Calculations and experiments reveal that water microdroplets may play role in soil formation.


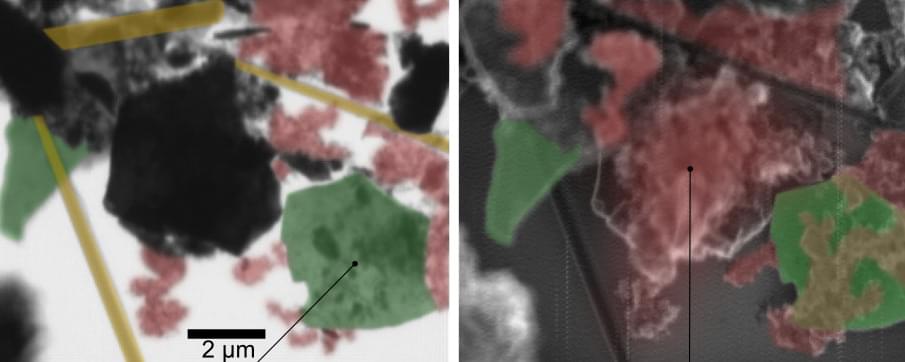
A new method in spectromicroscopy significantly improves the study of chemical reactions at the nanoscale, both on surfaces and inside layered materials. Scanning X-ray microscopy (SXM) at MAXYMUS beamline of BESSY II enables the investigation of chemical species adsorbed on the top layer (surface) or intercalated within the MXene electrode (bulk) with high chemical sensitivity. The method was developed by a HZB team led by Dr. Tristan Petit. The scientists demonstrated among others first SXM on MXene flakes, a material used as electrode in lithium-ion batteries.
Since their discovery in 2011, MXenes have gathered significant scientific interest due to their versatile tunable properties and diverse applications, from energy storage to electromagnetic shielding. Researchers have been working to decipher the complex chemistry of MXenes at the nanoscale.
The team of Dr. Tristan Petit now made a significant progress in MXene characterization, as described in their recent publication (Small Methods, “Nanoscale surface and bulk electronic properties of Ti 3 C 2 Tx MXene unraveled by multimodal X-ray spectromicroscopy”). They utilized SXM to investigate the chemical bonding of Ti 3 C 2 Tx MXenes, with Tx denoting the terminations (Tx=O, OH, F, Cl), with high spatial and spectral resolution. The novelty in this work is to combine simultaneously two detection modes, transmission and electron yield, enabling different probing depths.

For over five decades, futurist Raymond Kurzweil has shown a propensity for understanding how computers can change our world. Now he’s ready to anoint nanorobots as the key to allowing humans to transcend life’s ~120-year threshold.
As he wrote—both in the upcoming The Singularity is Nearer book (set for release on June 25) and in an essay published in Wired —the merging of biotechnology with artificial intelligence will lead to nanotechnology helping “overcome the limitations of our biological organs altogether.”
As our bodies accumulate errors when cells reproduce over and over, it invites damage. That damage can get repaired quickly by young bodies, but less so when age piles up.
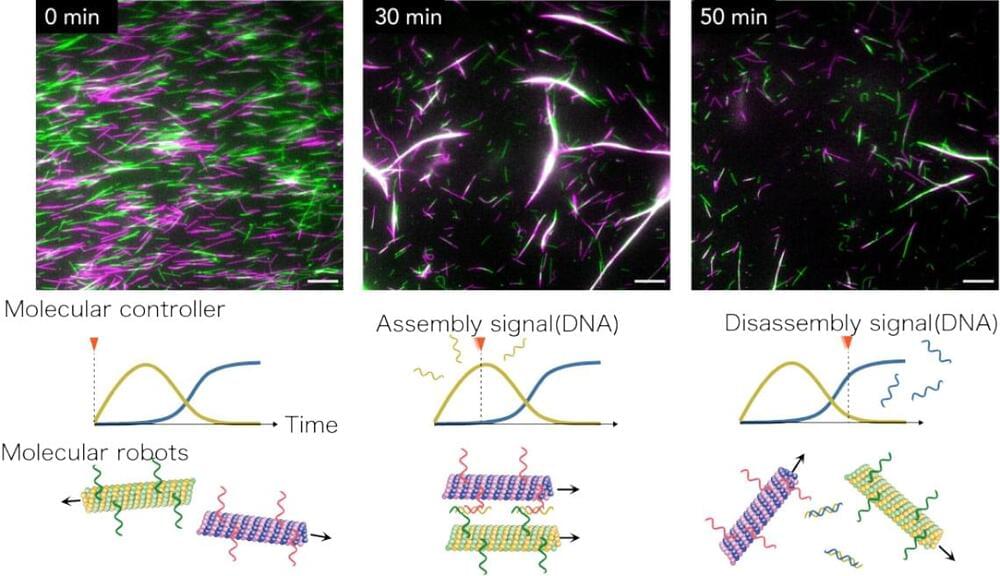
Researchers from Tohoku University and Kyoto University have successfully developed a DNA-based molecular controller that autonomously directs the assembly and disassembly of molecular robots. This pioneering technology marks a significant step towards advanced autonomous molecular systems with potential applications in medicine and nanotechnology.
Details of the breakthrough were published in the journal Science Advances (“Autonomous assembly and disassembly of gliding molecular robots regulated by a DNA-based molecular controller”).
“Our newly developed molecular controller, composed of artificially designed DNA molecules and enzymes, coexists with molecular robots and controls them by outputting specific DNA molecules,” points out Shin-ichiro M. Nomura, an associate professor at Tohoku University’s Graduate School of Engineering and co-author of the study. “This allows the molecular robots to self-assemble and disassemble automatically, without the need for external manipulation.”
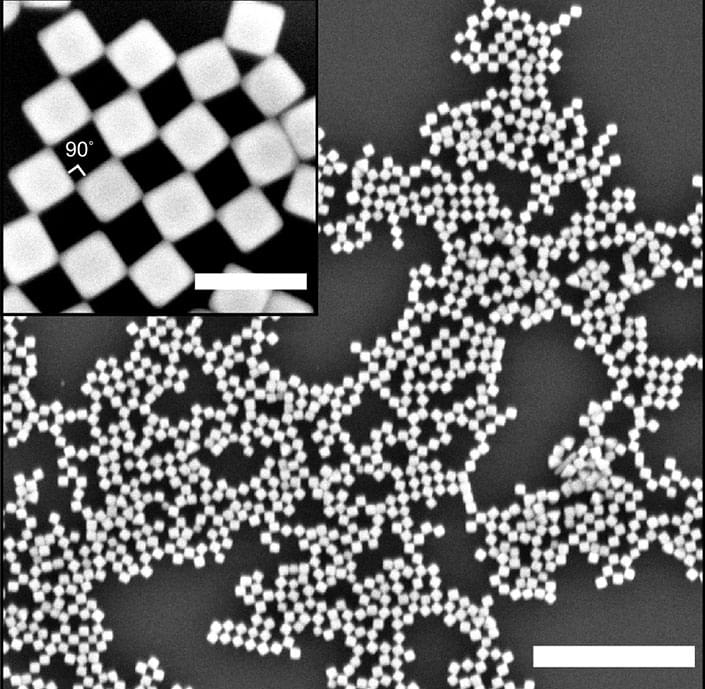
Researchers have engineered nanosized cubes that spontaneously form a two-dimensional checkerboard pattern when dropped on the surface of water. The work, published in Nature Communications (“Self-assembly of nanocrystal checkerboard patterns via non-specific interactions”), presents a simple approach to create complex nanostructures through a technique called self-assembly.
“It’s a cool way to get materials to build themselves,” said study co-senior author Andrea Tao, a professor in the Aiiso Yufeng Li Family Department of Chemical and Nano Engineering at the University of California San Diego. “You don’t have to go into a nanofabrication lab and do all these complex and precise manipulations.”
Each nanocube is composed of a silver crystal with a mixture of hydrophobic (oily) and hydrophilic (water-loving) molecules attached to the surface. When a suspension of these nanocubes is introduced to a water surface, they arrange themselves such that they touch at their corner edges. This arrangement creates an alternating pattern of solid cubes and empty spaces, resulting in a checkerboard pattern.
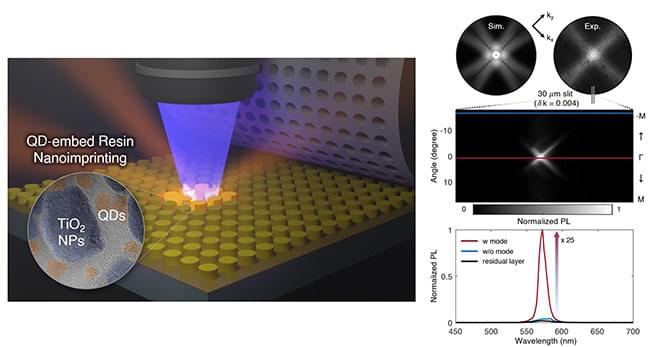
In relationships, sharing closer spaces naturally deepens the connection as bonds form and strengthen through increasing shared memories. This principle applies not only to human interactions but also to engineering. Recently, an intriguing study was published demonstrating the use of quantum dots to create metasurfaces, enabling two objects to exist in the same space.
Professor Junsuk Rho from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, the Department of Chemical Engineering, and the Department of Electrical Engineering, PhD candidates Minsu Jeong, Byoungsu Ko, and Jaekyung Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Chunghwan Jung, a PhD candidate, from the Department of Chemical Engineering at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) employed Nanoimprint Lithography (NIL) to fabricate metasurfaces embedded with quantum dots, enhancing their luminescence efficiency. Their research was recently published in Nano Letters (“Printable Light-Emitting Metasurfaces with Enhanced Directional Photoluminescence”).
(Left) Schematic diagram of the fabrication of a luminescence-controlled metasurface using the nanoimprint lithography process. (Right) Experiment evaluating the performance of the metasurface’s luminescence control. (Image: POSTECH)
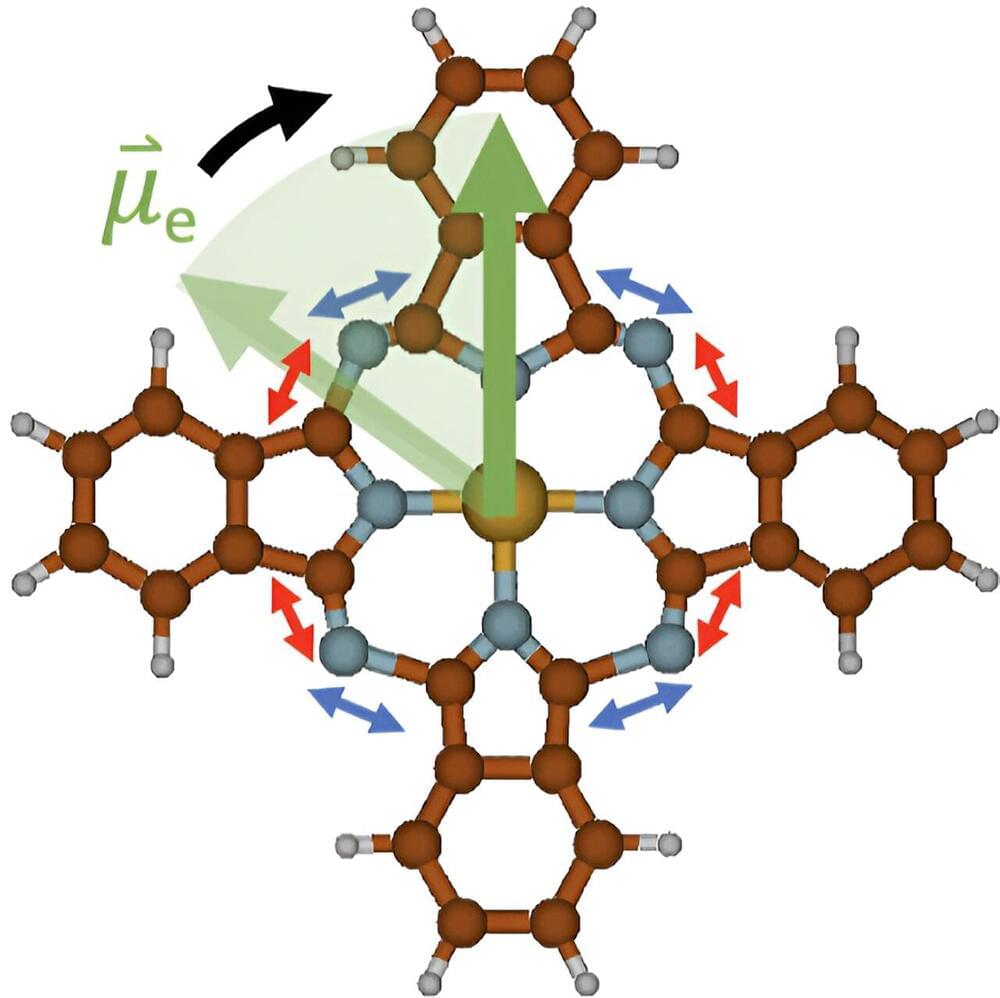
When molecules are irradiated with infrared light, they begin to vibrate due to the energy supply. For Andreas Hauser from the Institute of Experimental Physics at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz), this well-known phenomenon was the starting point for considering whether these oscillations could also be used to generate magnetic fields.
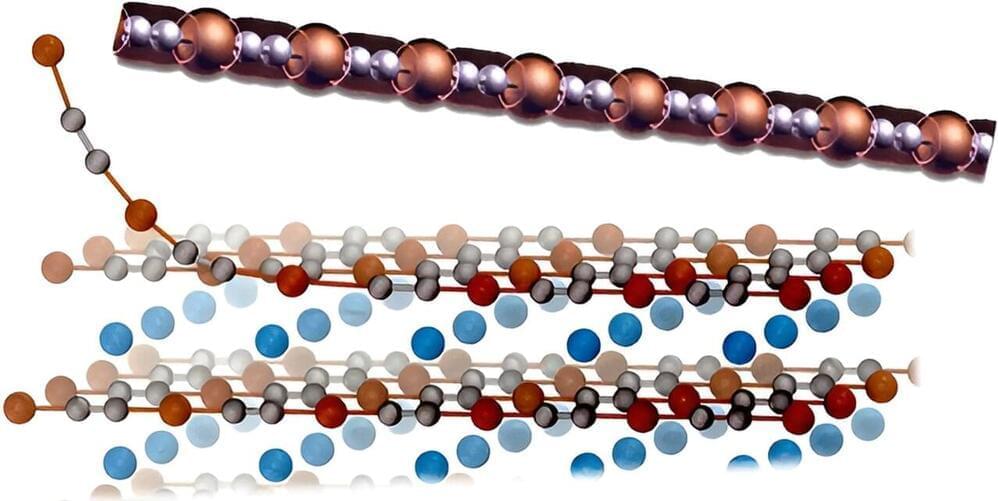
While carbon nanotubes are the materials that have received most of the attention so far, they have proved very difficult to manufacture and control, so scientists are eager to find other compounds that could be used to create nanowires and nanotubes with equally interesting properties, but easier to handle.
So, Chiara Cignarella, Davide Campi and Nicola Marzari thought to use computer simulations to parse known three-dimensional crystals, looking for those that—based on their structural and electronic properties —look like they could be easily “exfoliated,” essentially peeling away from them a stable 1-D structure. The same method has been successfully used in the past to study 2D materials, but this is the first application to their 1-D counterparts.
The researchers started from a collection of over 780,000 crystals, taken from various databases found in the literature and held together by van der Waals forces, the sort of weak interactions that happen when atoms are close enough for their electrons to overlap. Then they applied an algorithm that considered the spatial organization of their atoms looking for the ones that incorporated wire-like structures, and calculated how much energy would be necessary to separate that 1-D structure from the rest of the crystal.