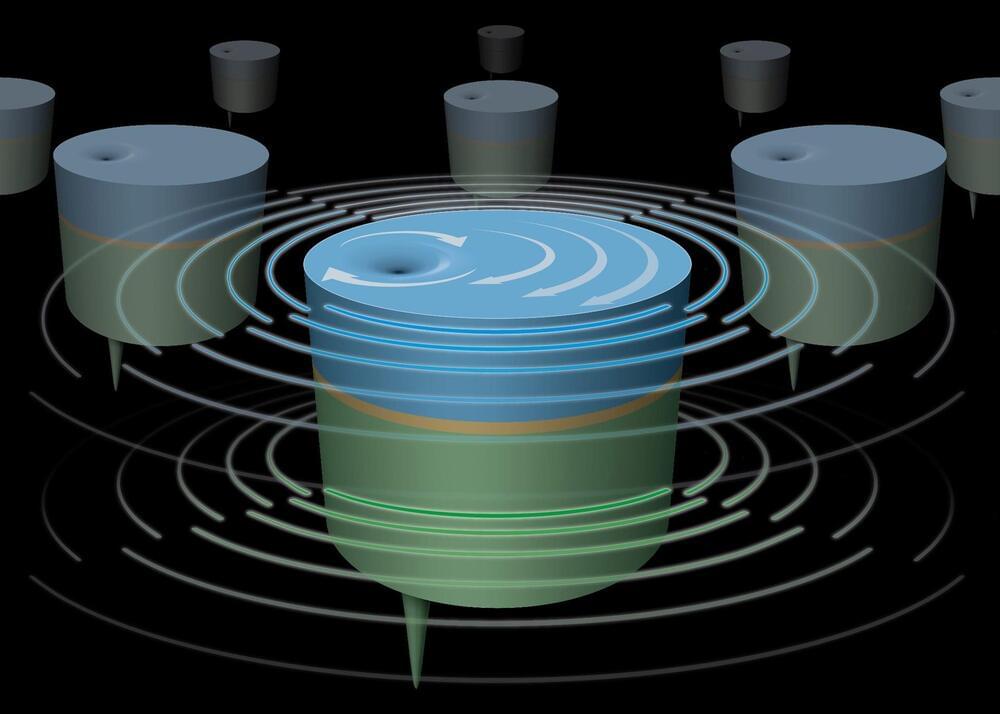
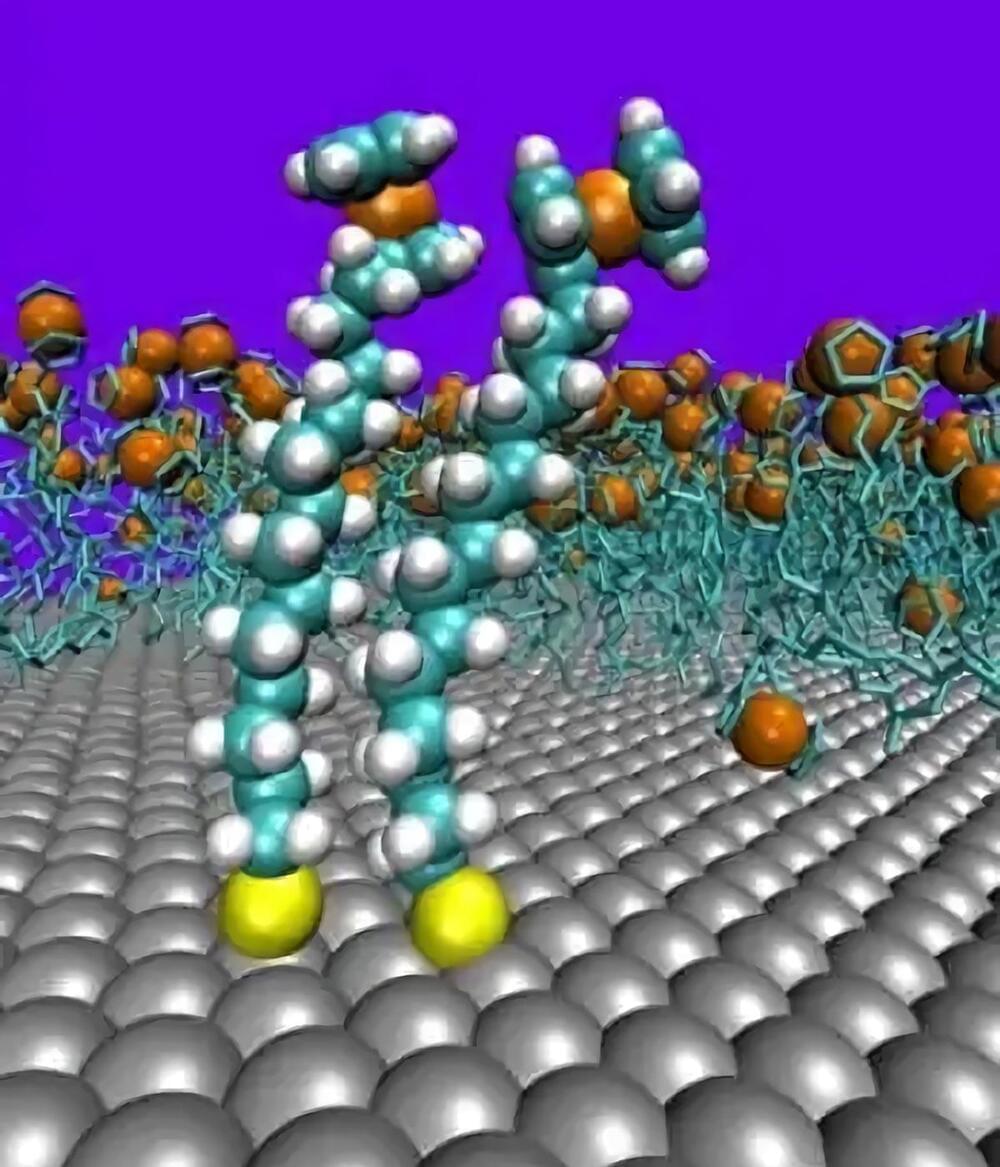
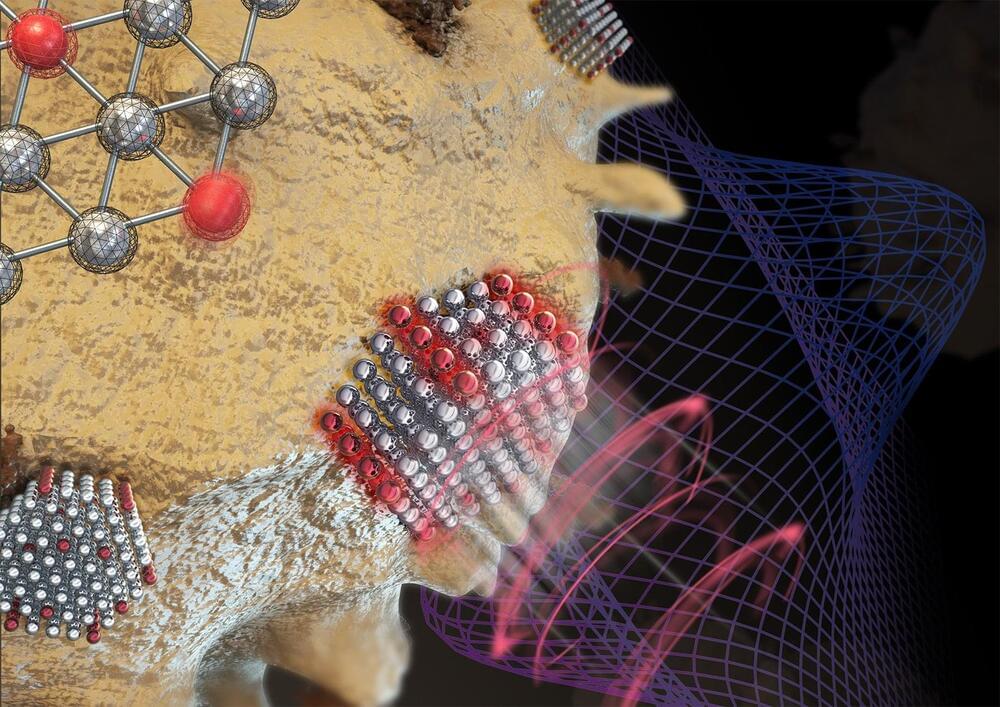
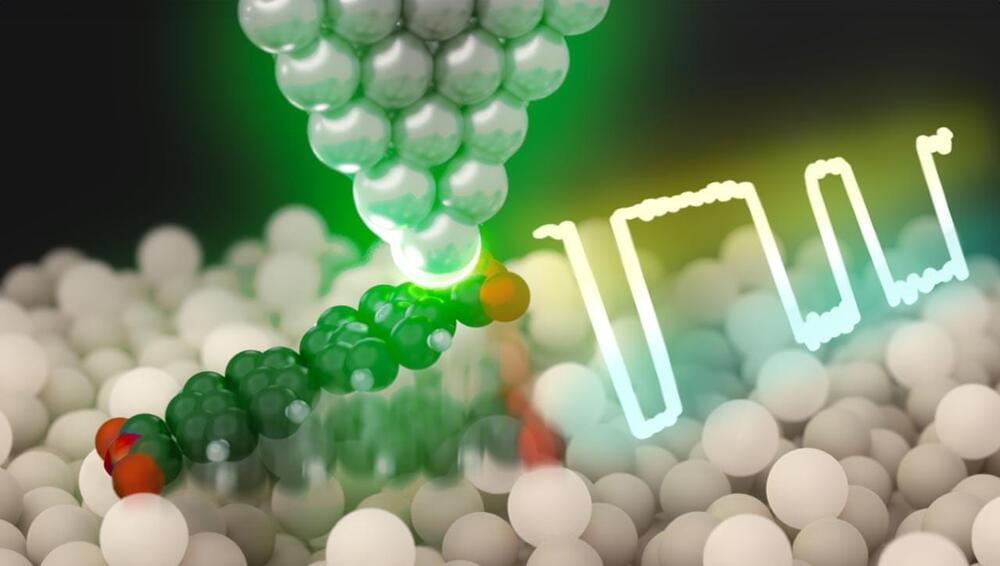
A team from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Stanford University and the University of Pennsylvania introduced a novel wet chemical etching process that modifies the surface of conventional metal powders used in 3D printing.
In a significant advancement for metal additive manufacturing, researchers at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) and their academic partners have developed a groundbreaking technique that enhances the optical absorptivity of metal powders used in 3D printing.
The innovative approach, which involves creating nanoscale surface features on metal powders, promises to improve the efficiency and quality of printed metal parts, particularly for challenging materials like copper and tungsten, according to researchers.
Additive manufacturing (AM) — more commonly known as 3D printing — has transformed the way products are designed and produced, allowing for the creation of complex geometries and customized components that traditional manufacturing methods struggle to achieve. However, one of the persistent challenges in laser powder-bed fusion (LPBF) metal 3D printing is the high reflectivity of certain metals, which can lead to inefficient energy absorption during the printing process and can even damage some printing machines. This inefficiency often results in inadequate print quality and increased energy consumption, according to researchers.