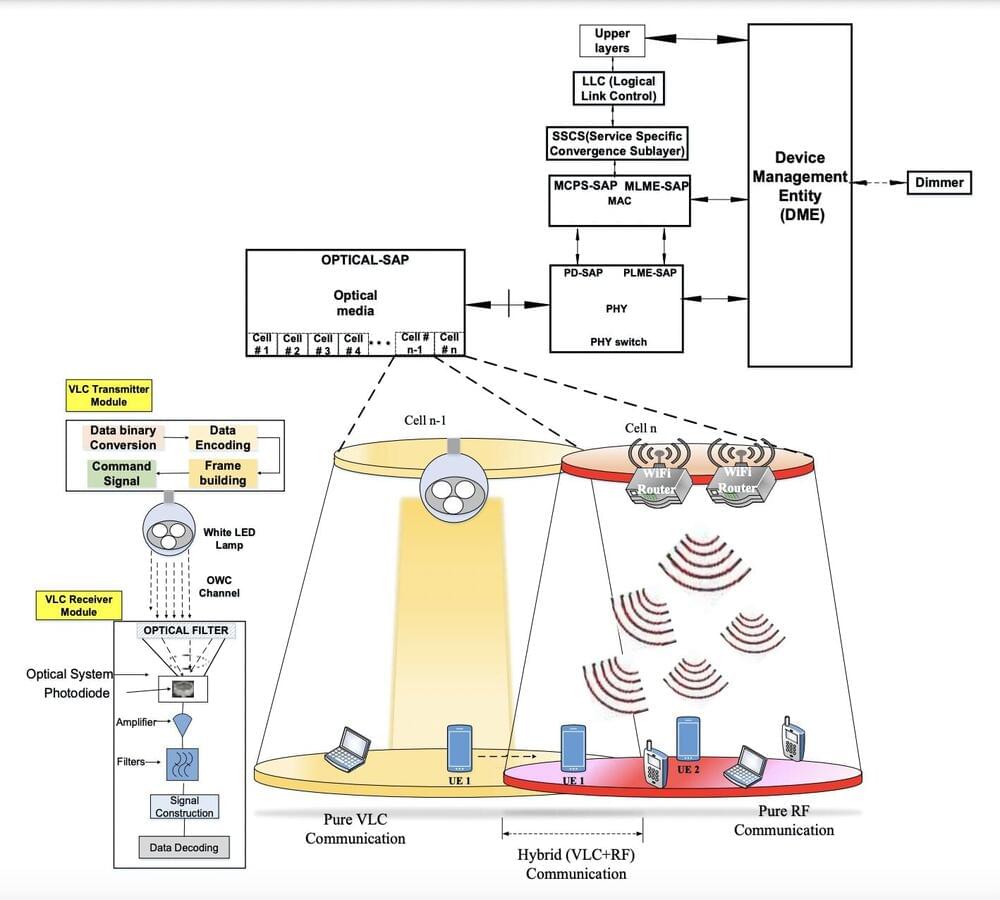
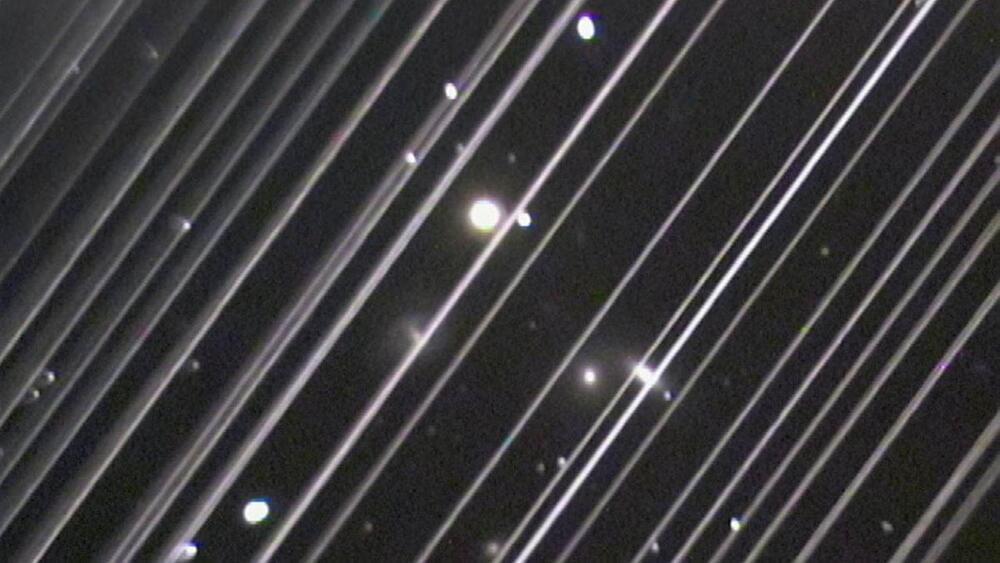
For the first time in human history, there are now 10,000 functioning satellites above our heads, whipping around the Earth at high speed. It’s a milestone that showcases decades of technical achievement but might also make it harder to sleep at night if you think about it for too long.
The count comes from the latest estimate by Jonathan McDowell, an astronomer at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and leading watcher of most things orbital. McDowell estimates there are 10,036 active satellites in orbit as of July 18.
Remarkably, this figure has roughly quadrupled over just the past half-decade, thanks almost entirely to Elon Musk, SpaceX and their massive Starlink constellation of broadband routers in low-earth orbit.