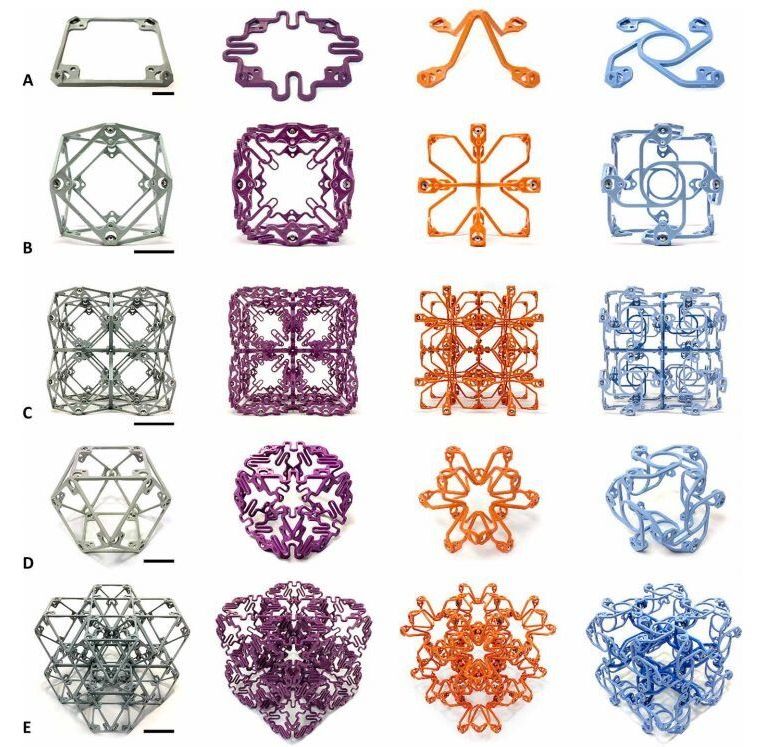
Researchers at MIT’s Center for Bits and Atoms have created tiny building blocks that exhibit a variety of unique mechanical properties, such as the ability to produce a twisting motion when squeezed. These subunits could potentially be assembled by tiny robots into a nearly limitless variety of objects with built-in functionality, including vehicles, large industrial parts, or specialized robots that can be repeatedly reassembled in different forms.
The researchers created four different types of these subunits, called voxels (a 3D variation on the pixels of a 2D image). Each voxel type exhibits special properties not found in typical natural materials, and in combination they can be used to make devices that respond to environmental stimuli in predictable ways. Examples might include airplane wings or turbine blades that respond to changes in air pressure or wind speed by changing their overall shape.
The findings, which detail the creation of a family of discrete “mechanical metamaterials,” are described in a paper published today in the journal Science Advances, authored by recent MIT doctoral graduate Benjamin Jenett PhD ’20, Professor Neil Gershenfeld, and four others.