The model can diagnose problems as well as a human specialist, and doesn’t need lots of labor-intensive training data.

The National Institutes of Health will invest $130 million over four years, pending the availability of funds, to accelerate the widespread use of artificial intelligence (AI) by the biomedical and behavioral research communities. The NIH Common Fund’s Bridge to Artificial Intelligence (Bridge2AI) program is assembling team members from diverse disciplines and backgrounds to generate tools, resources, and richly detailed data that are responsive to AI approaches. At the same time, the program will ensure its tools and data do not perpetuate inequities or ethical problems that may occur during data collection and analysis. Through extensive collaboration across projects, Bridge2AI researchers will create guidance and standards for the development of ethically sourced, state-of-the-art, AI-ready data sets that have the potential to help solve some of the most pressing challenges in human health — such as uncovering how genetic, behavioral, and environmental factors influence a person’s physical condition throughout their life.
“Generating high-quality ethically sourced data sets is crucial for enabling the use of next-generation AI technologies that transform how we do research,” said Lawrence A. Tabak, D.D.S., Ph.D., Performing the Duties of the Director of NIH. “The solutions to long-standing challenges in human health are at our fingertips, and now is the time to connect researchers and AI technologies to tackle our most difficult research questions and ultimately help improve human health.”
AI is both a field of science and a set of technologies that enable computers to mimic how humans sense, learn, reason, and take action. Although AI is already used in biomedical research and healthcare, its widespread adoption has been limited in part due to challenges of applying AI technologies to diverse data types. This is because routinely collected biomedical and behavioral data sets are often insufficient, meaning they lack important contextual information about the data type, collection conditions, or other parameters. Without this information, AI technologies cannot accurately analyze and interpret data. AI technologies may also inadvertently incorporate bias or inequities unless careful attention is paid to the social and ethical contexts in which the data is collected.

Social media users may trust artificial intelligence (AI) as much as human editors to flag hate speech and harmful content, according to researchers at Penn State.
The researchers said that when users think about positive attributes of machines, like their accuracy and objectivity, they show more faith in AI. However, if users are reminded about the inability of machines to make subjective decisions, their trust is lower.
The findings may help developers design better AI-powered content curation systems that can handle the large amounts of information currently being generated while avoiding the perception that the material has been censored, or inaccurately classified, said S. Shyam Sundar, James P. Jimirro Professor of Media Effects in the Donald P. Bellisario College of Communications and co-director of the Media Effects Research Laboratory.
The world has experienced a technological leap in the last decade. Innovations such as smartphones and tablets, 3D printing, artificial intelligence, and blockchain are coming with us. As is well known, these technologies have become indispensable, not only causing hype in one or the other but also permanently changing our daily lives and ways of working. Will this development slow down? I do not think so, the exact opposite. In the next 10 years, you can expect even more breakthroughs than you can imagine today.
In this programme the world’s leading experts attempt to build an artificial human based on actress Gemma Chan, star of the sci-fi series Humans, for a ground-breaking scientific stunt that will test just how far away we are from ‘synthetic’ humans.
Could science fiction be our reality much sooner than we think?
Find us on:
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/SparkDocs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/spark_channel/
Content licensed from DriveTV to Little Dot Studios.
Any queries, please contact us at: [email protected].
#Spark #Humans #ArtificialIntelligence
The future of mind-controlled machines might not be as far away as we think.
As director of DARPA’s Biological Technologies Office, Dr Justin Sanchez is part of a team that is looking at how to decode brain signals and use them to control robotic prosthetics.
His research includes the visualisation and decoding of brain activity, the development of devices that could help patients with memory deficits, and advanced prosthetic arm systems that could restore feeling and movement after an injury.
The former associate professor of Biomedical Engineering and Neuroscience at the University of Miami has also looked at the potential of neurotechnology for treating paralysis, Tourette’s Syndrome and Obsessive Compulsive Disorder.
In this talk Dr Justin Sanchez takes us through various real world applications of direct neural interfaces.
–
The resulting artwork has its own particular aesthetic, defined by swirling shapes and incoherent objects. The real magic, though, is that no matter what you type, the app will generate something visually compelling (at least until we get too used to these toys) and that matches your prompt in often surprisingly opposite ways.
UK-based robotics company Engineered Arts just gave an ultra-realistic-looking humanoid robot Ameca a voice. Ameca is the world’s most advanced human-shaped robot representing the forefront of human-robotics technology. In a new video, the company showed off Ameca having a conversation with a number of the company’s engineers, courtesy of a speech synthesizer and OpenAI’s GPT 3, a cutting-edge language model that uses deep learning to generate impressively human-like text.

Optimizing Human-System Performance — Dr. Greg Lieberman, Ph.D., Neuroscientist / Lead, U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command Army Research Laboratory, U.S. Army Futures Command
Dr. Greg Lieberman, Ph.D. (https://www.arl.army.mil/arl25/meet-arl.php?gregory_lieberman) is a Neuroscientist, and Lead, Optimizing Human-System Performance, at the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command, Army Research Laboratory (DEVCOM ARL).
DEVCOM ARL, as an integral part of the Army Futures Command, is the Army’s foundational research laboratory focused on operationalizing science to ensure overmatch in any future conflict. DEVCOM ARL shapes future concepts with scientific research and knowledge and delivers technology for modernization solutions to win in the future operating environment.
With a Ph.D. from the University of Vermont in Neuroscience, a Postdoctoral Fellowship in Cognitive Neuroscience from University of New Mexico, and a BA from University of Massachusetts Amherst in Psychology, Dr. Lieberman’s research and research leadership experience ranges from genetics to learning theory, animal behavior to artificial intelligence, and human variability to team dynamics; with additional expertise in S&T strategy and the opportunities afforded by the Future of Work.
Specific areas of Dr. Lieberman’s technical expertise include maximizing human potential, human-autonomy teaming; neuroanatomical organization and connectivity; brain structure-function coupling; learning-driven neuroplasticity; non-invasive neurostimulation and cognitive enhancement; neuroimaging; mind-body medicine and mindfulness meditation; and the mechanisms of neurodegenerative disease, neuropathology, and brain injury.
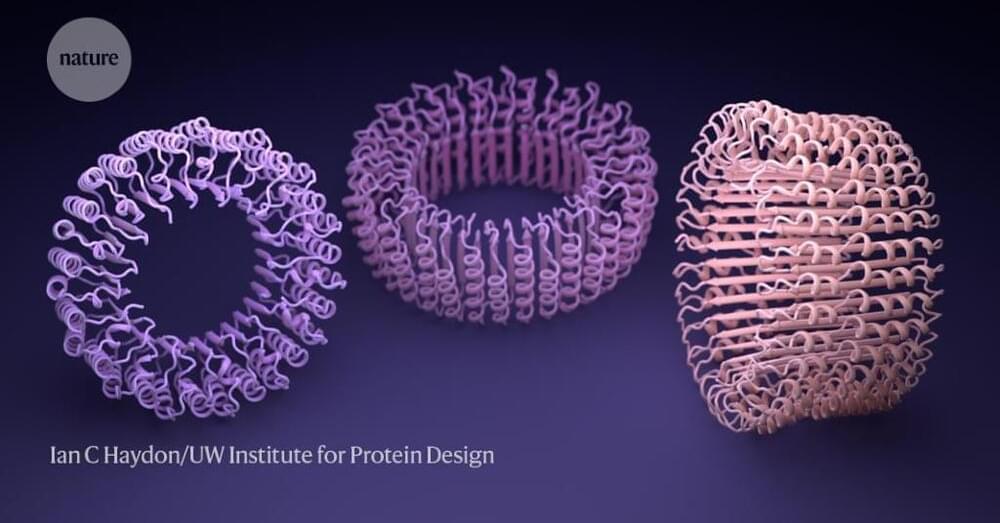
In June, South Korean regulators authorized the first-ever medicine, a COVID vaccine, to be made from a novel protein designed by humans. The vaccine is based on a spherical protein ‘nanoparticle’ that was created by researchers nearly a decade ago, through a labour-intensive trial-and error-process1.
Now, thanks to gargantuan advances in artificial intelligence (AI), a team led by David Baker, a biochemist at the University of Washington (UW) in Seattle, reports in Science2,3 that it can design such molecules in seconds instead of months.