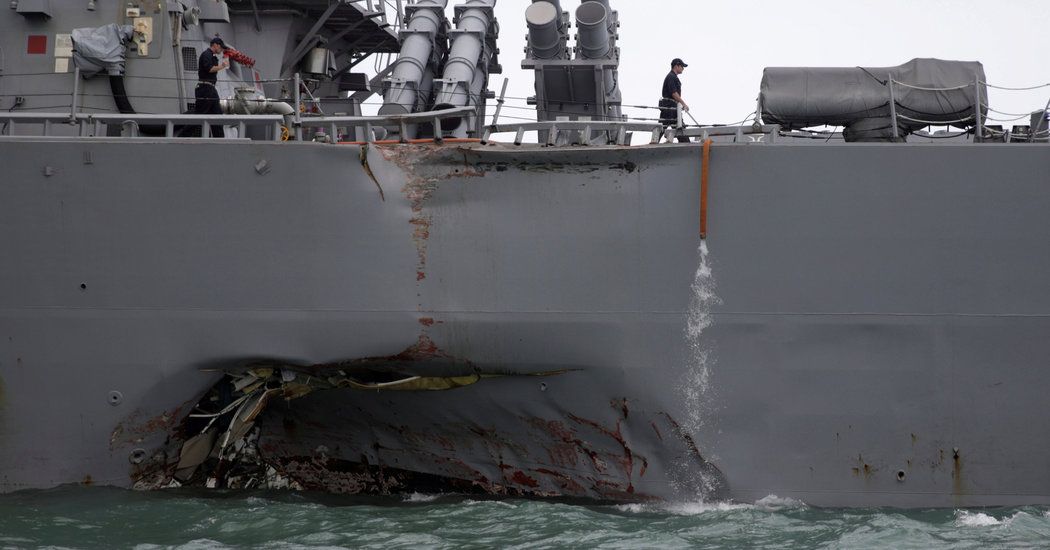
A crash involving the destroyer John S. McCain near Singapore raises questions about Navy safety two months after a similar collision killed seven people.


Scroll down for the [VIDEO] Some information and frequently asked questions about Advanced Denial System are :
Q1. Why do we need this technology? A1.The Active Denial System is needed because it’s the first non-lethal, directed-energy, counter-personnel system with an extended range greater than currently fielded non-lethal weapons. Most counter-personnel non-lethal weapons use kinetic energy (rubber rounds, bean bags, etc.). A kinetic-based system has a higher risk of human injury, and its effectiveness varies in relation to the size, age and gender of the target. The Active Denial System, however, is consistently effective regardless of size, age and gender and has a range greater than small-arms range. The Active Denial System will provide military personnel with a non-lethal weapon that has the same effect on all human targets.
Q2. What type of Department of Defense missions will the Active Denial System support? A2. The Active Denial System will support a full spectrum of operations ranging from non-lethal methods of crowd control, crowd dispersal, convoy and patrol protection, checkpoint security, perimeter security, area denial, and port protection, as well as other defensive and offensive operations from both fixed-site or mobile platforms. The Active Denial System is an advanced, long-range non-lethal, directed energy, counter-personnel capability that projects a man-sized (1.5 m) beam of millimeter waves (not microwaves) at a range up to 1,000 meters. It will have the same compelling non-lethal effect on all human targets, regardless of size, age and gender.

A renewed campaign of covert network attacks is more likely to spur Tehran’s nuclear efforts than hinder them.
The Iran nuclear deal is increasingly at risk, with President Trump threatening to overrule his top national security advisers and defy the assessment of international monitors to declare Iran non-compliant with the agreement’s stipulations. The problem for the administration, however, is that no viable alternative is better than the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action. If Trump rips up the JCPOA, the U.S. would forfeit the stringent limitations placed on Iran’s enrichment activities and the international community would lose the unprecedented transparency it now has on Iran’s nuclear program. Even more daunting, the United States would become isolated in its approach to Iran, opposed by Europe, Russia, China, and much of the rest of the world.
Perhaps a more realistic concern is the prospect that the administration will nominally uphold the deal, while engaging in aggressive covert action against Iran. Increasingly, when traditional military and diplomatic options appear too costly, states turn to cyber warfare. But a stepped-up cyber offensive against Iran is very unlikely to yield desirable results. Not only is it unlikely to be effective in its immediate objectives, but it risks antagonizing Iran into precisely the kinds of behavior the hawks want to forestall.

In 2015, a video showing a semi-automatic handgun being fired from a custom-built drone went viral, raising concerns for authorities, including the FAA. The development of such a DIY device was only a matter of time, as was the commercialization of the technology. Now Florida-based startup Duke Robotics has unveiled the TIKAD, a custom-built multirotor that can carry and fire various military weapons, including semi-automatic rifles and grenade launchers.
Russia unveils new fleet of ‘invisible’ supersonic fighter jets — and boasts that they will be the envy of air forces around the world.
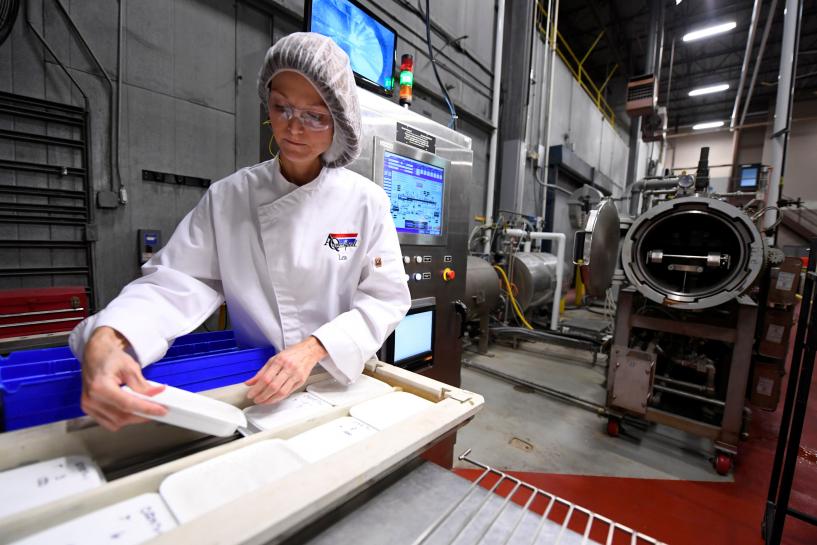

SAN FRANCISCO (Reuters) — Amazon.com Inc is exploring a technology first developed for the U.S. military to produce tasty prepared meals that do not need refrigeration, as it looks for new ways to muscle into the $700 billion U.S. grocery business.
The world’s biggest online retailer has discussed selling ready-to-eat dishes such as beef stew and a vegetable frittata as soon as next year, officials at the startup firm marketing the technology told Reuters.
The dishes would be easy to stockpile and ship because they do not require refrigeration and could be offered quite cheaply compared with take-out from a restaurant.
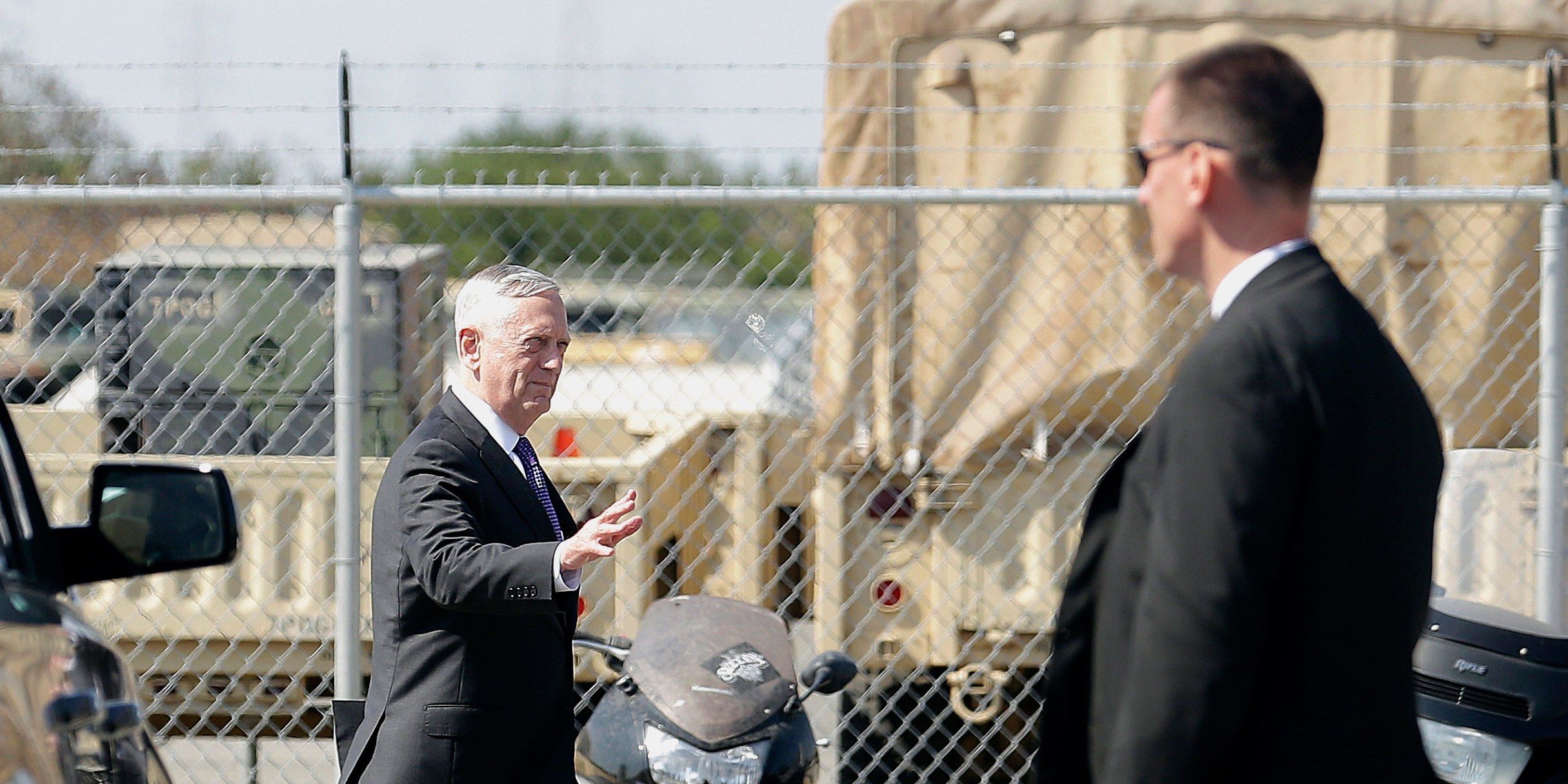

Mattis, speaking in Mountain View, a stone’s throw from Google’s campus, hopes the tech industry will help the Pentagon catch up. He was visiting the Defense Innovation Unit Experimental, an organization within the DoD started by his predecessor Ashton Carter in 2015 to make it easier for smaller tech companies to partner with the Department of Defense and the military. DIUx has so far sunk $100 million into 45 contracts, including with companies developing small autonomous drones that could explore buildings during military raids, and a tooth-mounted headset and microphone.
The academic and commercial spheres are seeing rapid advances in AI technology. And the Pentagon wants in.

@realDonaldTrump “Military solutions are now fully in place, locked and loaded, should North Korea act unwisely. Hopefully Kim Jong Un will find another path!”
#LockedAndLoaded

BEIJING (Reuters) — China has sent an “unbreakable” code from a satellite to the Earth, marking the first time space-to-ground quantum key distribution technology has been realized, state media said on Thursday.
China launched the world’s first quantum satellite last August, to help establish “hack proof” communications, a development the Pentagon has called a “notable advance”.
The official Xinhua news agency said the latest experiment was published in the journal Nature on Thursday, where reviewers called it a “milestone”.