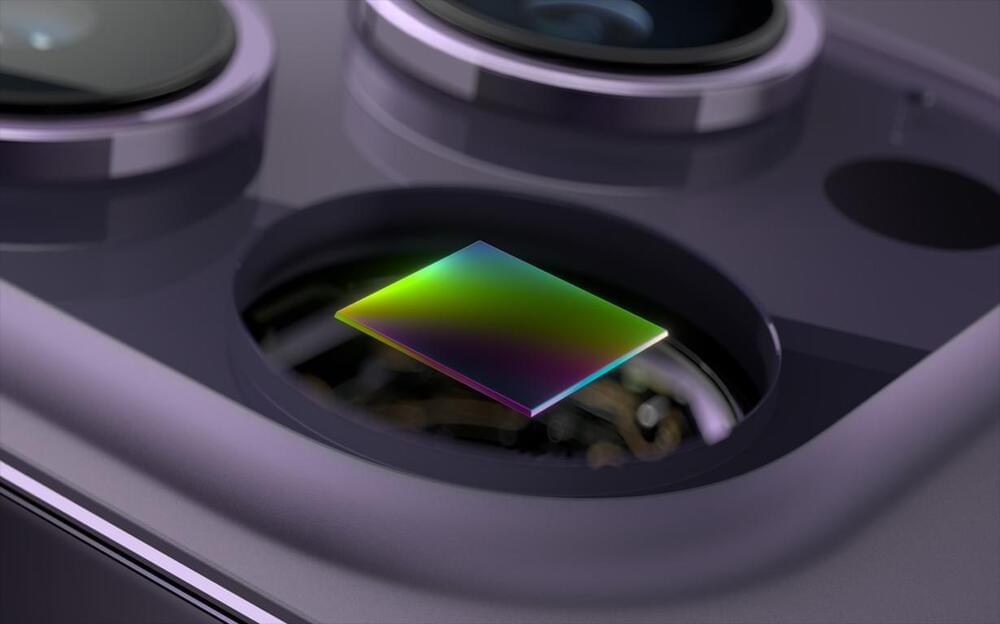
Apple could bring Samsung into its camera sensor supply chain, with a new rumor claiming that it is developing a new 3-layer stacked sensor.



The European market is making USB-C the sole interface for battery charging on mobile and portable gadgets. The EU Parliament approved the USB Type-C mandate in 2022, compelling even reluctant manufacturers to adopt the port for their chargers. By the end of 2024, all mobile phones, tablets, and cameras sold in the EU must feature a USB-C charging port – and that’s just the beginning.
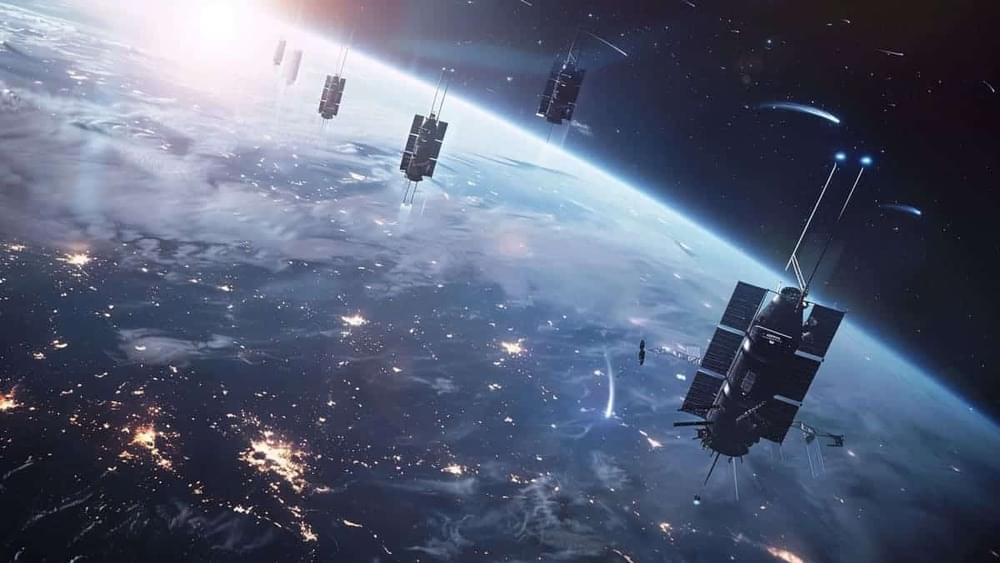

After revolutionizing global internet access, Elon Musk’s Starlink is poised to take smartphone connectivity to the next level. The ambitious satellite service will soon enable users to make calls from virtually anywhere on the planet, all without the need for specialized hardware.
Starlink, a division of SpaceX, has announced its plans to introduce Direct-to-Cell, a groundbreaking feature that uses its vast satellite network to allow voice calls on regular smartphones. What sets this apart is its simplicity—there’s no need for modifications to your device. As long as your phone is LTE-compatible, you’re ready to connect.
This innovation could fundamentally change how we think about mobile communication. Imagine being able to make calls from the remotest corners of the Earth—whether you’re deep in a rainforest, sailing in the middle of the ocean, or trekking across deserts—with no cell towers in sight. Starlink’s satellite system makes this scenario entirely possible.

Apple is on the brink of becoming the first company in history to surpass a $4 trillion market valuation, Fortune reports.
Apple’s stock (AAPL) has nearly risen 40% in 2024. Before the markets opened on December 27, Apple’s market capitalization stood at $3.92 trillion, leaving the company just a modest surge in stock value away from the unprecedented milestone. The growth is said to have been fueled largely by optimism surrounding Apple Intelligence and the continued strength of its iPhone upgrade cycles.

TAMPA, Fla. — Spacecoin said it is successfully communicating with its recently launched debut connectivity satellite, designed to test technology for a decentralized space-based network shared by multiple investors.
“We have established regular communication with the satellite,” Spacecoin founder Tae Oh said, following SpaceX’s Dec. 21 Falcon 9 rideshare mission to low Earth orbit.
The venture aims to start testing its CTC-0 small satellite early next year, initially demonstrating space-enabled text messaging to a specialized handheld antenna but ultimately directly to standard smartphones.

Cisco Systems senior visioneer, Annie Hardy, joins me to discuss AI and the future of the internet.
“We are all now connected to the internet, like neurons in a giant brain.” –Stephen Hawking.
Unless you are living in a remote cabin completely off-grid, it has reached the point where you cannot avoid artificial intelligence. It’s in our search engines, it’s on our phones, it’s on the social media on our phones. It’s permeating the internet at a breakneck pace.
Annie Hardy, a fellow member of the Association of Professional Futurists and a senior visioneer at Cisco Systems, spends most of her working hours assessing the future of artificial intelligence and the internet. She joins me in this episode of Seeking Delphi, for an in depth look at where it’s headed.

A QUT-led research team has developed an ultra-thin, flexible film that could power next-generation wearable devices using body heat, eliminating the need for batteries.
This technology could also be used to cool electronic chips, helping smartphones and computers run more efficiently.
Professor Zhi-Gang Chen, whose team’s new research was published in the prestigious journal Science , said the breakthrough tackled a major challenge in creating flexible thermoelectric devices that converted body heat into power.

Time is vital to the functioning of our everyday lives: from the watches on our wrists to the GPS systems in our phones. Communication systems, power grids, and financial transactions all rely on precision timing. Seconds are the vital units of measurement in timekeeping.
Surprisingly, there is still debate over the definition of the second. But recent advances in the world’s most accurate forms of timekeeping may have just changed the game.
Accurate timekeeping has always been part of humankind’s social evolution. At the Neolithic monument of Newgrange in Ireland, a special opening above an entrance allows sunlight to illuminate the passage and chamber on the shortest days of the year, around December 21st, the winter solstice.
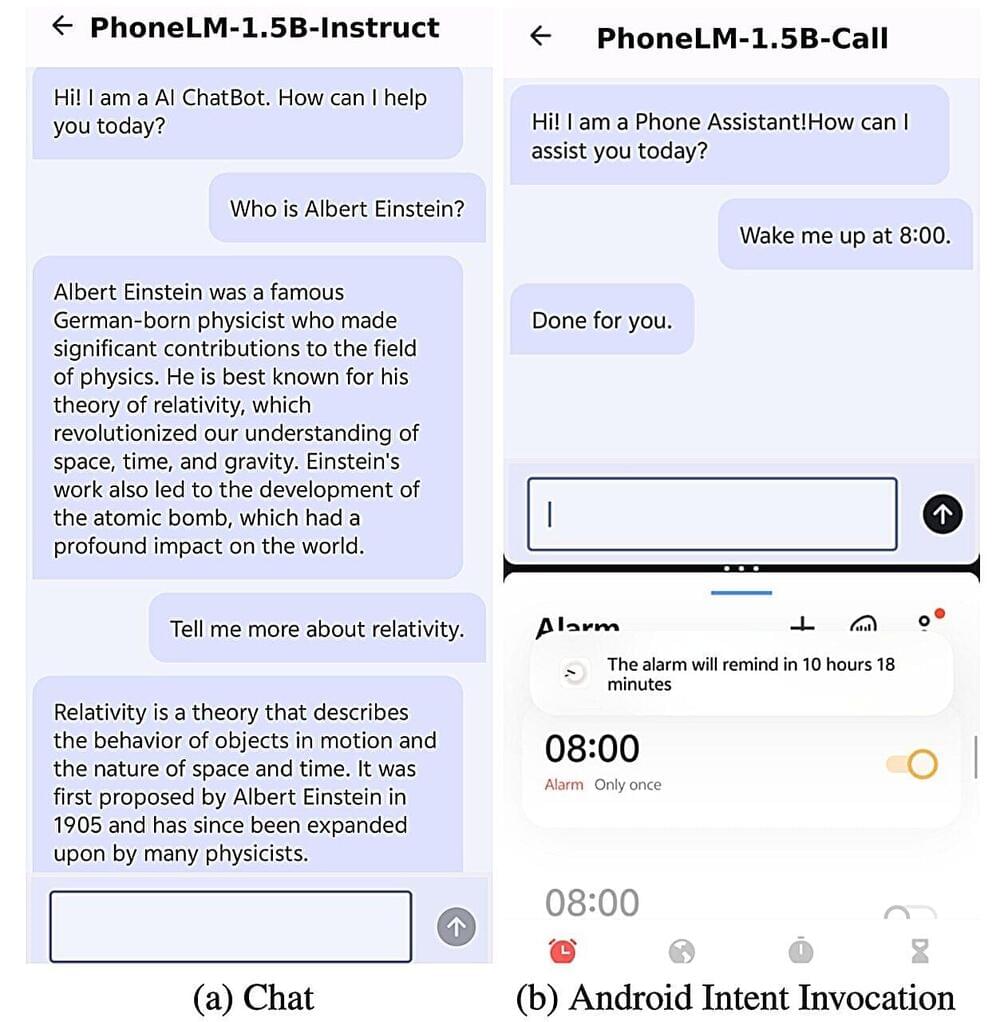
Large language models (LLMs), such as Open AI’s renowned conversational platform ChatGPT, have recently become increasingly widespread, with many internet users relying on them to find information quickly and produce texts for various purposes. Yet most of these models perform significantly better on computers, due to the high computational demands associated with their size and data processing capabilities.
To tackle this challenge, computer scientists have also been developing small language models (SLMs), which have a similar architecture but are smaller. These models could be easier to deploy directly on smartphones, allowing users to consult ChatGPT-like platforms more easily daily.
Researchers at Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications (BUPT) recently introduced PhoneLM, a new SLM architecture for smartphones that could be both efficient and highly performing. Their proposed architecture, presented in a paper published on the arXiv preprint server, was designed to attain near-optimal runtime efficiency before it undergoes pre-training on text data.
