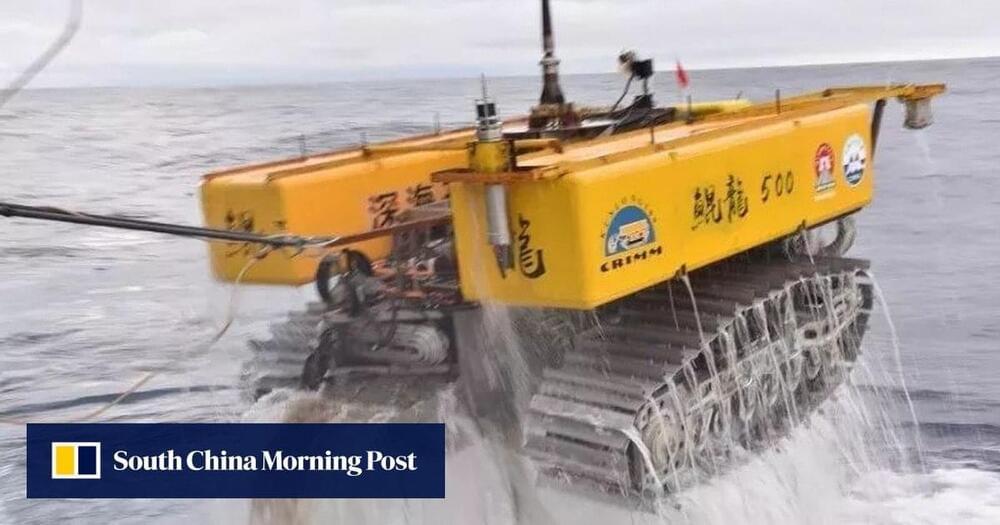
The website is eye-catching for its simplicity. Against a white backdrop, a giant blue button invites visitors to upload a picture of a face. Below the button, four AI-generated faces allow you to test the service. Above it, the tag line boldly proclaims the purpose: turn anyone into a porn star by using deepfake technology to swap the person’s face into an adult video. All it requires is the picture and the push of a button.
MIT Technology Review has chosen not to name the service, which we will call Y, or use any direct quotes and screenshots of its contents, to avoid driving traffic to the site. It was discovered and brought to our attention by deepfake researcher Henry Ajder, who has been tracking the evolution and rise of synthetic media online.