Explore 10 new works related to particle physics and astrophysics, plus a bonus book on math.



Today’s quantum computers are complicated to build, difficult to scale up, and require temperatures colder than interstellar space to operate. These challenges have led researchers to explore the possibility of building quantum computers that work using photons—particles of light. Photons can easily carry information from one place to another, and photonic quantum computers can operate at room temperature, so this approach is promising. However, although people have successfully created individual quantum “logic gates” for photons, it’s challenging to construct large numbers of gates and connect them in a reliable fashion to perform complex calculations.
Now, Stanford University researchers have proposed a simpler design for photonic quantum computers using readily available components, according to a paper published Nov. 29 in Optica. Their proposed design uses a laser to manipulate a single atom that in turn, can modify the state of the photons via a phenomenon called “quantum teleportation.” The atom can be reset and reused for many quantum gates, eliminating the need to build multiple distinct physical gates, vastly reducing the complexity of building a quantum computer.
“Normally, if you wanted to build this type of quantum computer, you’d have to take potentially thousands of quantum emitters, make them all perfectly indistinguishable, and then integrate them into a giant photonic circuit,” said Ben Bartlett, a Ph.D. candidate in applied physics and lead author of the paper. “Whereas with this design, we only need a handful of relatively simple components, and the size of the machine doesn’t increase with the size of the quantum program you want to run.”
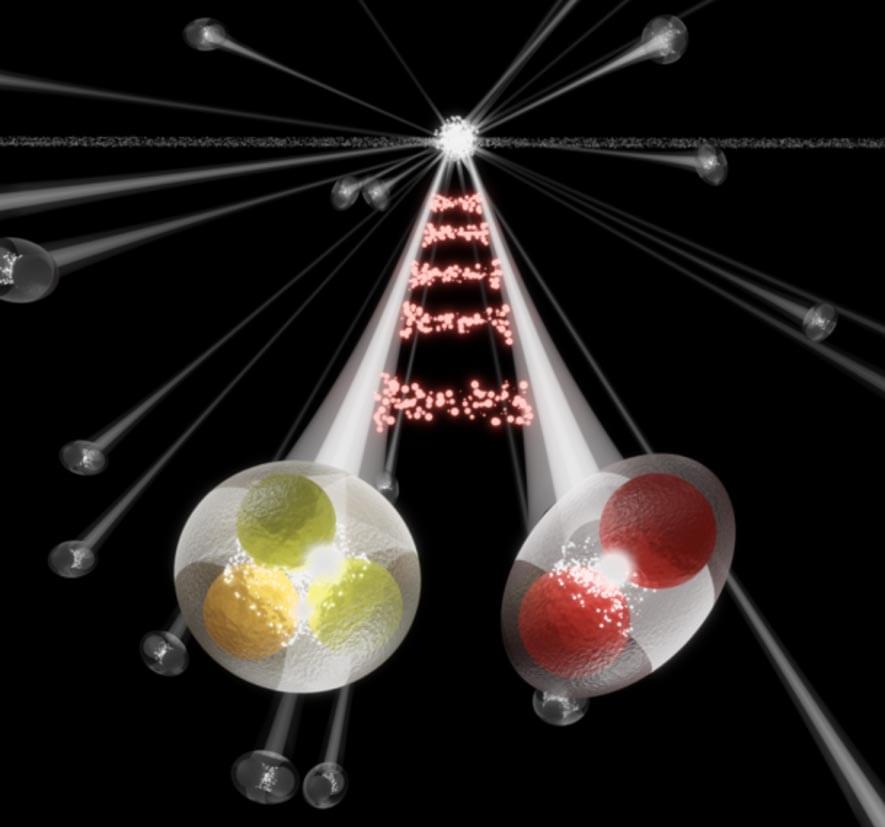
The ALICE collaboration has for the first time observed the residual strong interaction between protons and phi mesons. In an article recently published in Physical Review Letters, the ALICE collaboration has used a method known as femtoscopy to study the residual interaction between two-quark an.
Sustainable agriculture continues to spread at an accelerated pace and farmers need all the help they can get in order to cope with the increasing workload. California-based company Iron Ox specializes in the use of robotics and artificial intelligence in agriculture, and Grover is the latest robot to join its team.
Start your Audible trial today: http://www.audible.com/spacetime.
Hello from the other side. In this episode find out how quanta can can move through solid objects.
Get your own Space Time tshirt at http://bit.ly/1QlzoBi.
Tweet at us! @pbsspacetime.
Facebook: facebook.com/pbsspacetime.
Email us! pbsspacetime [at] gmail [dot] com.
Comment on Reddit: http://www.reddit.com/r/pbsspacetime.
Support us on Patreon! http://www.patreon.com/pbsspacetime.
Help translate our videos! https://www.youtube.com/timedtext_cs_panel?tab=2&c=UC7_gcs09iThXybpVgjHZ_7g.
Where are you right now? Until you interact with another particle you could be any number of places within a wave of probabilities. This is only one way that quantum mechanics challenges our perception of reality. Matt dives into these counter-intuitive ideas and explains the bizarre phenomenon known as quantum tunneling in this episode of Space Time.
Written and hosted by Matt O’Dowd.
Tachyons are not just the stuff of science fiction.
Tachyons are hypothetical particles that move faster than the speed of light and travel backward through time. Whether they exist is still up for debate.
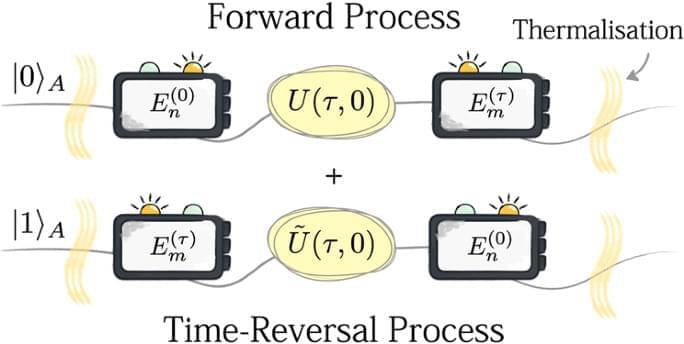
Taking a gas enclosed in a vessel as a pictorial example, the aforementioned state can be constructed by entangling the position of the piston with a further auxiliary quantum system, thereby establishing a quantum superposition of the following two processes: (i) a process wherein the gas particles are initially in thermal equilibrium confined in one half of the vessel by a piston, and the piston is pulled outwards, and (ii) the reverse process, in which the piston is pushed towards the gas, starting from an initial state where the gas occupies the entire vessel in thermal equilibrium.
We will now measure the work of the system undergoing the above-mentioned superposition of forward and time-reversal dynamics. In order to implement such a measurement, we formally construct a procedure described by a set of measurement operators forming a completely positive and trace-preserving (CPTP) map. In this regard, we will refer to a standard TPM procedure to measure work in quantum thermodynamic processes13. Implementations of the TPM in quantum setups25,26,27,28,29, as well as suitable extensions30,31,32,33, have recently received increasing attention. Our procedure can be seen as a generalisation of the TPM scheme to situations where different thermodynamic processes are allowed to be superposed, and can consequently interfere.
In the TPM scheme, work is defined as the energy difference between the initial and final states of the system, which are measured through ideal projective measurements of the system Hamiltonian implemented before and after the thermodynamic process associated with the protocol Λ34,35. This measurement scheme can be performed, individually, both for the forward and the time-reversal processes, enabling the construction of the work probability distributions P (W) and \(\tilde{P}(W)\) 0, respectively.
Circa 2017
Antimatter sounds mysterious and powerful. In science fiction, it often has properties like defying gravity or taking on opposite colors. But in reality, antimatter is really no different than regular matter, except that antimatter atoms have positrons instead of electrons and antiprotons instead of protons. At CERN in Switzerland, scientists have actually been able to create antimatter and store it in a magnetic field that keeps it from touching regular matter. If that happens, the antimatter annihilates, producing a burst of energy. In sci-fi like Star Trek, this energy is used to power spaceships. We’re still very far from something like that, but it’s still pretty incredible that we can create something that was for a long time just a hypothesis.
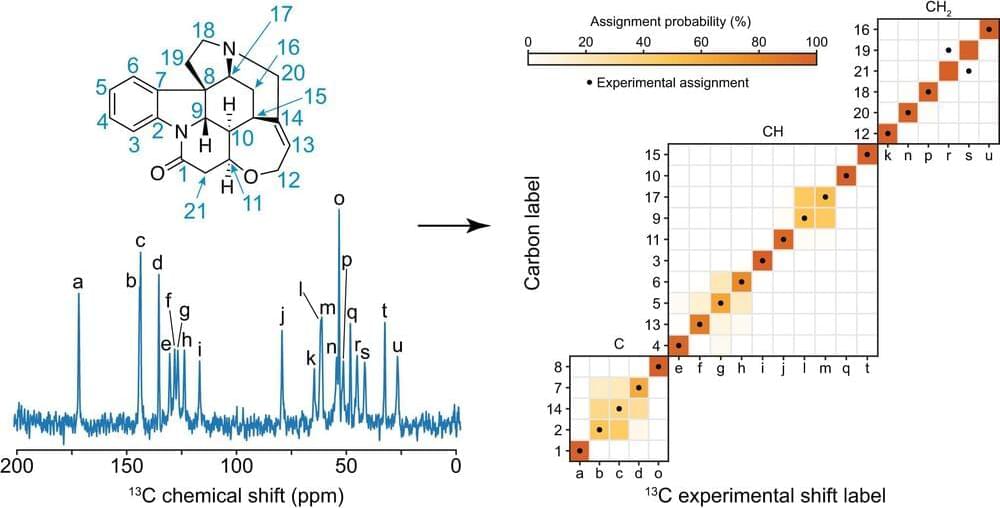
Solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy—a technique that measures the frequencies emitted by the nuclei of some atoms exposed to radio waves in a strong magnetic field—can be used to determine chemical and 3D structures as well as the dynamics of molecules and materials.
A necessary initial step in the analysis is the so-called chemical shift assignment. This involves assigning each peak in the NMR spectrum to a given atom in the molecule or material under investigation. This can be a particularly complicated task. Assigning chemical shifts experimentally can be challenging and generally requires time-consuming multi-dimensional correlation experiments. Assignment by comparison to statistical analysis of experimental chemical shift databases would be an alternative solution, but there is no such database for molecular solids.
A team of researchers including EPFL professors Lyndon Emsley, head of the Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance, Michele Ceriotti, head of the Laboratory of Computational Science and Modeling and Ph.D. student Manuel Cordova decided to tackle this problem by developing a method of assigning NMR spectra of organic crystals probabilistically, directly from their 2D chemical structures.