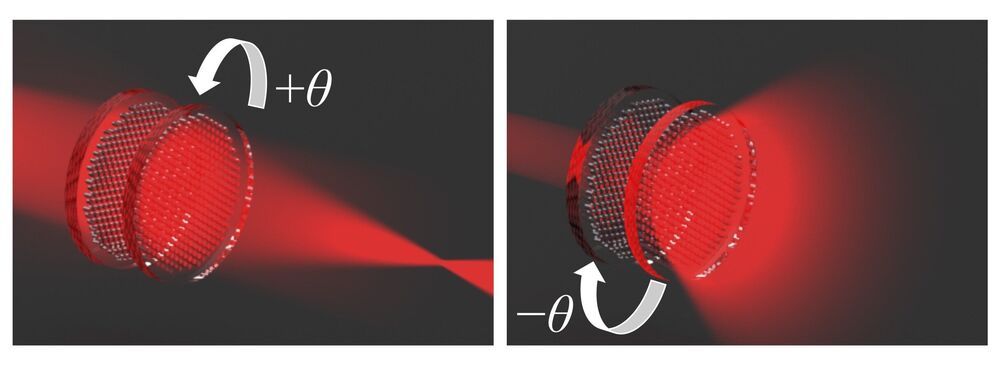
The odd, wavy pattern that results from viewing certain phone or computer screens through polarized glasses has led researchers to take a step toward thinner, lighter-weight lenses. Called moiré, the pattern is made by laying one material with opaque and translucent parts at an angle over another material of similar contrast.
A team of researchers from Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology, TUAT, in Japan have demonstrated that moiré metalenses—tiny, patterned lenses composed of artificial ‘meta’ atoms—can tune focal length along a wider range than previously seen. They published their results on November 23 in Optics Express.
“Metalenses have attracted a lot of interest because they are so thin and lightweight, and could be used in ultra-compact imaging systems, like future smart phones, virtual reality goggles, drones or microbots,” said paper author Kentaro Iwami, associate professor in the TUAT Department of Mechanical Systems Engineering.