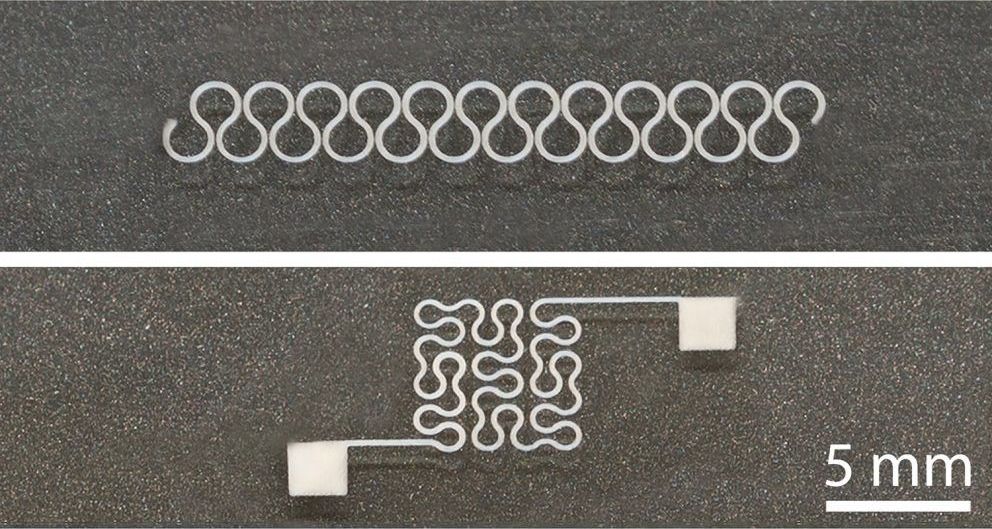
Researchers at North Carolina State University have developed a new technique that allows them to print circuits on flexible, stretchable substrates using silver nanowires. The advance makes it possible to integrate the material into a wide array of electronic devices.
Silver nanowires have drawn significant interest in recent years for use in many applications, ranging from prosthetic devices to wearable health sensors, due to their flexibility, stretchability and conductive properties. While proof-of-concept experiments have been promising, there have been significant challenges to printing highly integrated circuits using silver nanowires.
Silver nanoparticles can be used to print circuits, but the nanoparticles produce circuits that are more brittle and less conductive than silver nanowires. But conventional techniques for printing circuits don’t work well with silver nanowires; the nanowires often clog the printing nozzles.