It was exciting so early in my career to see a speculative project work out so successfully.

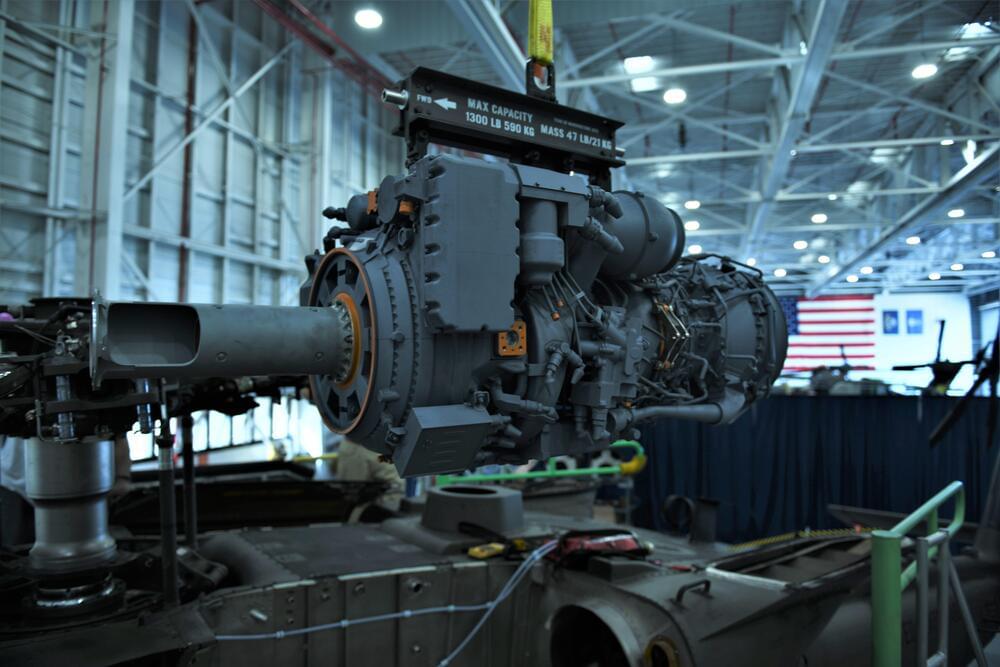
Kratos Defense & Security Solutions (Kratos) has announced the successful test flight of its Erinyes hypersonic test vehicle.
Developed by the company’s Space & Missile Defense Systems Business Unit, the test was completed on June 12, 2024, according to the announcement.
The test vehicle reached Mach 5 in its first test flight. Erinyes is being developed under the auspices of the Missile Defense Agency (MDA) and the Naval Surface Warfare Center (NSWC).

China has released video footage of its rifle-toting robot dogs, and it’s about as scary as you were probably imagining.
Last week, Agence France-Presse reported that China had flaunted the gun-carrying robodogs in a 15-day joint military exercise with Cambodia dubbed the “Golden Dragon.”
And if images of the literal killing machines weren’t troubling enough, a new video of the robots released yesterday by the state-owned broadcaster China Central Television shows the killing machine dutifully hopping and diving, leading teams in reconnaissance, and shooting its back-strapped machine gun at targets.
Who says you need a bomber or stealth fighter to air-launch a hypersonic missile? Boeing just unveiled a new concept that it’s developing called the Revolver launch system. Straight Arrow News on social media:
Facebook: / straightarrownews.
Twitter: / straightarrow__
Instagram: / straightarrownews.
TikTok: / straightarrownews.
For more SAN content: https://san.com/
Sign up for our weekly newsletters: https://san.com/newsletters/

That was five decades ago. Catapult yourself to today and ask this question: What’s the U.S. Navy’s Gerald R. Ford nuclear aircraft carrier got to do with the moon?
Late last year, General Atomics Electromagnetic Systems filed a final report to the Air Force Office of Scientific Research’s (AFOSR). That report was titled “Lunar Electromagnetic Launch for Resource Exploitation to Enhance National Security and Economic Growth.”
The author of that appraisal is Robert Peterkin, director of operations for the organization’s Albuquerque, New Mexico office.
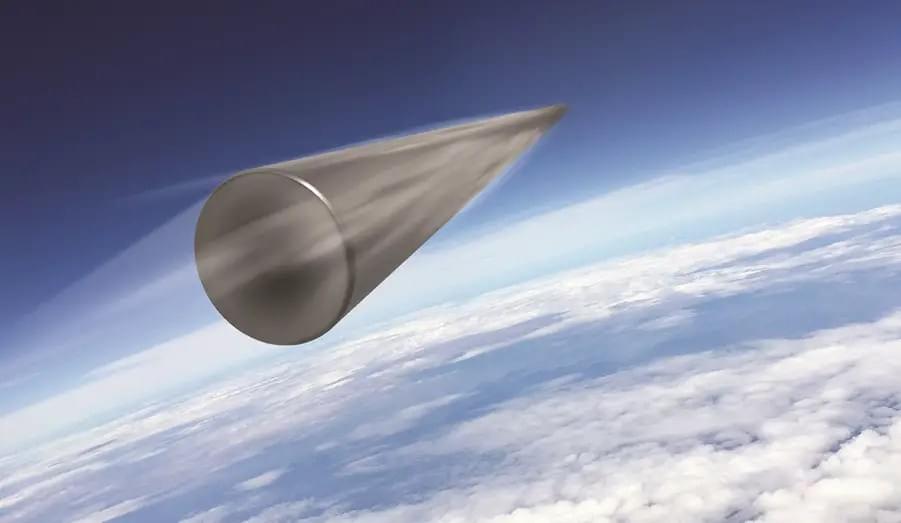

The Lockheed Martin and U.S. Air Force conducted a planned flight test of the unarmed, developmental Mk21A reentry vehicle in the Pacific Ocean on June 17. Mk21A is the U.S. Air Force’s integrated reentry vehicle and the critical front-end of the service’s future intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) weapon system. This flight test from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, tested Lockheed Martin’s Mk21A design components and technologies for the vehicle. It also continues Lockheed Martin’s leadership and expertise in developing effective and reliable reentry vehicle technology.
This testing is done through Lockheed Martin’s Engineering and Manufacturing Development contract with the Air Force Nuclear Systems Center. Data collected during the event will further inform Mk21A design and future flight test activities. The company’s Mk21A program is on-schedule. Lockheed Martin is maturing its Mk21A design, which includes the arming and fuzing subsystem and support equipment, using advanced digital engineering tools, including advanced modeling and simulation. This allows for efficiency in schedule, reduced cost and risk, and increased confidence in system performance.
“This progress is built on a strong foundation—Lockheed Martin’s 65-plus years of demonstrated exceptional performance in reentry technologies and a pioneering digital engineering approach on this program from its beginning,” said Jay Watson, vice president of Strategic Reentry at Lockheed Martin. “We remain focused on delivering this capability for the warfighter as a trusted partner to the U.S. Air Force for ICBM reentry systems and modernization of the deterrent triad.”
“Portrait (He Knew)” was released in 1977 on the album Point Of Know Return. It was clearly about Albert Einstein although not a lot of people seemed to be aware of the fact. It was a great song for a video, and one of my favorite on this particular album, the other’s being “Nobody Home”, “Closet Chronicles”, and “Dust In The Wind”. Point of Know Return was HUGE in 1978! I remember listening to it over and over and over…loved the many instrumental breaks and solos. The video is just layers and layers of masked images and masked video. Tried for some really cool effects and found some pretty neat ones…’specially fond of that tree recoil effect from the atom bomb at that cool little note drag! Anyway, as usual…I hope you find something to enjoy. [Lyrics] He had a thousand ideas, you might have heard his name He lived alone with his vision Not looking for fortune or fame Never said too much to speak of He was off on another plane The words that he said were a mystery Nobody’s sure he was sane But he knew, he knew more than me or you No one could see his view, Oh where was he going to He was in search of an answer The nature of what we are He was trying to do it a new way He was bright as a star But nobody understood him “His numbers are not the way” He’s lost in the deepest enigma Which no one’s unraveled today But he knew, he knew more than me or you No one could see his view, Oh where was he going to And he tried, but before he could tell us he died When he left us the people cried, Oh where was he going to? He had a different idea A glimpse of the master plan He could see into the future A true visionary man But there’s something he never told us It died when he went away If only he could have been with us No telling what he might say But he knew, he knew more than me or you No one could see his view Oh, where was he going to But he knew, you could tell by the picture he drew It was totally something new, Oh where was he going to?


As one of the Department of Defense’s 14 critical technology areas, artificial intelligence has taken center stage in the organization’s research and development endeavors.
According to Matt Turek, deputy director of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency’s Information Innovation Office, approximately 70 percent of the agency’s programs now use AI and machine learning. Its priorities are not just to develop systems for U.S. warfighters, but to prevent “strategic surprise” from adversary AI systems.