Receiver blocks interference early:
MIT researchers also state that the interference-blocking components can be switched on and off as needed to conserve energy.
Receiver blocks interference early:
MIT researchers also state that the interference-blocking components can be switched on and off as needed to conserve energy.

Specifically, the release says, carriers would simply have to provide unlocking services 60 days after activation. A welcome standard, but it may run afoul of today’s phone and wireless markets.
For instance, although the dreaded two-year contract is no longer forced on most consumers, many still opt for them to lock in the price and get other benefits. And perhaps more to the point, the phones themselves are often paid for in what amount to installment plans: You get a phone for “free” and then pay it off over the next few years.
The NPRM is the stage of FCC rulemaking where it has a draft rule but has not yet solicited public feedback. On July 18, the agency will publish the full document and open up commentary on the above issues. And you can be sure there will be some squawking from mobile providers!

For more than 15 years, a group of scientists in Texas have been hard at work creating smaller and smaller devices to “see” through barriers using medium-frequency electromagnetic waves — and now, they seem closer than ever to cracking the code.
In an interview with Futurism, electrical engineering professor Kenneth O of the University of Texas explained that the tiny new imager chip he made with the help of his research team, which can detect the outlines of items through barriers like cardboard, was the result of repeat advances and breakthroughs in microprocessor technology over the better half of the last two decades.
“This is actually similar technology as what they’re using at the airport for security inspection,” O told us.

Geospatial data has undergone significant transformations due to the internet and smartphones, revolutionizing accessibility and real-time updates.
A collaborative international team reviewed this evolution, highlighting growth opportunities and challenges.
‘Seismic Shift’ to Crowdsourced Scientific Data Presents Promising Opportunities.

Now I’ve seen everything.
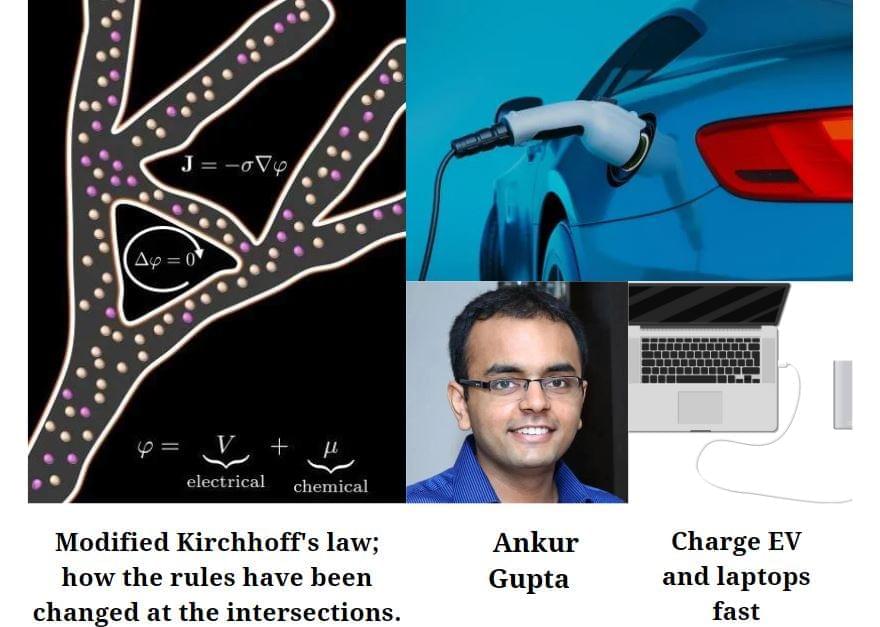
Imagine if your dead laptop or phone could charge in a minute or if an electric car could be fully powered in 10 minutes. While not possible yet, new research by a team of CU Boulder scientists could potentially lead to such advances.
Published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers in Ankur Gupta’s lab discovered how ions, move within a complex network of minuscule pores. The breakthrough could lead to the development of more efficient energy storage devices, such as supercapacitors, said Gupta, an assistant professor of chemical and biological engineering.
“Given the critical role of energy in the future of the planet, I felt inspired to apply my chemical engineering knowledge to advancing energy storage devices,” Gupta said. “It felt like the topic was somewhat underexplored and, as such, the perfect opportunity.”
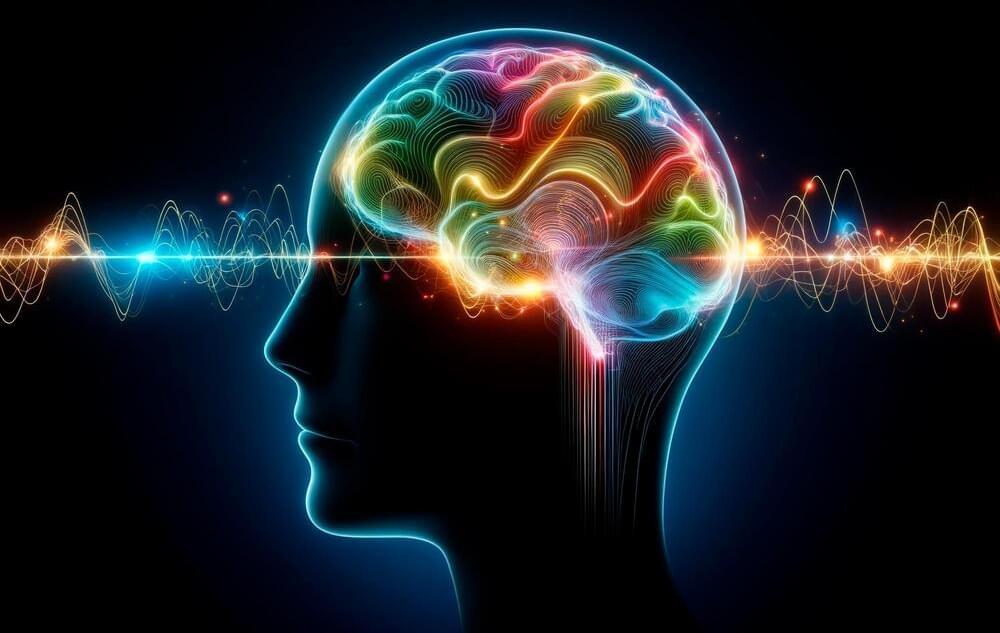

MIT neuroscientists propose a new framework that describes how thought arises from the coordination of neural activity driven by oscillating electric fields — a.k.a. brain “waves” or “rhythms.”
It could be very informative to observe the pixels on your phone under a microscope, but not if your goal is to understand what a whole video on the screen shows. Cognition is much the same kind of emergent property in the brain. It can only be understood by observing how millions of cells act in coordination, argues a trio of MIT neuroscientists. In a new article, they lay out a framework for understanding how thought arises from the coordination of neural activity driven by oscillating electric fields — also known as brain “waves” or “rhythms.”
The Significance of Brain Rhythms.

Researchers at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) discovered that adding a highly conductive substance called carbon black to a water and cement mixture created a construction material that could also serve as a supercapacitor.
Supercapacitors can charge and discharge extremely efficiently but are typically not capable of storing energy for long amounts of time. So while they lack the functionality of traditional lithium-ion batteries – which are found in everything from smartphones to electric cars – they are a useful method of storing excess electricity generated from renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
Since first unveiling the technology last year, the team has now built a working proof-of-concept concrete battery, the BBC reported. The MIT researchers are now hoping to build a 45-cubic-metre (1,590-cubic-feet) version capable of meeting the energy needs of a residential home.

Apple’s first reveal of the new macOS Sequoia includes a way to remote control your iPhone directly from the Mac, and a new Apple Passwords app.
Announced in the WWDC 2024 keynote, macOS 15 is called macOS Sequoia, and as expected, it brings AI — or Apple Intelligence — to every platform and practically every feature.
Across macOS Sequoia and Apple’s other platforms, users can write, summarize, and proofread text almost system-wide with Writing Tools. It will be able to generate sketches, animations, or illustrations with Image Playground, which is built into apps including Messages — and has its own brand-new app too.