The move appears to demonstrates a commitment to the public good by the embattled agency.


Keeping up with Meta’s scandals could easily be a part-time job. All joking aside, the development of its worldwide network ramifications helped decrease communication distances between individuals with an average of three and a half degrees of separation between its members in 2016.
As a reminder, this network and its numerous variations, which certainly don’t need to be named anymore, have enabled us to:
· reach our friends, family members, business collaborators, or partners;
· create and join discussion groups;
· organize events;promote icons and content in very different formats.
The downside is that all of this became possible the moment we agreed to join the online club for free. The benefit of accessing brand new and efficient communication tools has left us with no choice but to keep returning to a highly segmented network (comprising both acquaintances and close friends). Such a network, which includes more and more of our “friends,” convinces us to never really read the terms and conditions (boring, right?).
Yet, they clearly involve the real-time sale of our personal profiles and predictable behaviors the moment we tick the boxes just to get in.
Using a free service is very different from being the unwitting provider of a value stream (via analytics data and advertising marketplaces). We act in good faith, as we would in real life, but often accept advertising as the only way to endorse our cultural preferences regarding this or that innovative trend (even when there is little innovation and mostly an unsustainable waste of our limited resources, namely time and attention).
Today, privacy advocates are also thrilled by the broad variety of initiatives enabling us to stop dissipating our shared moments between our interlocutors AND third parties interfering with our conversations. How do we progressively upgrade the software without requiring everybody (who feels like it could be a good idea, of course) to get on board? We’re facing quite a pickle here, perhaps not as hard as gluing back together large blocks of melting ice, but still not trivial when considered at scale.
Here are two technological ways to connect with your peers outside of the “normative ways”,
plus one relying on one of the oldest networks, email. Here are their respective slogans:
· Delta Chat — Chat over email with encryption,
like Telegram or messaging apps owned by Meta but without the tracking or central control — https://delta.chat/en/
· Element — Own your conversations — https://element.io
(Its underlying protocols are now used by the French state for some of its administration services)
· Signal — Privacy is the default — https://signal.org
I invite you to try them out, share your insights, and support their contributors. Social challenges won’t be solved solely by switching communication tools.
However, conversations remain conversations; the better the host, the more comfortable and safe we feel in preserving a discussion that is as open, honest, and respectful as possible.
Hey New York, meet Forward. A new kind of doctor’s office with unlimited visits & no copays. Ever. Forward has two locations in NoMad & Midtown featuring unlimited access to world-class doctors, biometric body scans, genetic testing and so much more. Learn why The New Yorker called us “the doctor’s office of the future” → https://bit.ly/2sVXtfa
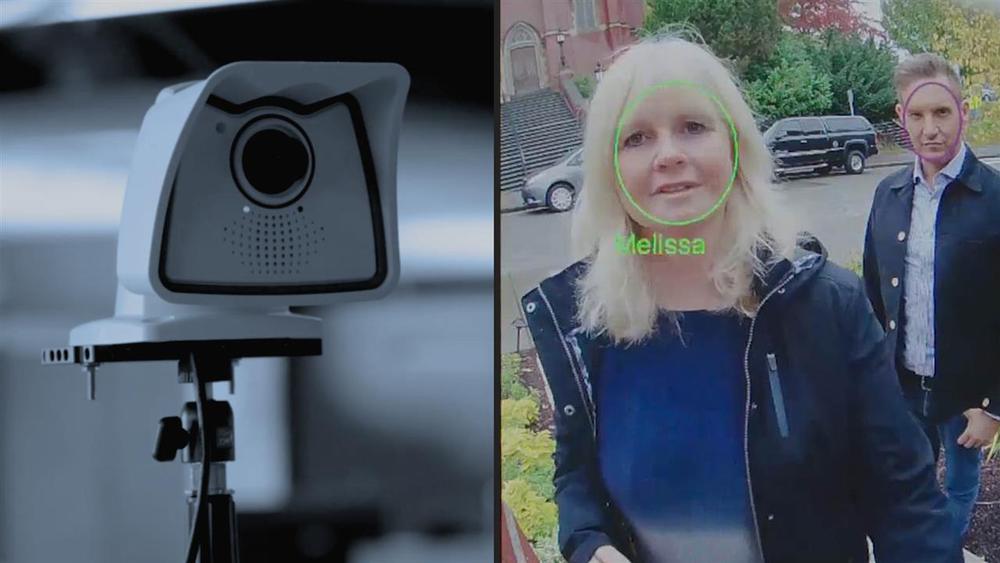

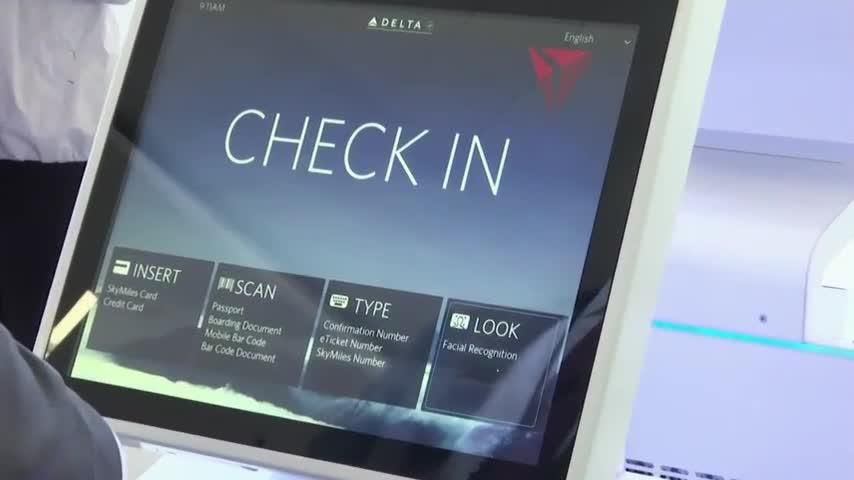
Facial recognition is going mainstream. The technology is increasingly used by law-enforcement agencies and in schools, casinos and retail stores, spurring privacy concerns. In this episode of Moving Upstream, WSJ’s Jason Bellini tests out the technology at an elementary school in Seattle and visits a company that claims its algorithm can identify potential terrorists by their facial features alone.

Are we about to see Apple reaching an even newer gold standard in ear buds? Apple has a patent for AirPods with built in biometrics. It’s being called “universal” because the idea calls for ear pods that can be worn in either ear. That would mean no more left-right business.
Much of the tech news coverage is focusing on the “interchangeable” aspect of the patent concept. 9to5Mac’s Alex Allegro said interchangeable earbuds “equipped with ‘at least one’ biometric sensor, which could detect left/right ear placement and accordingly adjust audio.” He assessed the potential advantages as “evolving AirPods from a separate left / right unit to a single component,” which could lower costs and simplify getting a replacement AirPod.
If the ear buds are interchangeable, then it is a big deal in terms of user satisfaction. OK, the product is popular now but The Verge reminds us that the AirPod is not a perfect fit for everyone. Nick Statt: “Due to the shape of some people’s inner ear, the headphones simply don’t fit every possible ear shape well.”

The new service lets consumers contribute to medical research, but still poses privacy concerns.
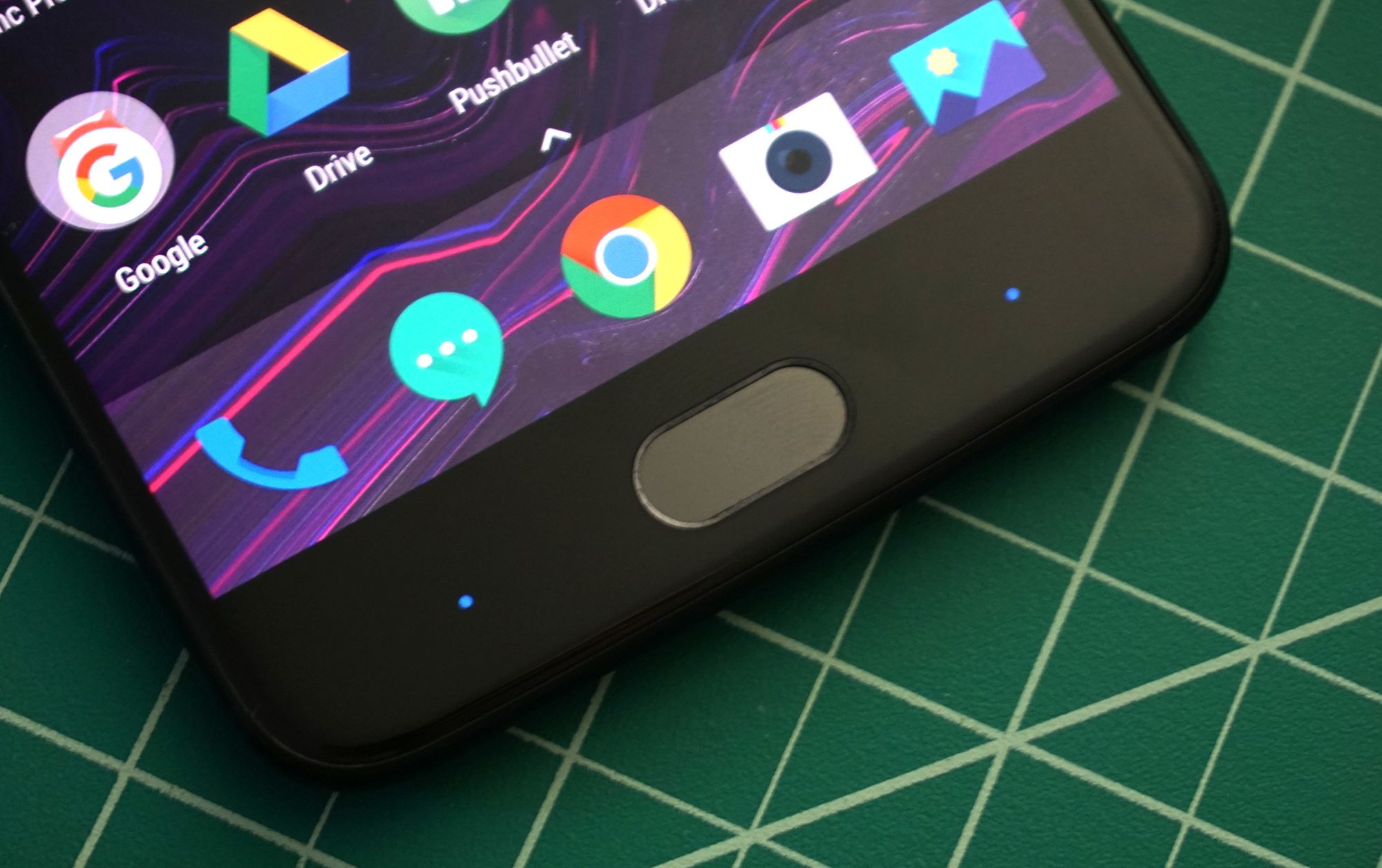

Biometric features like fingerprint sensors and iris scanners have made it easier to securely unlock phones, but they may never be as secure as a good old-fashioned password. Researchers have repeatedly worked out methods to impersonate registered users of biometric devices, but now a team from New York University and the University of Michigan has gone further. The team managed to create so-called “DeepMasterPrints” that can fool a sensor without a sample of the real user’s fingerprints.
Past attempts to bypass biometric systems usually involve getting access to a registered individual’s data — that could be a copy of their fingerprint or a 3D scan of their face. DeepMasterPrints involves generating an entirely new fingerprint from a mountain of data that’s close enough to fool the sensor. Like so many research projects these days, the team used neural networks to do the heavy lifting.
The process started with feeding fingerprints from 6,000 people into a neural network in order to train it on what a human fingerprint looks like. A neural network is composed of a series of nodes that process data. It feeds forward into additional “layers” of nodes if the output meets a certain threshold. Thus, you can train the network to get the desired output. In this case, the researchers used a “generative adversarial network” to tune the system’s ability to generate believable fingerprints. The network used its understanding of prints to make one from scratch, and then a second network would determine if they were real or fake. If the fingerprints didn’t pass muster, the network could be re-tuned to try again.
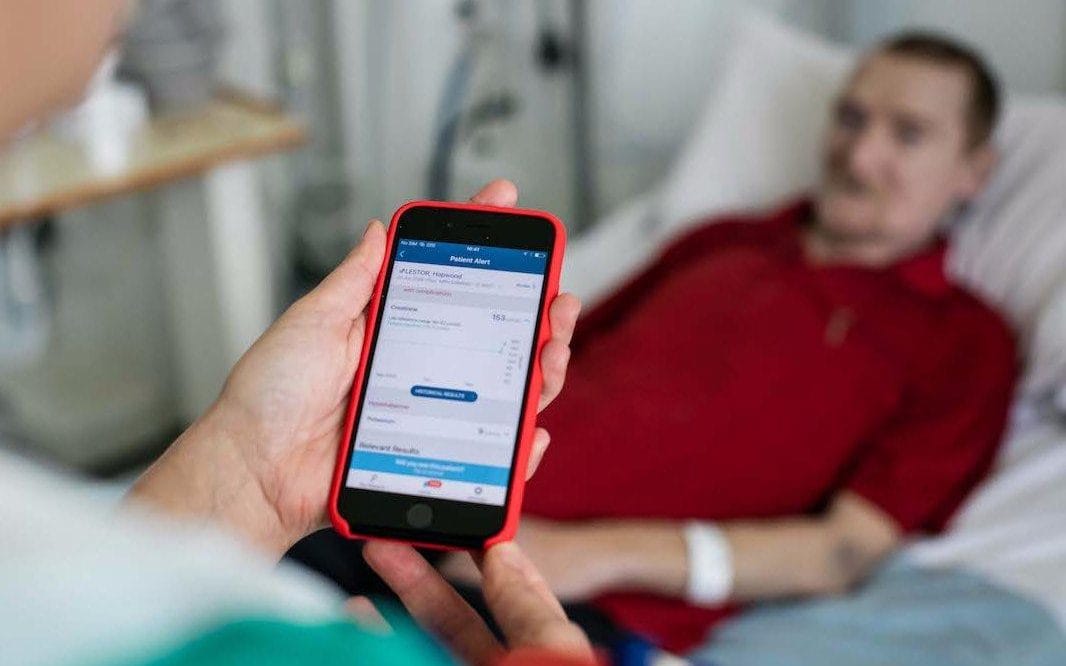
Privacy advocates have raised concerns about patients’ data after Google said it would take control of its subsidiary DeepMind’s healthcare division.
Google, which acquired London-based artificial intelligence lab DeepMind in 2014, said on Tuesday that the DeepMind Health brand, which uses NHS patient data, will cease to exist and the team behind its medical app Streams will join Google as part of Google Health.
It comes just months after DeepMind promised never to share data with the technology giant and an ethics board raised concerns over its independence.
Whether it’s left there or right here… the tactics and destination look pretty much the same to me…
China is the world leader in facial recognition technology. Discover how the country is using it to develop a vast hyper-surveillance system able to monitor and target its ethnic minorities, including the Muslim Uighur population.
Click here to subscribe to The Economist on YouTube: https://econ.st/2xvTKdy
Improving lives, increasing connectivity across the world, that’s the great promise offered by data-driven technology — but in China it also promises greater state control and abuse of power.
This is the next groundbreaking development in data-driven technology, facial recognition. And in China you can already withdraw cash, check in at airports, and pay for goods using just your face. The country is the world’s leader in the use of this emerging technology, and China’s many artificial intelligence startups are determined to keep it that way in the future.