<p>Modern warfare is constantly changing with numerous technologies, including machine vision, both driving and being used to keep up with it.</p>


China conducted a secret weapon test that has caught the US intelligence community off guard. Back in August, China lit up the sky when it tested a nuclear-capable hypersonic missile, which travels faster than the speed of sound. The global shipping supply crisis might affect Christmas, thanks in part to China’s power shortage. And a man in Jiangsu Province takes drastic measures after his daughter fails to solve a math problem correctly. Watch this episode of China Uncensored for that and more of this week’s China news headlines.
Jack ma’s dirty secret | power struggle rips ant financial • jack ma’s dirty secret | power strugg…
China’s POWER SHORTAGE could cause economic collapse • china’s POWER SHORTAGE could cause ec…
YouTube demonetizes our channels, we need your support!
www.patreon.com/ChinaUncensored.
https://chinauncensored.locals.com.
We also accept bitcoin!
https://chinauncensored.tv/bitcoin.
Buy our merchandise!
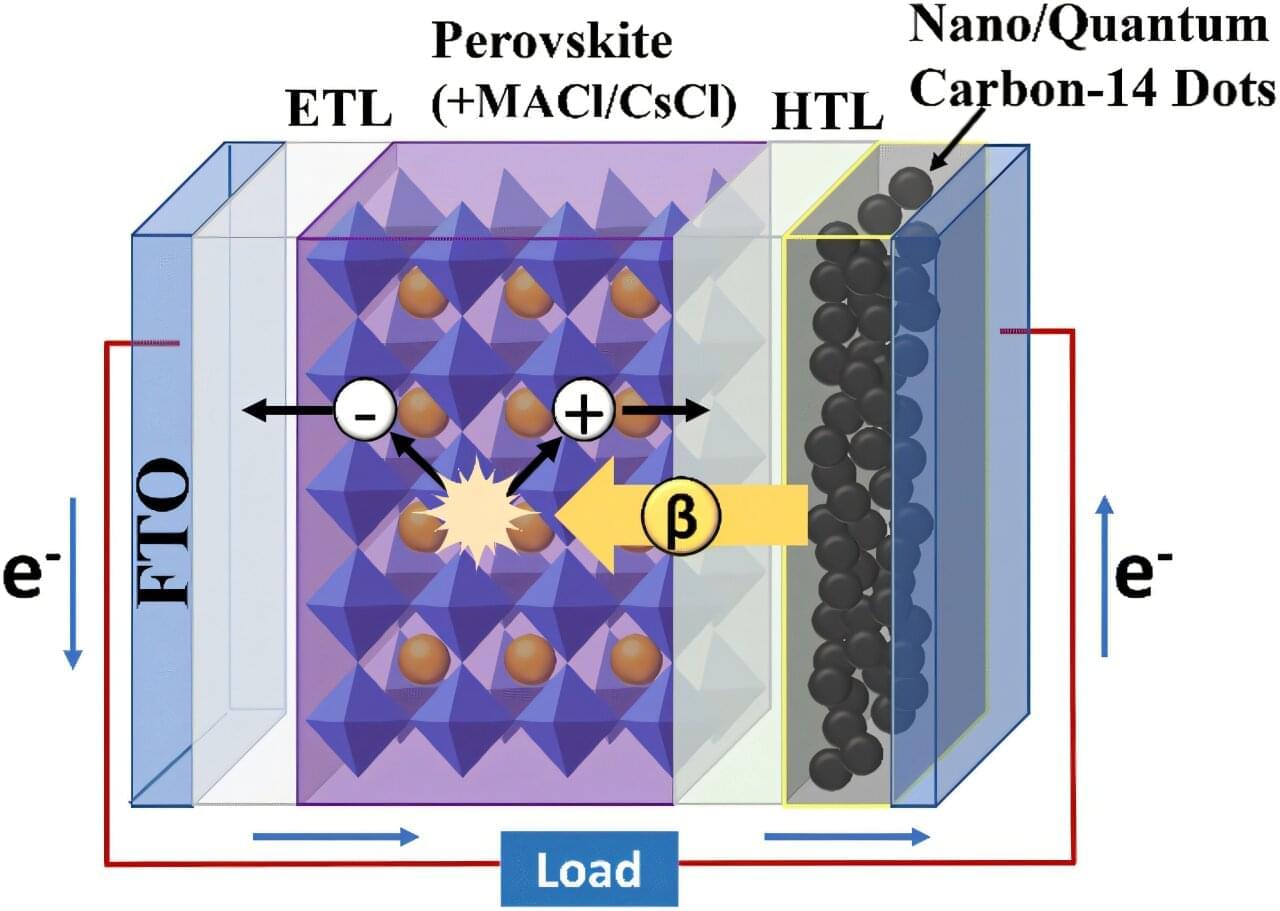
A research team has developed the world’s first next-generation betavoltaic cell by directly connecting a radioactive isotope electrode to a perovskite absorber layer. By embedding carbon-14-based quantum dots into the electrode and enhancing the perovskite absorber layer’s crystallinity, the team achieved both stable power output and high energy conversion efficiency.
The work is published in the journal Chemical Communications. The team was led by Professor Su-Il In of the Department of Energy Science & Engineering at DGIST.
The newly developed technology offers a stable, long-term power supply without the need for recharging, making it a promising next-generation energy solution for fields requiring long-term power autonomy, such as space exploration, implantable medical devices, and military applications.
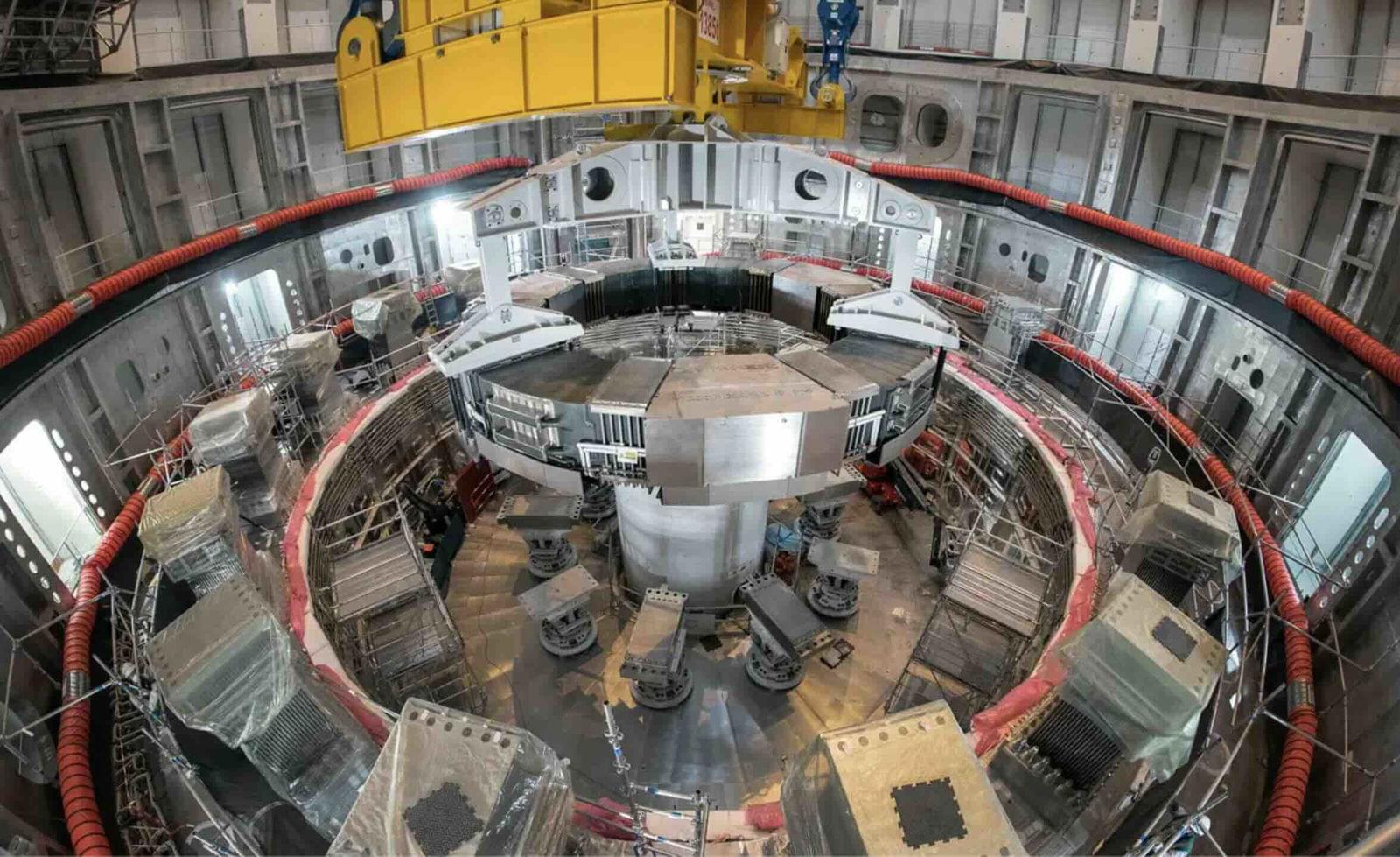

In a critical fusion breakthrough, scientists from the international ITER nuclear fusion energy project have announced the completion of the sixth and final component of the reactor’s central solenoid, a magnet powerful enough to levitate an aircraft carrier.
Described as a “landmark achievement” by the 30-country ITER collaboration, the pulsed superconducting electromagnet and other completed components will be assembled at the group’s designated site in southern France.
“By integrating all the systems needed for fusion at industrial scale, ITER is serving as a massive, complex research laboratory for its 30-plus member countries, providing the knowledge and data needed to optimize commercial fusion power,” the group explained in a statement announcing the achievement.
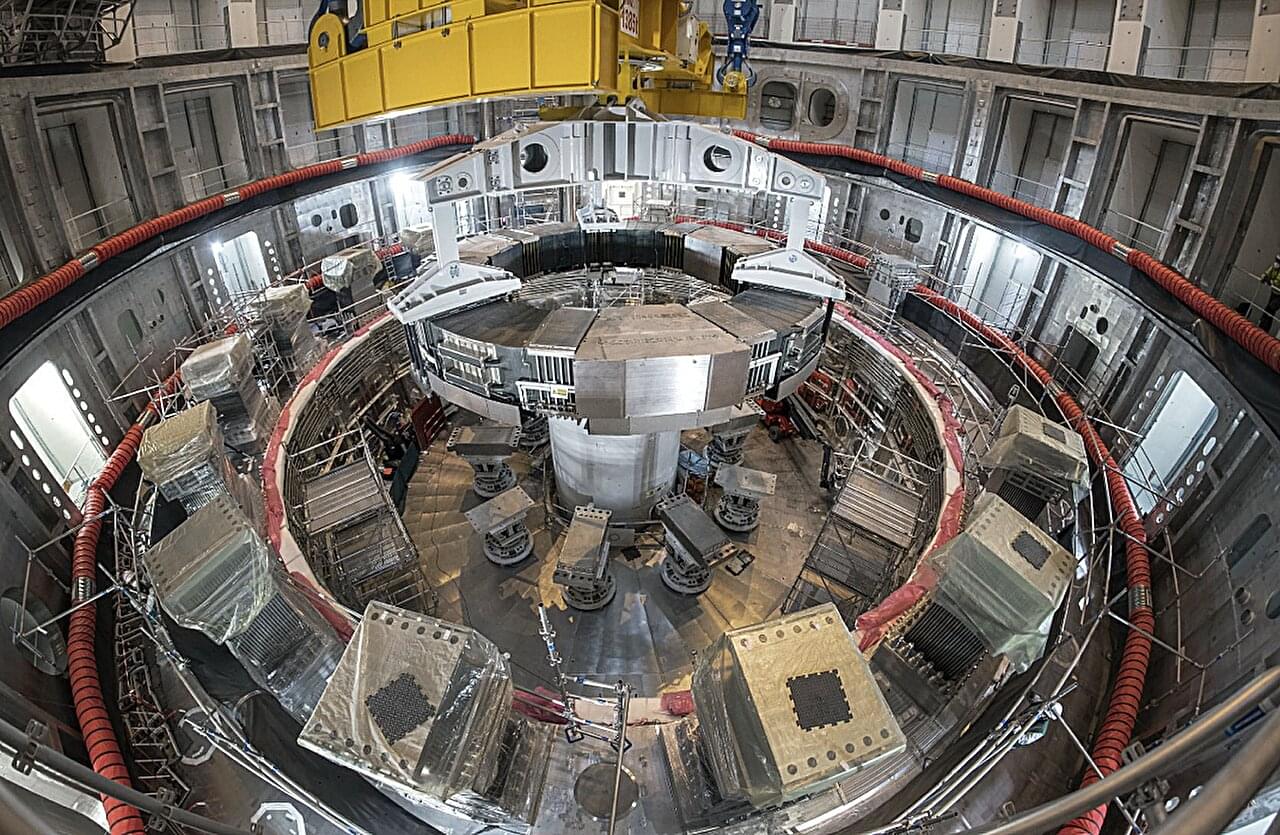

In a landmark achievement for fusion energy, ITER has completed all components for the world’s largest, most powerful pulsed superconducting electromagnet system.
ITER is an international collaboration of more than 30 countries to demonstrate the viability of fusion—the power of the sun and stars—as an abundant, safe, carbon-free energy source for the planet.
The final component was the sixth module of the Central Solenoid, built and tested in the United States. When it is assembled at the ITER site in Southern France, the Central Solenoid will be the system’s most powerful magnet, strong enough to lift an aircraft carrier.

“Second Variety” is a science fiction novelette by American writer Philip K. Dick, first published in Space Science Fiction magazine, in May 1953. Set in a world where war between the Soviet Union and United Nations has reduced most of the world to a barren wasteland, the story concerns the discovery, by the few remaining soldiers left, that self-replicating robots originally built to assassinate Soviet agents have gained sentience and are now plotting against both sides. It is one of many stories by Dick to examine the implications of nuclear war, particularly after it has destroyed much or all of the planet. The story was adapted into the movie Screamers in 1995. 00:00 Intro 01:03 Peek into the plot 03:33 Self-Replication and Technological Autonomy 06:51 Current Autonomous Warfare Capabilities 10:30 Space Warfare and the Projection of Terrestrial Conflict 13:14 Current State of Space Warfare 15:22 Wrapping Up =============== 🎬 Loitering munitions system WARMATE • Loitering munitions system WARMATE 📙 🇺🇸 Superintelligence: Paths, Dangers, Strategies https://bookshop.org/a/98861/97801987… The Human Terrain Project — PENTAGON’S attempt to understand The Enemy | ENDEVR Documentary
• The Human Terrain Project — PENTAGON’… 📙 🇺🇸 War in the Age of Intelligent Machines https://monoskop.org/images/c/c0/DeLa… =============== Buy the book featured in this video: 📙 🇺🇸 Buy the book Second Variety https://bookshop.org/a/98861/97988883… 🎧 Free Audiobook
• Post-Apocalyptic Story “Second Variet… =============== You can find my take on things summarised in the books I wrote. 📙🇺🇸Chronicles of the Machine — Simulated conversations with Philip K. Dick https://buchshop.bod.ch/chronicles-of… 📙🇺🇸Zero Person: Reframing Autistic Cognition Beyond the Self https://buchshop.bod.ch/zero-person-e… 📙🇩🇪Zero Person: Autistische Kognition jenseits des Selbst https://buchshop.bod.ch/zero-person-e… 📙🇺🇸Book order: The end of the I https://www.bod.ch/buchshop/the-end-o… 📙🇩🇪Book order: Das Ende des Ichs https://www.bod.ch/buchshop/das-ende–… 📙🇺🇸 #actuallyautistic — Living with Autism – A Poetic Exploration of the Spectrum https://buchshop.bod.ch/actuallyautis… =============== Image credits: Freepik.

Cybersecurity researchers have revealed that Russian military personnel are the target of a new malicious campaign that distributes Android spyware under the guise of the Alpine Quest mapping software.
“The attackers hide this trojan inside modified Alpine Quest mapping software and distribute it in various ways, including through one of the Russian Android app catalogs,” Doctor Web said in an analysis.
The trojan has been found embedded in older versions of the software and propagated as a freely available variant of Alpine Quest Pro, a paid offering that removes advertising and analytics features.

A team of researchers at Q-CTRL, a quantum infrastructure software-maker based in Sydney, Australia, has announced the successful demonstration of its newly developed quantum navigation system called “Ironstone Opal.”
The group has written a paper describing how their system works and how well it tested against currently available backup GPS systems and has posted it on the arXiv preprint server.
With the advent and subsequent reliance on GPS by private and military vehicles and aircraft for navigation, governments have come to understand how vulnerable such systems can be. Outages can lead to drivers being stranded, pilots scrambling to use outdated systems and difficulties deploying military assets. Because of that, scientists around the world have been looking for reasonable backup systems, or even possible alternatives to GPS.