Gossamer film of tangled carbon nanotubes gives objects a lift.



Study describes passive cooling system that aims to help impoverished communities, reduce cooling and heating costs, lower CO2 emissions.
Passive cooling, like the shade a tree provides, has been around forever.
Recently, researchers have been exploring how to turbo charge a passive cooling technique — known as radiative or sky cooling — with sun-blocking, nanomaterials that emit heat away from building rooftops. While progress has been made, this eco-friendly technology isn’t commonplace because researchers have struggled to maximize the materials’ cooling capabilities.

Today, machine learning permeates everyday life, with millions of users every day unlocking their phones through facial recognition or passing through AI-enabled automated security checks at airports and train stations. These tasks are possible thanks to sensors that collect optical information and feed it to a neural network in a computer.
Scientists in China have presented a new nanoscale AI optical circuit trained to perform unpowered all-optical inference at the speed of light for enhanced authentication solutions. Combining smart optical devices with imaging sensors, the system performs complex functions easily, achieving a neural density equal to 1/400th that of the human brain and a computational power more than 10 orders of magnitude higher than electronic processors.
Imagine empowering the sensors in everyday devices to perform artificial intelligence functions without a computer—as simply as putting glasses on them. The integrated holographic perceptrons developed by the research team at University of Shanghai for Science and Technology led by Professor Min Gu, a foreign member of the Chinese Academy of Engineering, can make that a reality. In the future, its neural density is expected to be 10 times that of human brain.

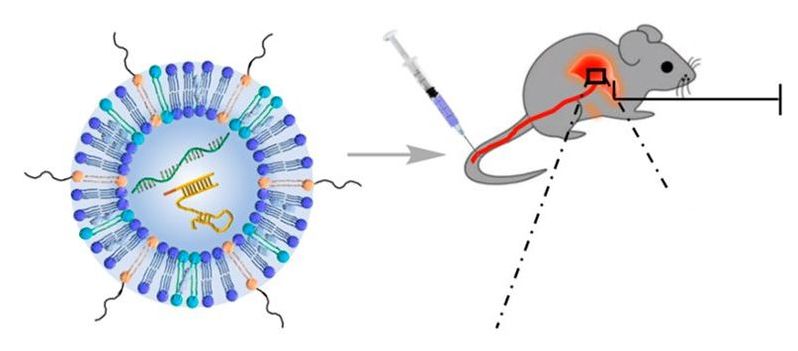
Imagine seeing the world in muted shades—gray sky, gray grass. Some people with color blindness see everything this way, though most can’t see specific colors. Tinted glasses can help, but they can’t be used to correct blurry vision. And dyed contact lenses currently in development for the condition are potentially harmful and unstable. Now, in ACS Nano, researchers report infusing contact lenses with gold nanoparticles to create a safer way to see colors.
The total amount of data generated worldwide is expected to reach 175 zettabytes (1 ZB equals 1 billion terabytes) by 2025. If 175 ZB were stored on Blu-ray disks, the stack would be 23 times the distance to the moon. There is an urgent need to develop storage technologies that can accommodate this enormous amount of data.
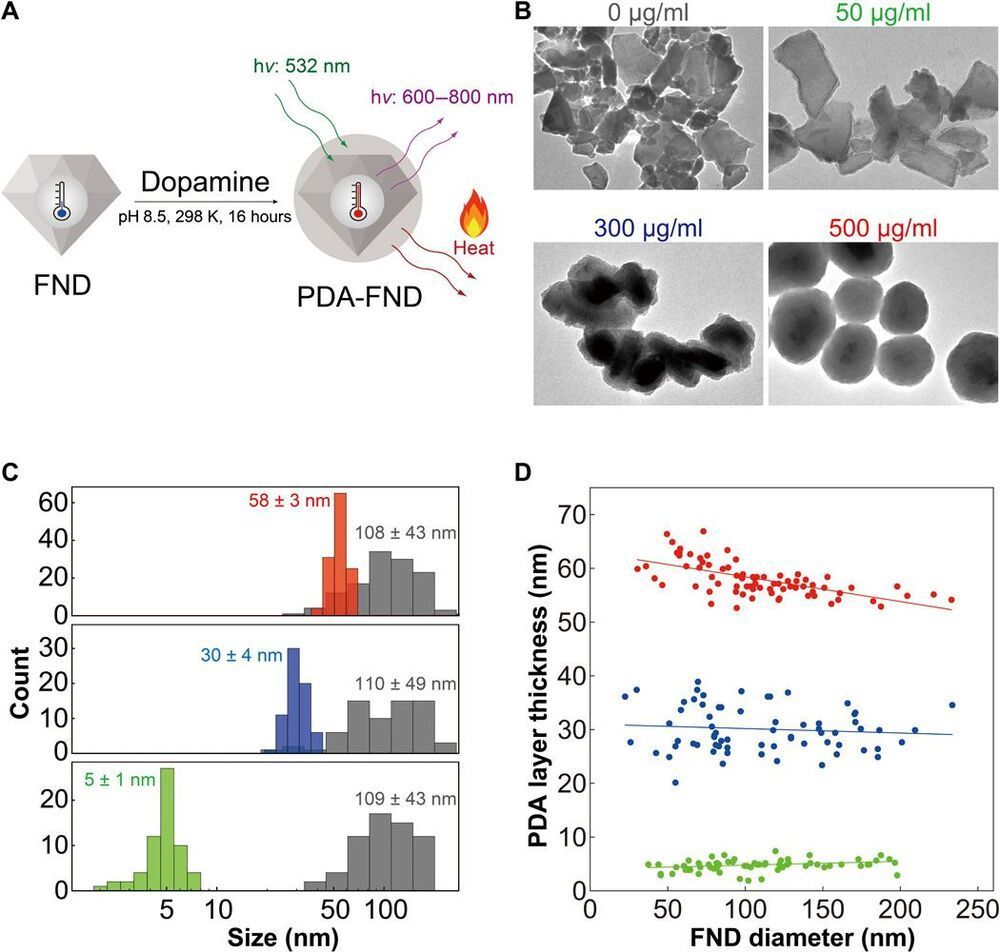
Understanding heat dissipation processes at nanoscale during cellular thermogenesis is essential to clarify the relationships between the heat and biological processes in cells and organisms. A key parameter determining the heat flux inside a cell is the local thermal conductivity, a factor poorly investigated both experimentally and theoretically. Here, using a nanoheater/nanothermometer hybrid made of a polydopamine encapsulating a fluorescent nanodiamond, we measured the intracellular thermal conductivities of HeLa and MCF-7 cells with a spatial resolution of about 200 nm. The mean values determined in these two cell lines are both 0.11 ± 0.04 W m−1 K−1, which is significantly smaller than that of water. Bayesian analysis of the data suggests there is a variation of the thermal conductivity within a cell.
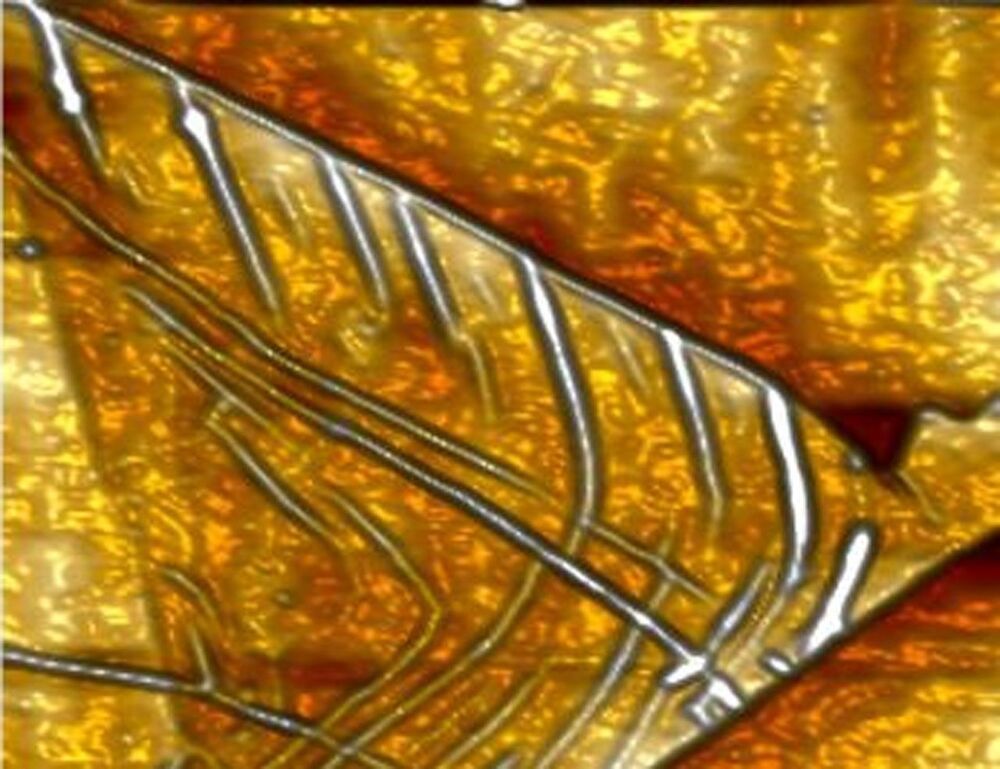
Physicists from the University of Sussex have created what they called the tiniest microchips yet. The little microchips are made using graphene and other 2D materials and a form of “nano-origami.” The technique used in creating the tiny microchips marks the first time any researchers have been able to do this.
Researchers succeeded in making the tiny microchips by creating kinks in the structure of graphene to make the nanomaterial behave like a transistor. In their study, the team showed that when a graphene strip is crinkled in a specific way, it behaves like a microchip only about 100 times smaller than a conventional microchip. New construction methods are needed for microchips because traditional semiconducting technology is at the limit of what it can do.
The researchers believe that using the materials in their technique will make computer chips smaller and faster. The technology is dubbed “straintronics” and uses nanomaterials rather than electronics, allowing space for more chips inside a given device. The researchers believe everything we want to do with computers to speeding them up can be done by crinkling graphene.