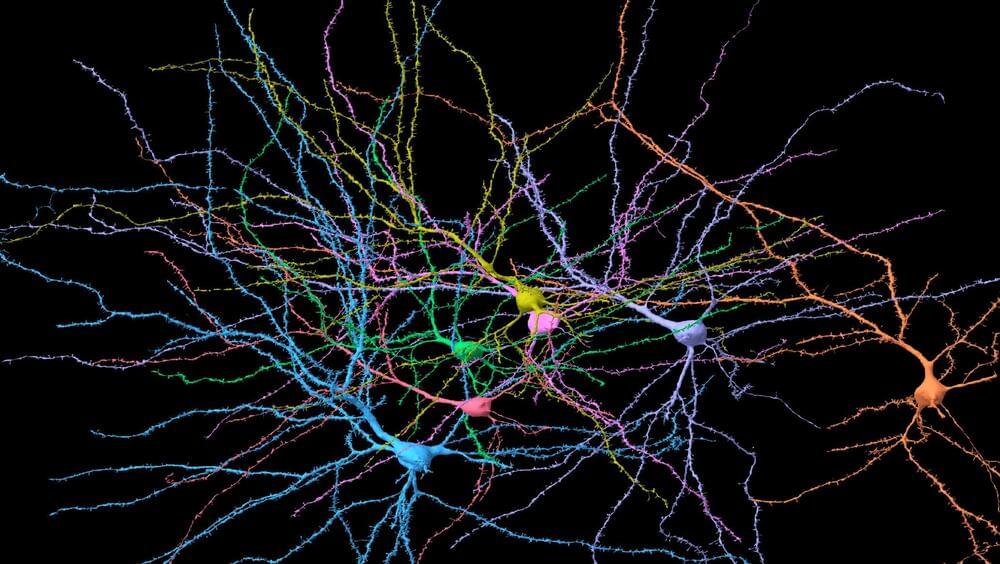
While researchers have long studied brain dynamics using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalograms (EEG), advances in neuroscience have only recently provided massive datasets for the brain’s cellular structure. These data opened possibilities for Kovács and his team to apply statistical physics techniques to measure the physical structure of neurons.
For the new study, Kovács and Ansell analyzed publicly available data of 3D brain reconstructions from humans, fruit flies and mice. By examining the brain at nanoscale resolution, the researchers found the samples showcased hallmarks of physical properties associated with criticality.
One such property is the well-known, fractal-like structure of neurons. This nontrivial fractal-dimension is an example of a set of observables, called “critical exponents,” that emerge when a system is close to a phase transition.