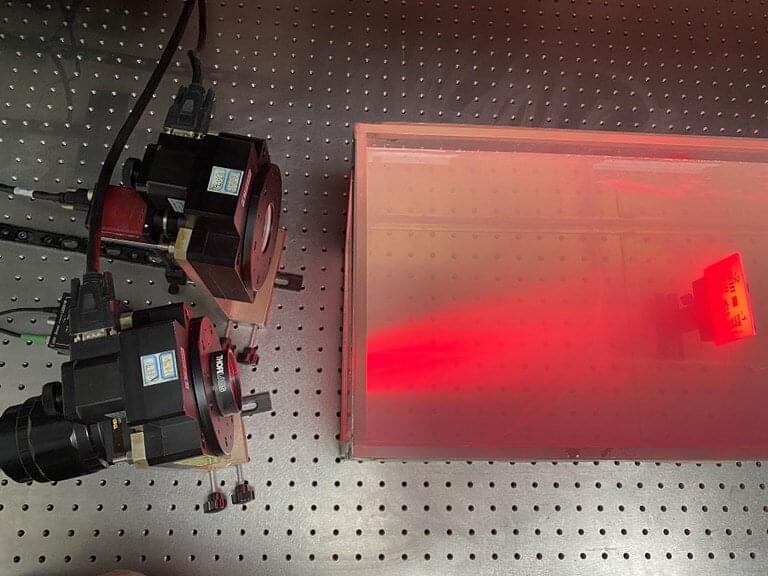
Researchers have developed a new method that can automatically produce clear images through murky water. The new technology could be useful for searching for drowning victims, documenting submerged archaeological artifacts and monitoring underwater farms.
Imaging clearly underwater is extremely challenging because the water and the particles in it tend to scatter light. But, because scattered light is partially polarized, imaging using a camera that is sensitive to polarization can be used to suppress scattered light in underwater images.
“Our new method overcomes the limitations of traditional polarimetric underwater imaging, laying the groundwork for taking this method out of the lab and into the field,” said research team leader Haofeng Hu from Tianjin University in China. “Unlike previous methods, there’s no requirement for the image to include a background area to estimate the backscattered light.”