The Pentagon has made quantum technology a central priority in a new six-part strategy outlining the future of U.S. military capability.


Elon Musk just made a bold announcement that could completely redefine Tesla’s future — but almost no one noticed. At the 2025 Tesla Shareholder Meeting, Elon revealed a deeper vision that goes far beyond cars. From AI and humanoid robots to clean energy and automation, Tesla is positioning itself as the driving force behind humanity’s next great leap.
In this video, Chris Smedley and the Ideal Wealth Grower team break down the hidden message behind Elon’s words, why the singularity may already be unfolding, and how Tesla’s shift toward artificial intelligence could reshape the global economy — and your investment strategy. Stay tuned till the end to discover why this could be the most important turning point in Tesla’s history.
Know what Type of Business suits you first at https://quiz.franchisewithbob.com/rg — and COPY THE RIGHT BUSINESS FOR YOU!
Thanks, Franchise with Bob, for sponsoring this episode!
Watch on Social media profiles:
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/posts/ameier…
https://twitter.com/IdealGrower/status/1986
… Welcome to Ideal Wealth Grower, the channel that helps you build real wealth, create passive income, and achieve true time freedom. I’m Axel Meierhoefer — former US Air Force officer, real estate investor, and lifelong learner inspired by visionaries like Elon Musk. After more than 20 years of successful real estate investing, I reached my own financial freedom point, and now I’m here to help you do the same. If you’re ready to stop trading time for money, take control of your financial future, and live life on your terms — you’re in the right place. Stay connected with us! ✅ X: twitter.com/idealgrower ✅ Our community: cutt.ly/0rDZ1fNI ✅ Linked In: / ameierhoefer ✨ ✨
/ @idealwealthgrower Top Data Scientist Exposes Quantum AI Disruption, Digital AI Twins | Anthony Scriffignano
• Top Data Scientist Exposes Quantum AI Disr… Is INFINITE BANKING the Future of Sustainable Wealth? with Chris Naugle | Age of Abundance
• Is INFINITE BANKING the Future of Sustaina… Elon Musk Just Changed Everything at Tesla — And No One’s Talking About It #elonmusk #tesla #chrissmedley #idealwealthgrower #teslanews #teslastock #teslainvestors #teslashareholdermeeting #teslaupdate #teslafuture #teslabot #teslaai #artificialintelligence #teslainnovation #futuretech #robotics #teslainvesting #wealthbuilding #financialfreedom #stockmarket #investing #technologynews #innovation #elonmusknews #teslamasterplan #ai what elon musk said at tesla 2025 meeting tesla AI day 2025 full presentation tesla master plan 4 explained tesla robot update 2025 elon musk latest tesla news elon musk tesla 2025 updates tesla shareholder meeting highlights.
X: https://twitter.com/IdealGrower/status/1986…

In today’s AI news, Southeast Asia’s largest bank is rolling out an AI chatbot for its corporate clients, giving “round-the-block” access for customer care needs. A pilot version of the generative AI-powered chatbot, named DBS Joy, was rolled out in February. It has since managed over 120,000 unique chats, DBS claimed in a statement. The virtual assistant also cut waiting times, and customer satisfaction scores rose by 23%. The bank’s virtual assistant was first rolled out in 2018, under the same name.
In other advancements, Artificial intelligence giant OpenAI on Monday announced a new initiative that aims to make it easier for service members and veterans to use AI tools when they’re transitioning from military service to the workforce. The ChatGPT-maker announced that service members within 12 months of separation or retirement from, or any veteran within their first year of leaving military service, can access a free year of access to ChatGPT Plus, the company’s subscription-based tool.
Meanwhile, Neurodiverse professionals may see unique benefits from artificial intelligence tools and agents, research suggests. With AI agent creation booming in 2025, people with conditions like ADHD, autism, dyslexia and more report a more level playing field in the workplace thanks to generative AI. A recent study from the UK’s Department for Business and Trade found that neurodiverse workers were 25% more satisfied with AI assistants and were more likely to recommend the tool than neurotypical respondents.
And, San Francisco became a meme — a symbol of American urban decay. Between 2019 and 2024, the city lost 4 per cent of its population, one of the largest declines in America. But thanks to AI — and new “tough on crime” mayor Daniel Lurie — the vibe has, unquestionably, shifted. Since 2020, more than 2,400 AI companies have been founded in San Francisco, a city of just 830,000 people. “Hacker houses”, where bright-eyed coders live communally and build what they hope will be the next Google, have cropped up across the city.
In videos, Six of the most influential minds in artificial intelligence joined FT Live for an exclusive conversation on how their breakthroughs and the current state of AI are shaping our world. Jensen Huang, Yoshua Bengio, Geoffrey Hinton, Fei-Fei Li, Yann LeCun, and Bill Dally spoke with the FT’s AI editor, Madhumita Murgia at the FT Future of AI Summit in London. Together, they reflected on decades of pioneering work — from neural networks to generative AI and discuss the ethical, social, and economic implications of the technology they helped to create.
Then, Ellis Hamburger and Alex Heath chat about the Sources launch party, and living in late-stage extractionism. Then, they are then joined by Runway CEO Cristobal Valenzuela to discuss the hardest part about AI, why golf courses are a bigger problem than data centers, and how world models are changing our world forever.
And, David Sacks, White House AI and Crypto Czar, joins Marc, Ben, and Erik on the a16z podcast to explore what’s really happening inside the Trump administration’s AI and crypto strategy. They expose the regulatory capture playbook being pushed by certain AI companies, explain why open source is America’s secret weapon, and detail the infrastructure crisis that could determine who wins the global AI race.
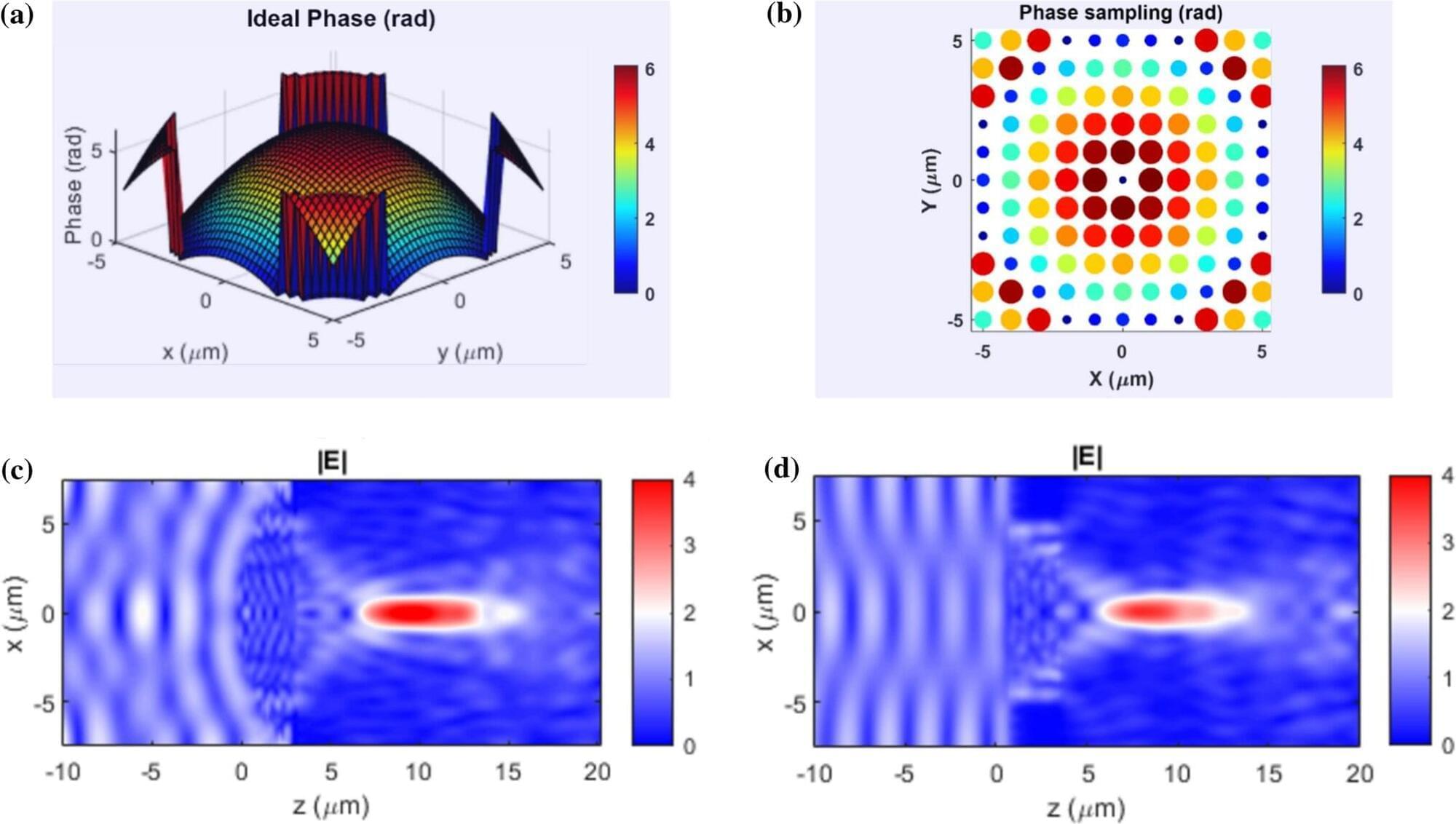
Researchers have developed a highly sensitive method for detecting hotspots in the environment, such as bushfires or military threats, by harnessing the focusing power of meta-optical systems.
The key to the approach is innovative lens technology thinner than a human hair, which can collect and process infrared radiation from fires and other heat sources with much improved efficiency. Crucially, it does not need cryogenic cooling, unlike current sensors.
The result is sensor technology that promises to enhance devices in both the civilian and military spheres, said Dr. Tuomas Haggren, lead researcher on the project.
ExpressVPN: Right now you can get an extra four months of ExpressVPN for free. Just scan the QR code on the screen, or go to https://ExpressVPN.com/PIERS and get four extra months for free.
Two years ago, Elon Musk was among a thousand experts to sign an open letter demanding an urgent pause on the advancement of Artificial Intelligence because of the risks concerning job losses, misinformation and more.
But now Musk is now spending a billion dollars a month to compete in an AI arms race, which is inflating the stock market to bursting point.
Amazon just laid off 14,000 workers in its ongoing A.I pivot — so, are the worst fears of doomsaying experts already coming true?
Joining Piers Morgan to discuss are respected thinkers in this field; Dr Roman Yampolskiy, Dr Michio Kaku, Alex Smola and Avi Loeb.
Then; he’s performed for presidents, billionaires and sports stars, but Oz Pearlman’s recent extraction of Joe Rogan’s pin number may have been his biggest hit yet.
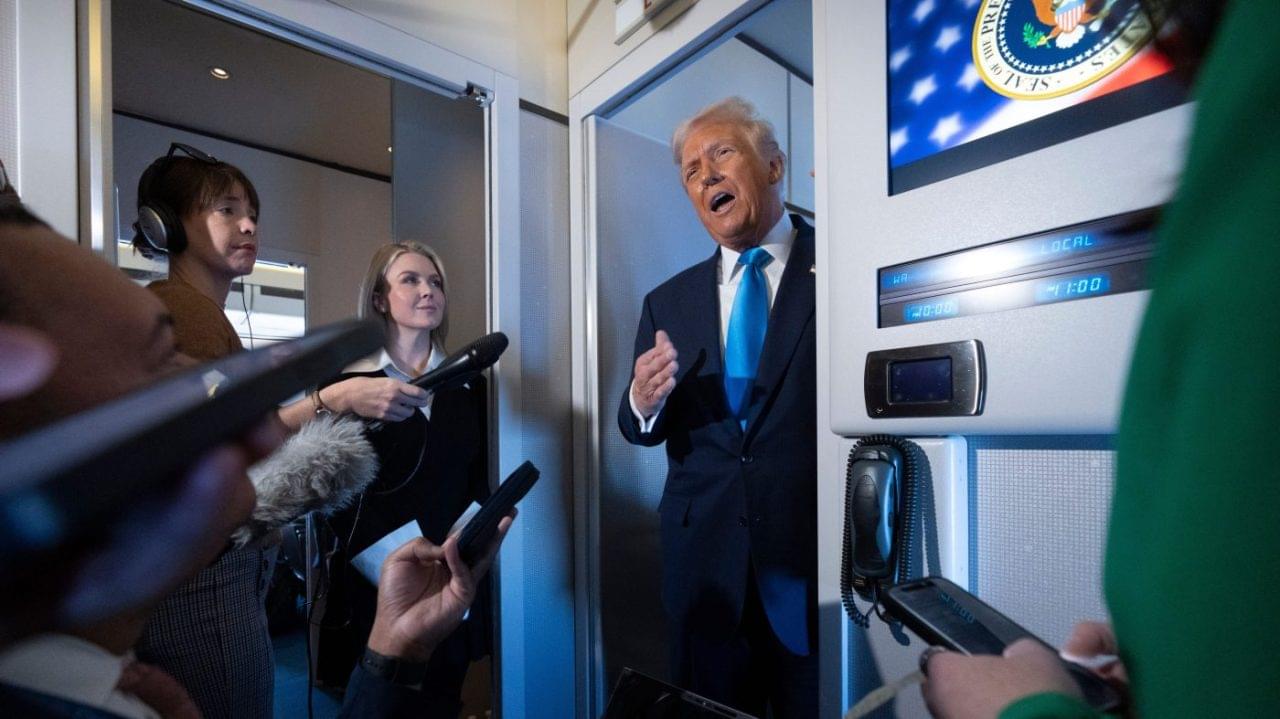

President Trump said on Wednesday that he has instructed the Defense Department (DOD) to immediately begin testing U.S. nuclear weapons on an equal basis to China and Russia.
‘The United States has more Nuclear Weapons than any other country,’ Trump wrote. ‘This was accomplished, including a complete update and renovation of existing weapons, during my First Term in office. Because of the tremendous destructive power, I HATED to do it, but had no choice! Russia is second, and China is a distant third, but will be even within 5 years.’…
…Trump’s announcement on TruthSocial came shortly before he was slated to meet face-to-face with Chinese President Xi Jinping for the first time since 2019 in South Korea on Thursday.
Artificial general intelligence (AGI) could be humanity’s greatest invention… or our biggest risk.
In this episode of TechFirst, I talk with Dr. Ben Goertzel, CEO and founder of SingularityNET, about the future of AGI, the possibility of superintelligence, and what happens when machines think beyond human programming.
We cover:
• Is AGI inevitable? How soon will it arrive?
• Will AGI kill us … or save us?
• Why decentralization and blockchain could make AGI safer.
• How large language models (LLMs) fit into the path toward AGI
• The risks of an AGI arms race between the U.S. and China.
• Why Ben Goertzel created Meta, a new AGI programming language.
📌 Topics include AI safety, decentralized AI, blockchain for AI, LLMs, reasoning engines, superintelligence timelines, and the role of governments and corporations in shaping the future of AI.
⏱️ Chapters.
00:00 – Intro: Will AGI kill us or save us?
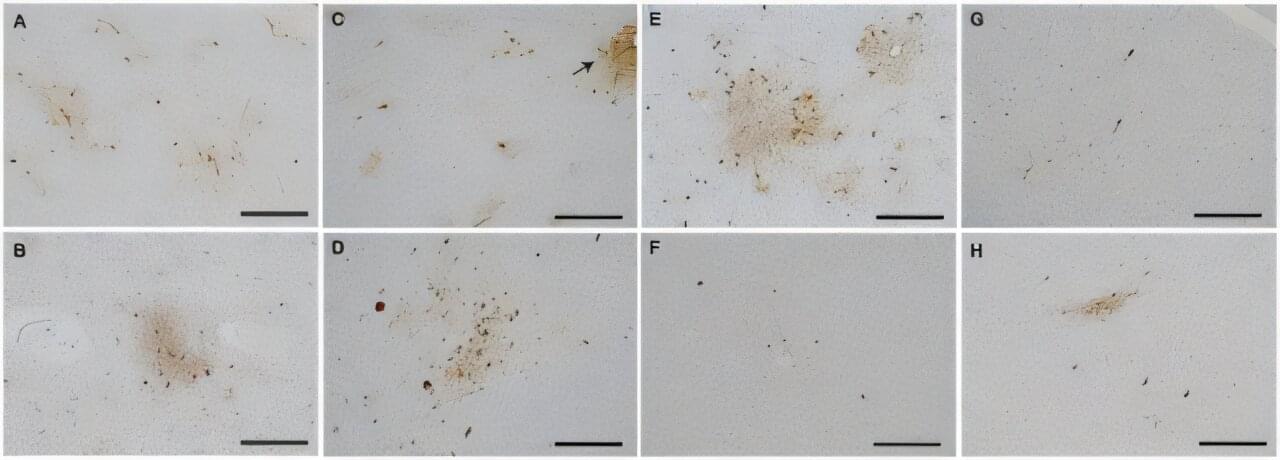
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is more common in people who experience extensive repetitive head impacts, and infrequent among individuals with isolated brain injuries or less extensive impacts, researchers from the Brain Injury Research Center of Mount Sinai have found.
The study, published in the Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology, adds to knowledge of CTE, which has received extensive media attention amidst limited research in representative samples.
CTE is characterized by a neurodegenerative pathology involving abnormal accumulations of tau protein in the brain associated with head trauma, primarily identified in deceased people who sustained extensive exposure to repetitive head impacts while playing contact sports—especially American-style football. CTE has been reported more rarely in individuals who sustained repetitive head impacts through head-banging, military service, or intimate partner violence.
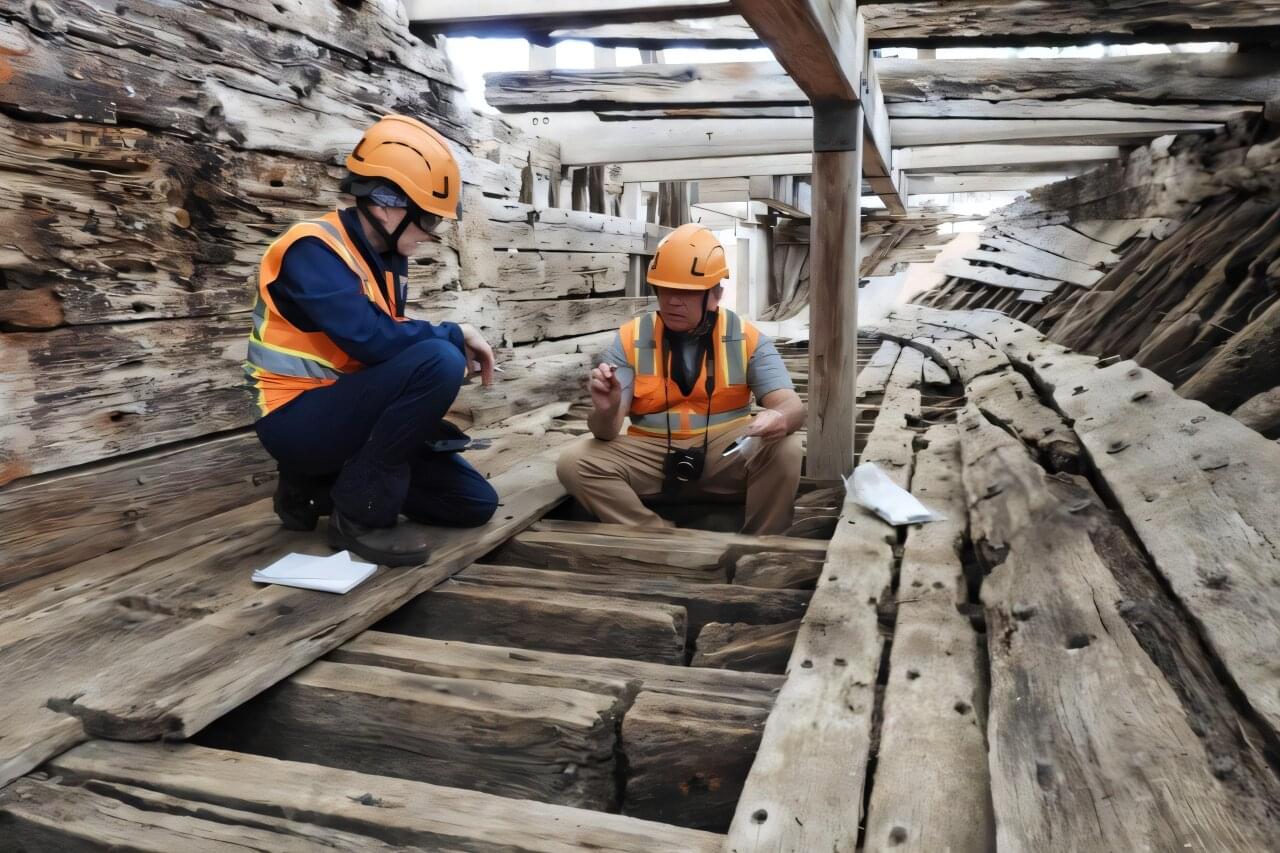

University of Minnesota researchers studied the microbial degradation of the USS Cairo, one of the first ironclad and steam-powered gunboats used in the United States Civil War. Studies of microbial degradation of historic woods are essential to help protect and preserve important cultural artifacts.
Built in 1861, the ship hit a torpedo and sank in December 1862 and was recovered about 100 years later from the Yazoo River. It has been on display at the Vicksburg National Military Park in Mississippi. Although the ship has a canopy cover, it is exposed to environmental elements.
“Continued degradation of this historic Civil War ship is causing serious concerns for its long-term preservation. To determine the appropriate conservation efforts, it is essential to understand the current condition of the wood and the microorganisms causing the degradation,” said lead author Robert Blanchette, a professor in the College of Food, Agricultural and Natural Resource Sciences.