Future smartphones, sensors, solar panels and wind turbines will contain electronics in which graphullerene is present.



Since its launch in November last year, ChatGPT has become an extraordinary hit. Essentially a souped-up chatbot, the AI program can churn out answers to the biggest and smallest questions in life, and draw up college essays, fictional stories, haikus, and even job application letters. It does this by drawing on what it has gleaned from a staggering amount of text on the internet, with careful guidance from human experts. Ask ChatGPT a question, as millions have in recent weeks, and it will do its best to respond – unless it knows it cannot. The answers are confident and fluently written, even if they are sometimes spectacularly wrong.
The program is the latest to emerge from OpenAI, a research laboratory in California, and is based on an earlier AI from the outfit, called GPT-3. Known in the field as a large language model or LLM, the AI is fed hundreds of billions of words in the form of books, conversations and web articles, from which it builds a model, based on statistical probability, of the words and sentences that tend to follow whatever text came before. It is a bit like predictive text on a mobile phone, but scaled up massively, allowing it to produce entire responses instead of single words.

MicroLED’ or Electroluminescent quantum dot screens and sensors are coming to your neighborhood soon. The linked article states: What does this mean? Just about any flat or curved surface could be a screen. This has long been the promise of a variety of technologies, not to mention countless sci-fi shows and movies, but electroluminescent QD has the potential to actually make it happen.
We’ve seen a new, top-secret prototype display technology that will soon be in TVs, phones and more.

With new tools like the James Webb Space Telescope, we’re discovering more exoplanets than ever and even peering into their atmospheres. Now, NASA is asking for the public’s help in learning more about some of the exoplanets that have already been detected in a citizen science program called Exoplanet Watch.
“With Exoplanet Watch you can learn how to observe exoplanets and do data analysis using software that actual NASA scientists use,” said Rob Zellem, the creator of Exoplanet Watch and an astrophysicist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in a statement. “We’re excited to show more people how exoplanet science is really done.”
The Exoplanet Watch project has two parts, one involving observing for those who have access to a telescope, and one involving identifying exoplanets in existing data. Even if you don’t have access to equipment other than a computer or smartphone, you can still help in learning about exoplanets by requesting access to data collected by robotic telescopes and assisting with data analysis. That’s needed because observing exoplanets passing in front of their host stars — in events called transits — is only half of the challenge of finding a new planet. These transits result in dips in the star’s brightness, but these dips are very small at typically less than 1% of the star’s brightness.
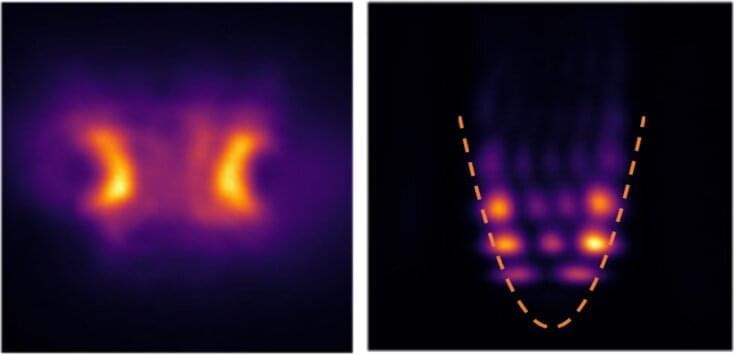
A quantum harmonic oscillator—a structure that can control the location and energy of quantum particles that could, in the future, be used to develop new technologies including OLEDs and miniature lasers—has been made at room temperature by researchers led by the University of St Andrews.
The research, conducted in collaboration with scientists at Nanyang Technological University in Singapore and published in Nature Communications recently, used an organic semiconductor to produce polaritons, which show quantum states even at room temperature.
Polaritons are quantum mixtures of light and matter that are made by combining excitations in a semiconductor material with photons, the fundamental particles that form light. To create polaritons, the researchers trapped light in a thin layer of an organic semiconductor (the kind of light-emitting material used in OLED smartphone displays) 100 times thinner than a single human hair, sandwiched between two highly reflective mirrors.
This flaw, which has been identified that affects the ksmbd NTLMv2 authentication in the Linux kernel, is known to quickly cause the operating system on Linux-based computers to crash. Namjae Jeon is the developer of KSMBD, which is an open-source In-kernel CIFS/SMB3 server designed for the Linux Kernel. It is an implementation of the SMB/CIFS protocol in the kernel space that allows for the sharing of IPC services and files over a network.
In order to take advantage of the vulnerability, you will need to transmit corrupted packets to the server, personal computer, tablet, or smartphone that you are targeting. The attack causes what is known as “a memory overflow flaw in ksmbd decodentlmssp auth blob,” which states that nt len may be less than CIFS ENCPWD SIZE in some circumstances. Because of this, the blen parameter that is sent to ksmbd authntlmv2, which runs memcpy using blen on memory that was allocated by kmalloc(blen + CIFS CRYPTO KEY SIZE), is now negative. It is important to take note that the CIFS ENCPWD SIZE value is 16, and the CIFS CRYPTO KEY SIZE value is 8. As the heap overflow happens when blen is in the range [-8,-1], we think that the only possible outcome of this problem is a remote denial of service and not a privilege escalation or a remote code execution.
The vulnerability is caused by the way that the Linux kernel handles NTLMv2 authentication in versions 5.15-rc1 and later. The developers of the Linux kernel have not made a fix available.


Is AI coming for voice artists now?
Researchers at technology major Microsoft have unveiled their latest text-to-speech (TTS) generator, VALL-E that can be trained to mimic anybody’s voice in just three seconds. Unlike previous voice generators that sounded robotic, VALL-E sounds naturally human, and that may not be a very good thing.
Text-to-speech generators that gave voice to one of the greatest minds on the planet, Stephen Hawking, have come a long way. From reading messages on your smartphone to reading out pages from a book, these services are now everywhere and used by everyone.

It is also looking at a possible investment from Microsoft.
OpenAI, the artificial intelligence research company, is building an iOS app powered by its globally popular chatbot ChatGPT which helps users search for answers using an iMessage like interface. A beta version of the app is being tested currently, and a demo version was shared on the professional networking site LinkedIn.
Launched in November last year, ChatGPT made global news for its ease of answering even complex questions in a conversational manner. The algorithm that powers the chatbot, GPT3.5 is built by Open AI and is trained to learn what humans mean when they ask a question.

Google has warned that growth in the use of Android in India may stall due to an antitrust order issued by the Indian antitrust watchdog last year over the U.S. company’s domination in the country.
The order, which was issued by the Competition Commission of India (CCI) in September, found that Google had abused its dominant position in the market for mobile operating systems by imposing restrictive contracts on mobile manufacturers.
The CCI ordered Google to change its contracts with manufacturers, allowing them more freedom to install rival apps and services on Android devices. According to a Reuters report, Google filed a challenge with India’s Supreme Court and said that the order would require some modifications of its existing contracts and new license agreements. It would alter the company’s existing arrangements with over 1,100 device manufacturers and thousands of app developers.