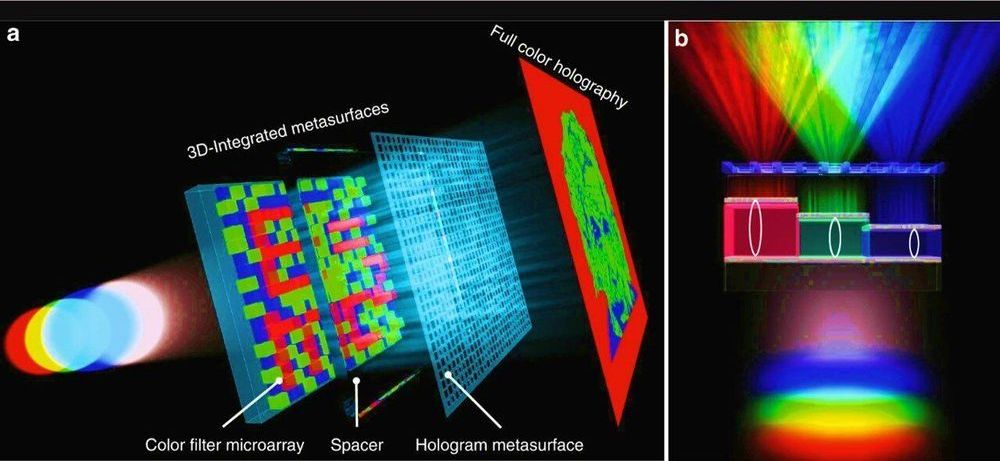
Physicists and materials scientists have developed a compact optical device containing vertically stacked metasurfaces that can generate microscopic text and full-color holograms for encrypted data storage and color displays. Yueqiang Hu and a research team in Advanced Design and Manufacturing for Vehicle Body in the College of Mechanical and Vehicle Engineering in China implemented a 3D integrated metasurface device to facilitate miniaturization of the optical device. Using metasurfaces with ultrathin and compact characteristics, the research team designed optical elements by engineering the wavefront of light at the subwavelength scale. The metasurfaces possessed great potential to integrate multiple functions into the miniaturized optoelectronic systems. The work is now published on Light: Science & Applications.
Since existing research on multiplexing in the 2-D plane remains to fully incorporate capabilities of metasurfaces for multi-tasking, in the present work, the team demonstrated a 3D integrated metasurface device. For this, they stacked a hologram metasurface on a monolithic Fabry-Pérot (FP) cavity-based color filter microarray to achieve simultaneous cross-talk, polarization-independent and highly efficient full-color holography and microprint functions. The dual function of the device outlined a new scheme for data recording, security, encryption color displays and information processing applications. The work on 3D integration can be extended to establish flat multi-tasking optical systems that include a variety of functional metasurface layers.
Metasurfaces open a new direction in optoelectronics, allowing researchers to design optical elements by shaping the wavefront of electromagnetic waves relative to size, shape and arrangement of structures at the subwavelength. Physicists have engineered a variety of metasurface-based devices including lenses, polarization converters, holograms and orbital angular momentum generators (OAM). They have demonstrated the performance of metasurface-based devices to even surpass conventional refractive elements to construct compact optical devices with multiple functions. Such devices are, however, withheld by shortcomings due to a reduced efficiency of plasmonic nanostructures, polarization requirements, large crosstalk and complexity of the readout for multiwavelength and broadband optical devices. Research teams can therefore stack 3D metasurface-based devices with different functions in the vertical direction to combine the advantages of each device.