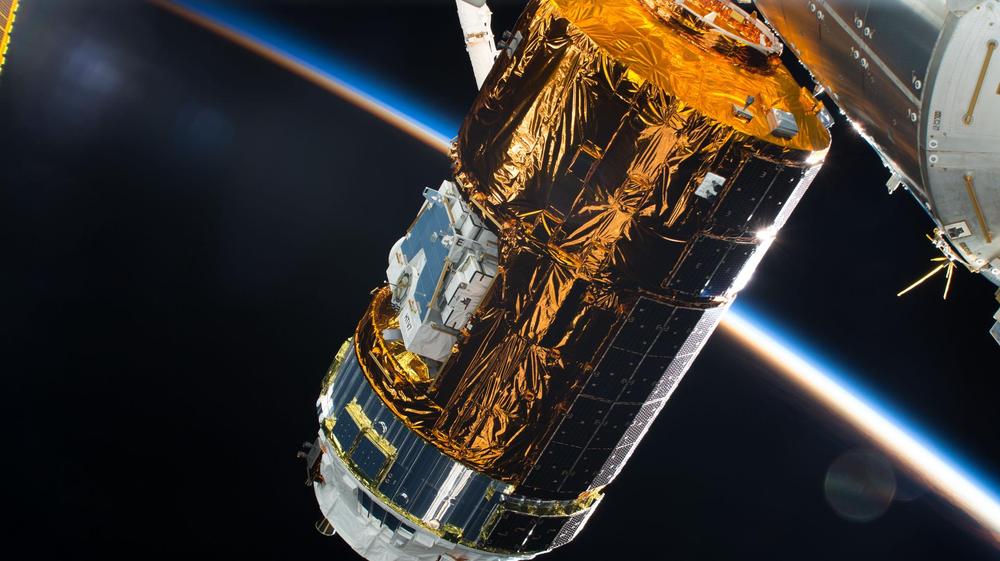



A Japanese cargo spacecraft loaded with more than four tons of supplies, spare parts and experiment hardware is scheduled to launch from the Tanegashima Space Center in southern Japan to the International Space Station at 5:33 p.m. EDT Tuesday, Sept. 10 (6:33 a.m. Sept. 11 in Japan). Live coverage of the launch and capture will air on NASA Television and the agency’s website.
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) unpiloted H-II Transport Vehicle-8 (HTV-8) will launch on a Japanese H-IIB rocket on the tenth anniversary of the first HTV cargo spacecraft launch. Live coverage will begin at 5 p.m.
The spacecraft will arrive at the station Saturday, Sept. 14. Live coverage of the spacecraft rendezvous and capture will begin at 5:30 a.m. Expedition 60 Flight Engineer Christina Koch of NASA, backed up by her NASA crewmate Andrew Morgan, will operate the station’s Canadarm2 robotic arm from the station’s cupola to capture the 12-ton spacecraft as it approaches from below. Robotics flight controllers will then take over the operation of the arm to install HTV-8 to the Earth-facing port of the Harmony module where it will spend a month attached. Flight Engineer Luca Parmitano of ESA (European Space Agency) will monitor HTV-8 systems during its approach to the station.

T HE CONTEST between China and America, the world’s two superpowers, has many dimensions, from skirmishes over steel quotas to squabbles over student visas. One of the most alarming and least understood is the race towards artificial-intelligence-enabled warfare. Both countries are investing large sums in militarised artificial intelligence (AI), from autonomous robots to software that gives generals rapid tactical advice in the heat of battle. China frets that America has an edge thanks to the breakthroughs of Western companies, such as their successes in sophisticated strategy games. America fears that China’s autocrats have free access to copious data and can enlist local tech firms on national service. Neither side wants to fall behind.
