
Category: internet – Page 149

RV-8 | Build Your Plane! From The Ground Up PART 9 | Van’s Aircraft RV-8 Instructional Video
Roel van DijnenI did not realize that India still has such a small economy, smaller then Germany and UK 😳
Eric KlienAdmin.
Roel van Dijnen In related news, India has so far stopped Tesla and Starlink from operating in their country. Governments can, and often do, screw up their economy.
Roel van DijnenEric Klien The screwing up part is rather subjective, imagine the effect on earth when countries like India and Nigeria will adopt the same luxurious lifestyle that we have. But then again, Tesla and Starlink are trying to be part of the solution for that also 😉
Freya WildeRoel van Dijnen even if they did adopt a more luxurious lifestyle, who is to say it would be the same. Wouldn’t that be up to the people there? I have no idea how any country will ultimately act. And I have zero right to guess and interfere. No one doe… See more.
Roel van DijnenFreya Wilde I’m not claiming to have any right to intervene (forcefully) and I sure hope better more sustainable ways of having a great lifestyle will be upon us, preferably sooner rather than later!
SpaceX’s Starship Booster 7 gone for repair after explosion, JWST First Images, CRS-25, Vega C
Head to https://www.squarespace.com/marcushouse to save 10% off your first purchase of a website or domain using code MARCUSHOUSE
Quite the inspirational week this one with the complete set of JWST First Images. Loads of Starship and Starbase news. Last week I mentioned that it was fire time for Starbase, and…WOW… I was not wrong there. SpaceX’s Starship Booster 7 has gone for repair after explosion. Falcon 9 launches for both Starlink and finally CRS-25. We also had the very first launch of Vega C. Rocket Lab firing off another Electron, and more. So enough of this intro. Let’s crack on with it!
Everyday Astronaut — Elon Musk Explains SpaceX’s Raptor Engine!
End Screen Music — Isle of Rain by Savfk.
Join the mailing list to be notified when I release a video.
https://marcushouse.space/email-list.
👕Like this shirt? Pick it up on any product you like here.
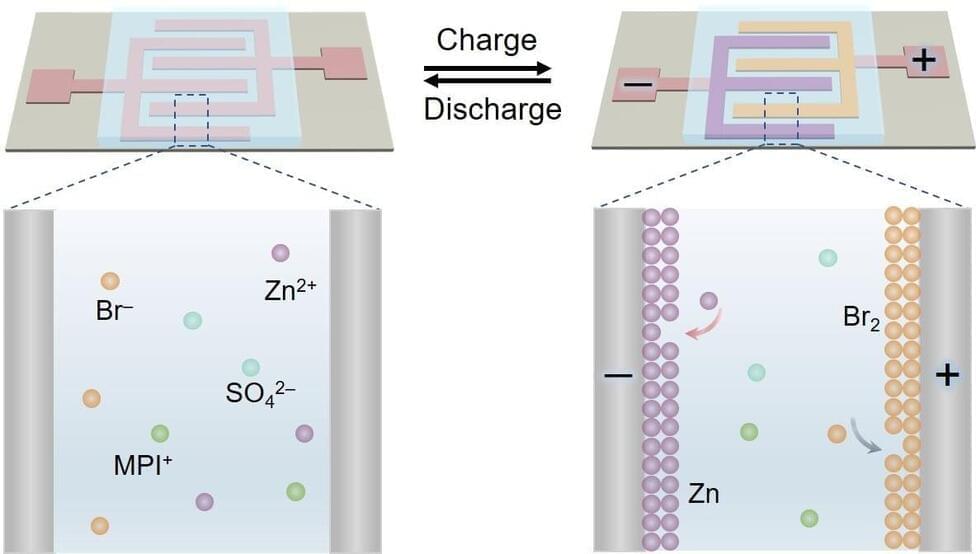
Researchers propose dual-plating strategy to rapidly construct microbatteries
High-performance, micro-sized electrochemical energy storage devices are essential for future miniaturized electronic devices, such as smart medical implants, wireless sensors, and the Internet of Things. Microbatteries (MBs) typically show higher energy density and more stable voltage output than micro-supercapacitors.
However, current MBs involve tedious construction procedures and unsatisfactory electrochemical performance. In addition, no methods exist to construct or manipulate a liquid microelectrode.
A joint research team led by Prof. Qu Liangti from Tsinghua University, Prof. Zhang Zhipan from the Beijing Institute of Technology, and Prof. Liu Feng from the Institute of Mechanics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IMCAS) recently proposed a dual-plating strategy to rapidly construct new zinc–bromine microbatteries (Zn–Br2 MBs) with ultrahigh areal energy density and polarity-switchable functionality.
Physicists Find The ‘Missing Link’ That Could Provide Quantum Internet Technology
Before quantum computers and quantum networks can fulfil their huge potential, scientists have got several difficult problems to overcome – but a new study outlines a potential solution to one of these problems.
As we’ve seen in recent research, the silicon material that our existing classical computing components are made out of has shown potential for storing quantum bits, too.
These quantum bits – or qubits – are key to next-level quantum computing performance, and they come in a variety of types.

A New Attack Can Unmask Anonymous Users on Any Major Browser
When you visit a website, the page can capture your IP address, but this doesn’t necessarily give the site owner enough information to individually identify you. Instead, the hack analyzes subtle features of a potential target’s browser activity to determine whether they are logged into an account for an array of services, from YouTube and Dropbox to Twitter, Facebook, TikTok, and more. Plus the attacks work against every major browser, including the anonymity-focused Tor Browser.
“If you’re an average internet user, you may not think too much about your privacy when you visit a random website,” says Reza Curtmola, one of the study authors and a computer science professor at NJIT. “But there are certain categories of internet users who may be more significantly impacted by this, like people who organize and participate in political protest, journalists, and people who network with fellow members of their minority group. And what makes these types of attacks dangerous is they’re very stealthy. You just visit the website and you have no idea that you’ve been exposed.”
The risk that government-backed hackers and cyber-arms dealers will attempt to de-anonymize web users isn’t just theoretical. Researchers have documented a number of techniques used in the wild and have witnessed situations in which attackers identified individual users, though it wasn’t clear how.
Researchers find the missing photonic link to enable an all-silicon quantum internet
Researchers at Simon Fraser University have made a crucial breakthrough in the development of quantum technology.
Their research, published in Nature today, describes their observations of more than 150,000 silicon “T center” photon-spin qubits, an important milestone that unlocks immediate opportunities to construct massively scalable quantum computers and the quantum internet that will connect them.
Quantum computing has enormous potential to provide computing power well beyond the capabilities of today’s supercomputers, which could enable advances in many other fields, including chemistry, materials science, medicine and cybersecurity.

Internet on the go: FCC greenlights Starlink service on moving cars, boats, and planes
If you’re ready for connectivity on the move, SpaceX’s Starlink satellite broadband may soon be the answer. The US Federal Communications Commission on Thursday gave the internet provider the greenlight to provide service on moving vehicles, boats, and planes.
The new authority should help SpaceX meet “the growing user demands that now require connectivity while on the move,” wrote FCC International Bureau Chief Tom Sullivan in the approval, “whether driving an RV across the country, moving a freighter from Europe to a U.S. port, or while on a domestic or international flight.”

SpaceX prices fast Starlink satellite Internet for ships, yachts, and oil rigs at US$5,000 with the highest download speeds
Barely did the ink under the FCC approval signature dry, and SpaceX’s Starlink satellite Internet announced a new pricey Maritime service for commercial ships, oil rigs, or premium yachts. Nothing is stopping people with recreational boats to get Starlink Maritime, too, save for the monthly tag and equipment fees.
