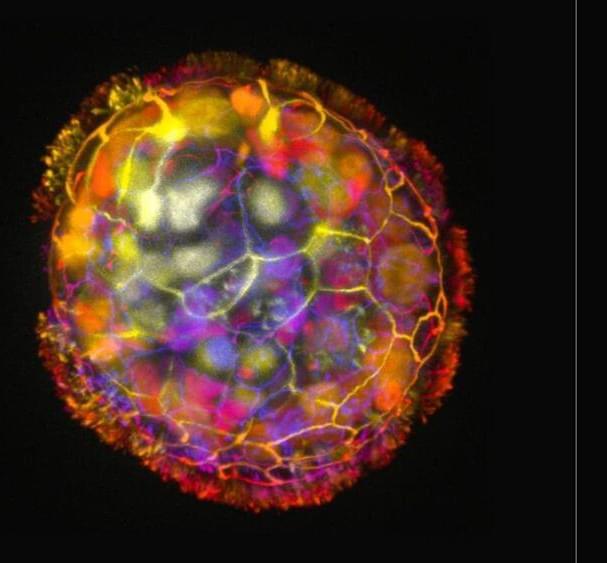
The researchers are excited by the potential of how cells cooperate and communicate in the body and how they can be reprogrammed to create new structures and functions.
With the help of Simon Garnier at the New Jersey Institute of Technology, the team characterized the different types of Anthrobots that were produced.
They observed that bots fell into a few discrete categories of shape and movement, ranging in size from 30 to 500 micrometers (from the thickness of a human hair to the point of a sharpened pencil), filling an important niche between nanotechnology and larger engineered devices.
Some were spherical and fully covered in cilia, and some were irregular or football-shaped with more patchy coverage of cilia or just covered with cilia on one side. They traveled in straight lines, moved in tight circles, combined those movements, or just sat around and wiggled.