Researchers at the Allen Institute for AI created Ask Delphi to make ethical judgments — but it turned out to be awfully bigoted and racist instead.
Category: robotics/AI – Page 1,882
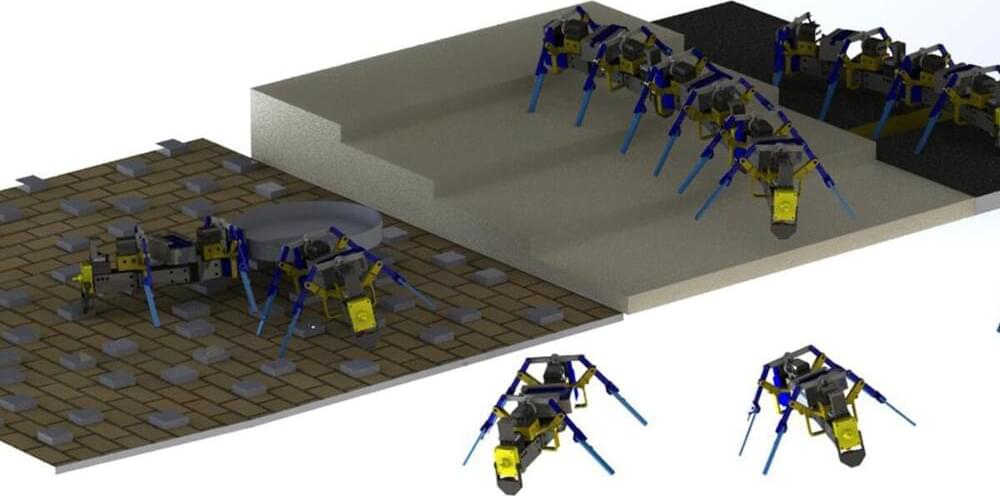
Researchers successfully build four-legged swarm robots
As a robotics engineer, Yasemin Ozkan-Aydin, assistant professor of electrical engineering at the University of Notre Dame, gets her inspiration from biological systems. The collective behaviors of ants, honeybees and birds to solve problems and overcome obstacles is something researchers have developed in aerial and underwater robotics. Developing small-scale swarm robots with the capability to traverse complex terrain, however, comes with a unique set of challenges.
In research published in Science Robotics, Ozkan-Aydin presents how she was able to build multi-legged robots capable of maneuvering in challenging environments and accomplishing difficult tasks collectively, mimicking their natural-world counterparts.
“Legged robots can navigate challenging environments such as rough terrain and tight spaces, and the use of limbs offers effective body support, enables rapid maneuverability and facilitates obstacle crossing,” Ozkan-Aydin said. “However, legged robots face unique mobility challenges in terrestrial environments, which results in reduced locomotor performance.”
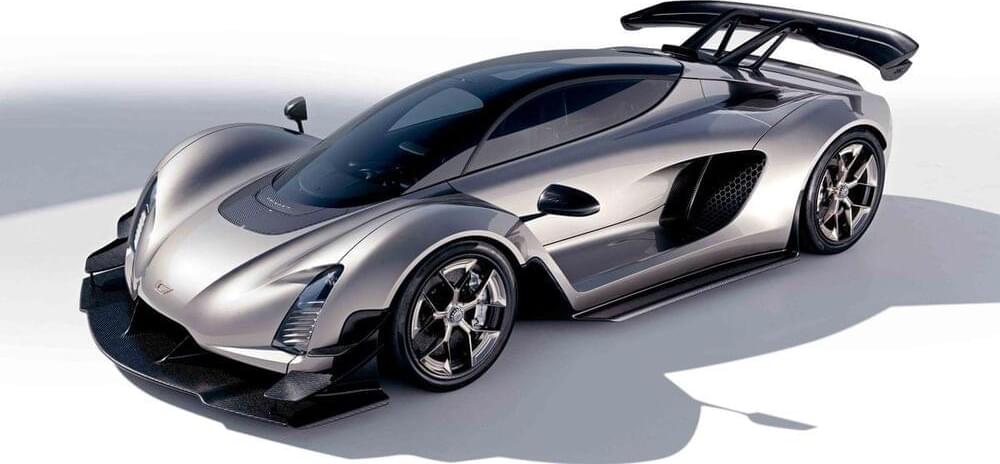

3D-Printing the Czinger 21C Supercar Shows Us the Future of Car Making
Known formally as additive manufacturing, or AM, in the business, the process can make almost anything—even a car.
“For our OEMs, we were able to show a print rate 50% faster than they needed for value production and an assembly rate about 35% faster than they need for full-volume production,” Kevin said. “We have a dozen programs for multi component structures,” said Kevin. “Our first production programs are going to be in vehicles on the road in early 2022. And these are with brands that are within groups that are in the top five global automotive groups by annual volume.”
So, just to review, it’s: computer-designed parts, 3D printers making those parts, which are assembled by robots, in a much smaller space than typical assembly lines.
So no more River Rouge. The Czingers say that carmakers could replace assembly lines that had been a mile long with assembly stations like the one I saw, greatly reducing the lead time, cost, and complexity of car making. And you can switch the car model that you’re building with every new assembly. No more downtime during model-year changeover. And all those spare parts carmakers have to keep in warehouses for 10 years? They will be replaced by instant 3D printing of whatever spare part you need.


Deep North, which uses AI to track people from camera footage, raises $16.7M
Deep North, a Foster City, California-based startup applying computer vision to security camera footage, today announced that it raised $16.7 million in a Series A-1 round. Led by Celesta Capital and Yobi Partners, with participation from Conviction Investment Partners, Deep North plans to use the funds to make hires and expand its services “at scale,” according to CEO Rohan Sanil.
Deep North, previously known as Vmaxx, claims its platform can help brick-and-mortar retailers “embrace digital” and protect against COVID-19 by retrofitting security systems to track purchases and ensure compliance with masking rules. But the company’s system, which relies on algorithms with potential flaws, raises concerns about both privacy and bias.
Full Story:

Nvidia releases robot toolbox to deepen support of AI-powered robotics in ROS
Nvidia announced today that Isaac, its developer toolbox for supporting AI-powered robotics, will deepen support of the Robot Operating System (ROS). The announcement is being made this morning at ROS World 2,021 a conference for developers, engineers, and hobbyists who work on ROS, a popular open-source framework that helps developers build and reuse code used for robotics applications.
Nvidia, which is trying to assert its lead as a supplier of processors for AI applications, announced a host of “performance perception” technologies that would be part of what it will now call Isaac ROS. This includes computer vision and AI/ML functionality in ROS-based applications to support things like autonomous robots.
Full Story:
One giant leap for the mini cheetah
A new control system, demonstrated using MIT’s robotic mini cheetah, enables four-legged robots to jump across uneven terrain in real-time. A loping cheetah dashes across a rolling field, bounding over sudden gaps in the rugged terrain. The movement may look effortless, but getting a robot to move this way is an altogether different prospect.
In recent years, four-legged robots inspired by the movement of cheetahs and other animals have made great leaps forward, yet they still lag behind their mammalian counterparts when it comes to traveling across a landscape with rapid elevation changes.
“In those settings, you need to use vision in order to avoid failure. For example, stepping in a gap is difficult to avoid if you can’t see it. Although there are some existing methods for incorporating vision into legged locomotion, most of them aren’t really suitable for use with emerging agile robotic systems,” says Gabriel Margolis, a PhD student in the lab of Pulkit Agrawal, professor in the Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) at MIT.
Artificial Muscles Robotic Arm Full Range of Motion + Static Strength Test (V11)
We have achieved strong, fast, power-dense, high-efficiency, biomimetic, soft, safe, clean, organic and affordable robotic technology. Dumbbell weights 7 kg (15,6 lbs) 0 forearm with hand only 1 kg (2,2 lbs).
This artificial muscles robotic arm is operated by water and consumes 200W at peak. We invent and produce portable power supply and our own electro-hydraulic mini valves to have complete controllability of speed contraction and compress the whole powering system (for a full body) inside humanlike robot torso.
At this moment our robotic arm is operated only by a half of artificial muscles when compared to a human body. Strongest finger-bending muscle still missing. Fingers are going to move from left to right but they don’t have muscles yet. Metacarpal and left-to-right wrist movement are also blocked. This version has a position sensor in each joint but they are yet to be software-implemented. We are going to add everything mentioned above in the next prototype.
The movement sequence was written and sent by simple commands to a hand. We wish to develop a platform for reinforcement learning purposes, prosthetic arms and ultimately a full humanoid robots to serve people for fun, as butlers, cleaners, chauffeurs, construction workers (also in space) and even achieve human immortallity by transplanting the brain into the machine.
If you want to see updates on the project, please share, like, comment and hit that subscribe button. You can also support us directly on Patreon:
https://www.patreon.com/automatonrobotics.
Wesprzyj Rodaku nasz projekt na Patronite:
Asset Performance Management
Learn More.
Boston Dynamics.
Accelerate your digital transformation and discover how dynamic sensing unlocks flexible, reliable data capture for.
Turn to agile mobile robots like Spot to collect better data and optimize asset performance in industrial environments across manufacturing, power and utilities, oil and gas, mining, construction, and more.

Autonomous Racing Drones Dodge Through Forests at 40 kph
It seems inevitable that sooner or later, the performance of autonomous drones will surpass the performance of even the best human pilots. Usually things in robotics that seem inevitable happen later as opposed to sooner, but drone technology seems to be the exception to this. We’ve seen an astonishing amount of progress over the past few years, even to the extent of sophisticated autonomy making it into the hands of consumers at an affordable price.
The cutting edge of drone research right now is putting drones with relatively simple onboard sensing and computing in situations that require fast and highly aggressive maneuvers. In a paper published yesterday in Science Robotics, roboticists from Davide Scaramuzza’s Robotics and Perception Group at the University of Zurich along with partners at Intel demonstrate a small, self-contained, fully autonomous drone that can aggressively fly through complex environments at speeds of up to 40kph.