Nanoscale materials present us with astonishing chemical and physical properties that help materialize applications such as single molecular sensing and minimally invasive photothermal therapy—which were once just theories—into reality.

Nanostructured high entropy alloys—metals made from a chaotic mix of several different elements—show a lot of promise for use in industries such as aerospace and automotive because of their strength and stability at high temperatures compared with regular metals.
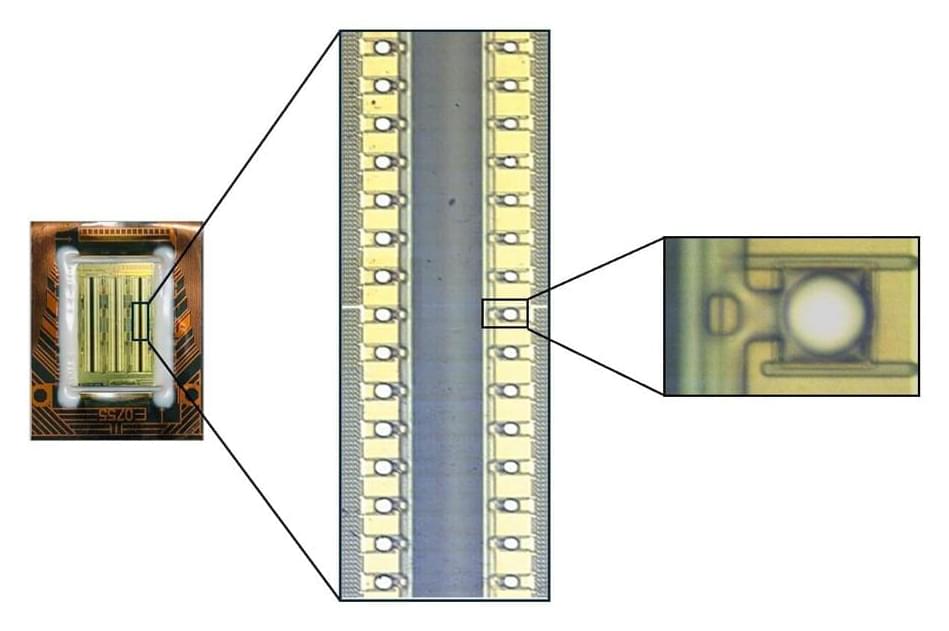

Researchers at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine have developed a nanoparticle that can penetrate the blood-brain barrier. Their goal is to kill primary breast cancer tumors and brain metastases in one treatment, and their research shows the method can shrink breast and brain tumors in laboratory studies.

A Birmingham researcher has developed a new high-throughput device that produces libraries of nanomaterials using sustainable mechanochemical approaches.
Dr. Jason Stafford from the University’s School of Engineering invented the platform to create highly controllable reaction conditions and reduce the substantial amount of time researchers spend generating materials in the laboratory.
The benchtop device is a fully automated unit that can be programmed for parallel synthesis to produce a series of novel materials made in subtly different ways, so creating a library of advanced materials or product formulations for further testing and optimization.
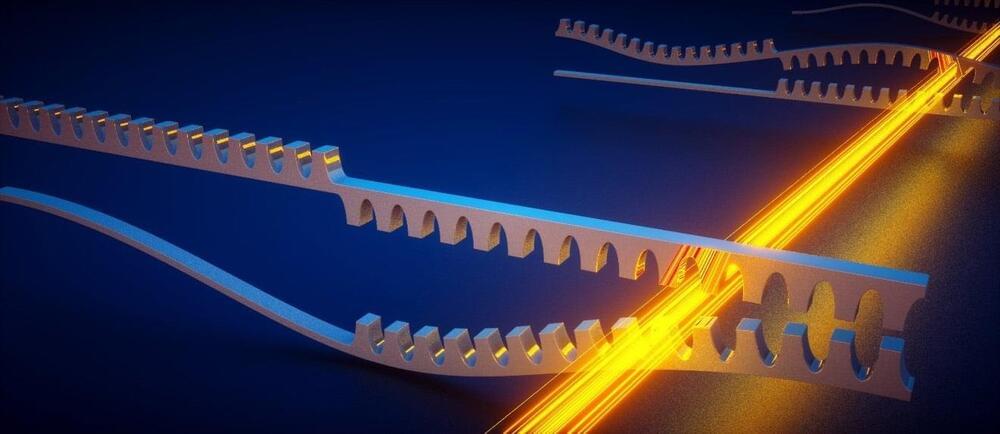
Researchers at AMOLF, working alongside colleagues from Germany, Switzerland, and Austria, have realized a new type of metamaterial through which sound waves flow in an unprecedented fashion. It provides a novel form of amplification of mechanical vibrations, which has the potential to improve sensor technology and information processing devices.
This metamaterial is the first instance of a so-called ‘bosonic Kitaev chain’, which gets its special properties from its nature as a topological material. It was realized by making nanomechanical resonators interact with laser light through radiation pressure forces. The discovery, which is published on March 27 in the renowned scientific journal Nature, was achieved in an international collaboration between AMOLF, the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light, the University of Basel, ETH Zurich, and the University of Vienna.
The ‘Kitaev chain’ is a theoretical model that describes the physics of electrons in a superconducting material, specifically a nanowire. The model is famous for predicting the existence of special excitations at the ends of such a nanowire: Majorana zero modes. These have gained intense interest because of their possible use in quantum computers.