Law enforcement needs to be innovative and act now in order to keep face with near future criminal threats, warns ‘Do criminals dream of electric sheep’ paper.



How dictators work in the 21st century.
The new president of Kazakhstan is now proving that he will keep the old, oppressive systems alive for the 21st century, using advanced technical tools.
The man in the middle: Beginning last week, Kazakhstan’s government is intercepting all HTTPS traffic inside the country, ZDNet reports. HTTPS is a protocol meant to offer encryption, security, and privacy to users, but now the nation’s internet service providers are forcing all users to install certificates that enable pervasive interception and surveillance.
On Wednesday, Kazakh internet users were redirected to web pages instructing them to install the government’s root certificate in their web browser, which enables what’s called “man in the middle” interception of internet traffic, decryption, and surveillance.
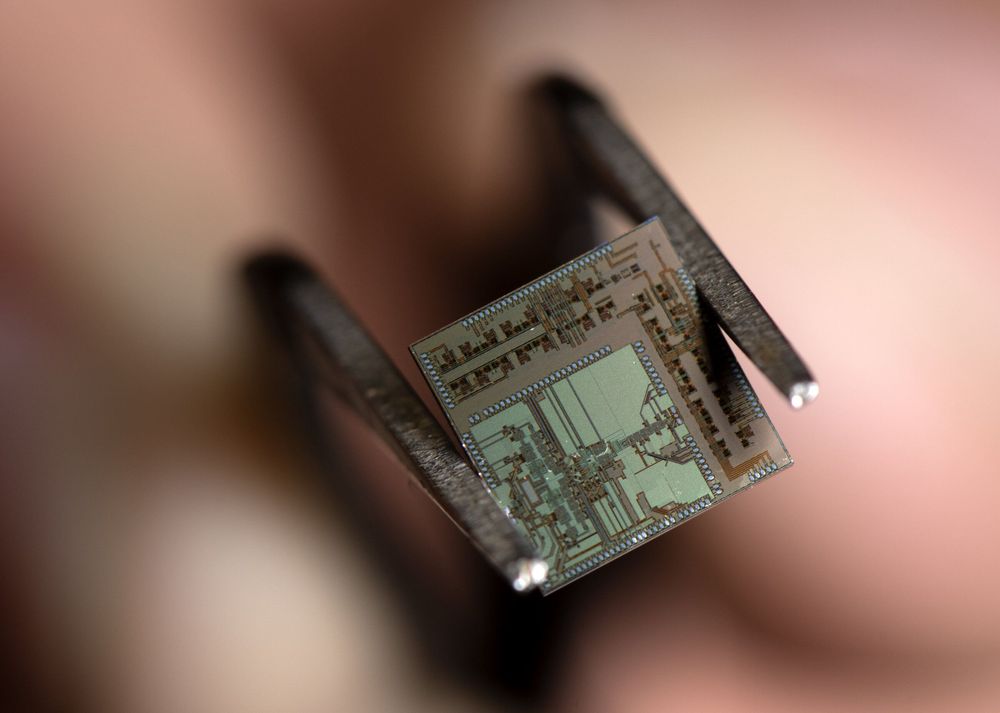
A new wireless transceiver invented by electrical engineers at the University of California, Irvine boosts radio frequencies into 100-gigahertz territory, quadruple the speed of the upcoming 5G, or fifth-generation, wireless communications standard.
Labeled an “end-to-end transmitter-receiver” by its creators in UCI’s Nanoscale Communication Integrated Circuits Labs, the 4.4-millimeter-square silicon chip is capable of processing digital signals significantly faster and more energy-efficiently because of its unique digital-analog architecture. The team’s innovation is outlined in a paper published recently in the IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits.
“We call our chip ‘beyond 5G’ because the combined speed and data rate that we can achieve is two orders of magnitude higher than the capability of the new wireless standard,” said senior author Payam Heydari, NCIC Labs director and UCI professor of electrical engineering & computer science. “In addition, operating in a higher frequency means that you and I and everyone else can be given a bigger chunk of the bandwidth offered by carriers.”

The internet is rife with myths and articles making dubious claims about certain foods and their anti-cancer properties. We have all seen the articles of questionable scientific merit gracing social media suggesting that such-and-such foods can cure cancer, the majority of which are highly questionable. A new study offers a unique kind of insight into the potential true effectiveness of food in fighting cancer [1].
Investigating molecules in food with machine learning
There is no doubt that there are many foods that contain a myriad of active molecules, and perhaps some of these food myths may have a grain of truth to them. A team of researchers decided to do some real myth-busting and put a variety of bioactive molecules found in foods to the test to see if they might potentially help to combat cancer.

As with many of my recent posts, this was originally a reply to a member of Quora, a Q&A web forum. But, it fits within Lifeboat’s educational mission and our fascination to push the limits of creativity and tech.
Is there a theoretical speed limit to WiFi devices over the next 10 years?
Because of four recent practices,* it is difficult to predict an upper limit for future overall throughput:

Early this morning, I was asked this question at Quora. It’s a pretty basic request of network administrators, including parents, schools and anyone who administers a public, sensitive or legally exposed WiFi hot spot.
Is there a quick and easy way to view, log, or otherwise monitor the web sites visited by people on your home or office network?
Yes. It’s free and and it is pretty easy to do.
It gets a bit trickier, if the individual on your network is using a VPN service that they have configured on their device.[1] A VPN does not stop you from logging their browsing, but all of their activity will point to the VPN address instead of the site that they are actually visiting. In that case, there is another way to monitor their activity. See note #1, below.


In many projects there comes a time when you’ll need to store some data off-line. It may be a requirement or just an improvement for your users, but you have to decide which of the available storage options you will use in your application. This article will help you choose the best one, for your app.
Introduction
HTML5 introduced a few off-line storage options. AppCache, localStorage, sessionStorage and IndexedDB. Every one of them is suitable for a specific use. For example, AppCache can boost your application or let some parts of it work without an Internet connection. Below, I will describe all of these options and show a few code snippets with example usage.

