Starlink is a space internet project run by aerospace company SpaceX.


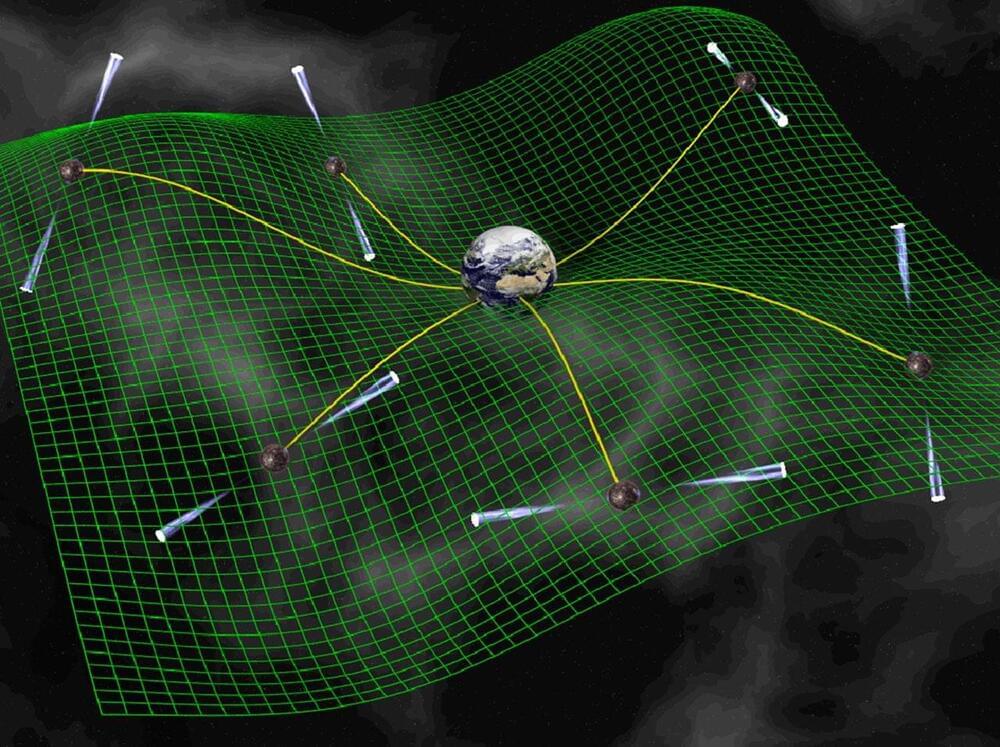
Stephen Taylor, assistant professor of physics and astronomy and former astronomer at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), said, “Using the pulsars we observe across the Milky Way galaxy, we are trying to be like a spider sitting in stillness in the middle of her web. How well we understand the solar system barycenter is critical as we attempt to sense even the smallest tingle to the web. The solar system barycenter, its center of gravity, is the location where the masses of all planets, moons, and asteroids balance out.”
So, where is the center of the solar system?
It is not in the center of the Sun as many might assume, instead it is closer to the surface of the star. This is due to Jupiter’s mass and our imperfect knowledge of its orbit.

Back in 1,859, long before the internet, a massive geoelectrical storm knocked out the telegraph systems in the world. Reports were given of telegraph operators being shocked, the paper catching fire, and the equipment being operated without the batteries being connected. This was caused by the massive surge of electrical power caused by the storm. These storms occur when a bubble of superheated gas from the sun hits the earth. These storms cause massive damage to our solar system. This occurrence causes a massive surge in electrical activity and damage. Scientists studying these events have concluded that they occur every 500 years. The event in 1,859, known as the Carrington Event, was the most recent. This could mean that in the year 2,359, another storm would wipe out the entire internet.
The Carrington Event was the largest recorded geoelectrical storm, but it wasn’t the first to happen. An even bigger storm happened in our solar system in A.D. 774, based on readings taken from ice core samples in the Antarctic. The solar flare that was launched from the sun during this event in the Antarctic caused the fastest and biggest rise in carbon-14. Carbon-14 is an isotope of Carbon, which is created from the sun and contains highly radioactive material. Though the Carrington Event was measured via observatories at the time, scientists were able to read the rings in the ice taken from the Antarctic event, which is now known as the Miyake event. Based on those readings, the Miyake event was even greater than the Carrington event. The readings of the ice showed a 14% increase in carbon-14. The Carrington event only saw an increase of less than 1% in carbon-14 readings.
Scientists have a rating system that measures the level of geoelectrical storms based on a scale of 1 to 5. The geoelectrical storms are then given a designation of G1 to G5 based on their intensity. The Carrington event was rated a G5. That would have meant the Miyake event was even more catastrophic in our solar system. A storm that was three times smaller than the Carrington event occurred in 1989. This event took place in Quebec, Canada, and caused the full collapse of the Hydro-Quebec electrical grid. The geoelectrical storm was so powerful that it also caused damage to a circuit breaker in New Jersey. This resulted in the grid’s circuit breakers going off, which caused five million people being without power for nine hours. Should an electrical storm like this occur in currently, the damage would be immeasurable.
I did a short youtube video discussing the space arena of the war in Ukraine.
Space War, what is it good for?
The space arena of the Russian invasion of Ukraine, spaceX, Starlink, Roscosmos and more… following an article I wrote on Quora with over 200k views.
Analyses of what kind of future conflicts may take place in space with some examples from the sci-fi TV series For All Mankind and Space Force.
And if you stay to the end, I’ll reveal my personal war story. I was an NCO in the Israeli Air-Force Intelligence during the 1991 Golf War. The first war where Space played a significant role.
With the web of undersea cables lacing the continents together now, it’s hard to imagine that it wasn’t until 1956 that the first transatlantic telephone cable was laid. Sure, there were telegraph cables under the Atlantic starting as early as the late 1800s, but getting your voice across the ocean on copper was a long time coming. So what was the discerning 1930s gentleman of business to do when only a voice call would do? He’d have used a radiotelephone, probably at an outrageous expense, which as this video on the receiving end of the New York to London radio connection shows, was probably entirely justified.
The video details the shortwave radiotelephone system that linked New York and London in the 1930s. It starts with a brief but thorough explanation of ionospheric refraction, and how that atmospheric phenomenon makes it possible to communicate over vast distances. It also offers a great explanation on the problems inherent with radio connections, like multipath interference and the dependency on the solar cycle for usable skip. To overcome these issues, the Cooling Radio Station was built, and its construction is the main thrust of the video.
Built on Cooling Marshes along the Thames well outside of London, the receive-only radio station was a gigantic undertaking. It consisted of a two-mile-long rhombic array antenna, pointed directly at the transmitting site in Lawrenceville, New Jersey. The pool-table-flat marshland made for a perfect place for the array; the fact that the ground was saturated with brackish tidal water had the added benefit of excellent electrical conduction, too. The amount of work it took to raise the antenna masts and booms is impressive — very little power equipment was used. And we loved the details about the hardline coaxial used to stitch the antennas together — it was made on-site from copper tube and insulating spacers.
Including one long-awaited and colossal German satellite. It’s never too late to join the party when you’re headed to space.
On Friday, April 1 at 12:24 p.m. ET, Falcon 9 launched Transporter-4, SpaceX’s fourth dedicated smallsat rideshare program mission, from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. This was the seventh launch and landing of this Falcon 9 stage booster, which previously supported launch of Crew-1, Crew-2, SXM-8, CRS-23, IXPE, and one Starlink mission. Following stage separation, Falcon 9’s first stage landed on the Just Read the Instructions droneship, which was stationed in the Atlantic Ocean.
On board this flight were 40 spacecraft, including CubeSats, microsats, picosats, non-deploying hosted payloads, and an orbital transfer vehicle carrying spacecraft to be deployed at a later time.
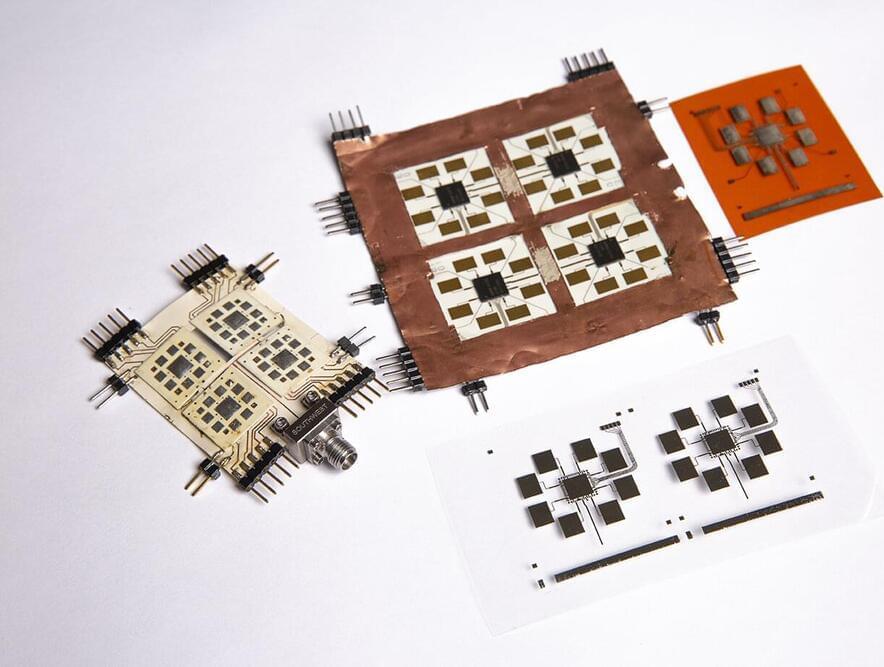
5G+ (5G/Beyond 5G) is the fastest-growing segment and the only significant opportunity for investment growth in the wireless network infrastructure market, according to the latest forecast by Gartner, Inc. But currently 5G+ technologies rely on large antenna arrays that are typically bulky and come only in very limited sizes, making them difficult to transport and expensive to customize.
Researchers from Georgia Tech’s College of Engineering have developed a novel and flexible solution to address the problem. Their additively manufactured tile-based approach can construct on-demand, massively scalable arrays of 5G+ (5G/Beyond 5G)‐enabled smart skins with the potential to enable intelligence on nearly any surface or object. The study, recently published in Scientific Reports, describes the approach, which is not only much easier to scale and customize than current practices, but features no performance degradation whenever flexed or scaled to a very large number of tiles.
“Typically, there are a lot of smaller wireless network systems working together, but they are not scalable. With the current techniques, you can’t increase, decrease, or direct bandwidth, especially for very large areas,” said Tentzeris. “Being able to utilize and scale this novel tile-based approach makes this possible.”


