Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang highlights the transformative impact of AI and accelerated computing on various industries, emphasizing rapid growth, enhanced productivity, and the evolution of software development through innovations like the Omniverse and advanced GPUs Questions to inspire discussion Physical AI and AGI 🤖
Category: innovation – Page 60

UP Aerospace and Los Alamos lab achieve successful suborbital launch at Spaceport America
In Nijmegen, Netherlands, researchers have installed the world’s first microscope capable of live imaging of biological processes in such detail that moving protein complexes are visible. This new microscopic technique was developed by researchers led by Nico Sommerdijk from Radboud university medical center. As a demonstration of this innovative technique, Sommerdijk is now showcasing how arterial calcification begins.
From Science Fiction to Reality: Simple Lens Swap Turns Ordinary Cameras Into Hyperspectral Devices
Scientists have created a compact spectral singlet lens that turns standard cameras into hyperspectral ones, reducing system size and complexity. This breakthrough could expand hyperspectral imaging into portable applications, with future improvements underway.
The information we gather shapes our understanding and perspectives of the world. For centuries, optics has sought to interpret the multidimensional data around us through the “toolbox” of light. In the 17th century, Sir Isaac Newton introduced the lens imaging formula and conducted his famous color spectrum experiment, laying foundational insights in the field.
Since then, lenses and spectrometers have been extensively studied as essential optical components for capturing information. Cascading these two components can allow us to acquire more information – both spatial and spectral data. However, such a configuration leads to tradeoffs among device footprint, spectral resolution, and imaging quality, impeding portability and miniaturization of hyperspectral cameras.


Argonne receives funding for artificial intelligence in scientific research
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has awarded DOE’s Argonne National Laboratory funding as part of its Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Scientific Research program.
Supported by DOE funding, two projects will drive innovations by improving how data is processed and protected, leading to faster and more secure discoveries.
Scientists Successfully Warp Time At The Smallest Scale Ever
In a groundbreaking study published in Nature, scientists from JILA—a partnership between the National Institute of Standards and Technology and the University of Colorado Boulder—have managed to measure time dilation at an unprecedentedly small scale. This breakthrough involved detecting time differences between two clocks spaced only a millimeter apart, a distance as small as the width of a pencil tip. The experiment marks a major step forward in the precision of atomic clocks and sheds new light on the effects of gravity on time as outlined in Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity.
Clocks that Measure the Effects of Gravity at the Millimeter Scale
Time dilation, a phenomenon where time moves more slowly in strong gravitational fields or at high speeds, was first predicted by Einstein’s relativity theory. JILA researchers, led by physicist Jun Ye, used highly precise atomic clocks in this experiment to measure these differences in gravitational time dilation over millimeter distances. By tracking frequency shifts among a sample of 100,000 ultra-cold strontium atoms held in a lattice, the team achieved a remarkable level of control, detecting how the gravitational pull from Earth slightly altered the passage of time over even this small distance.
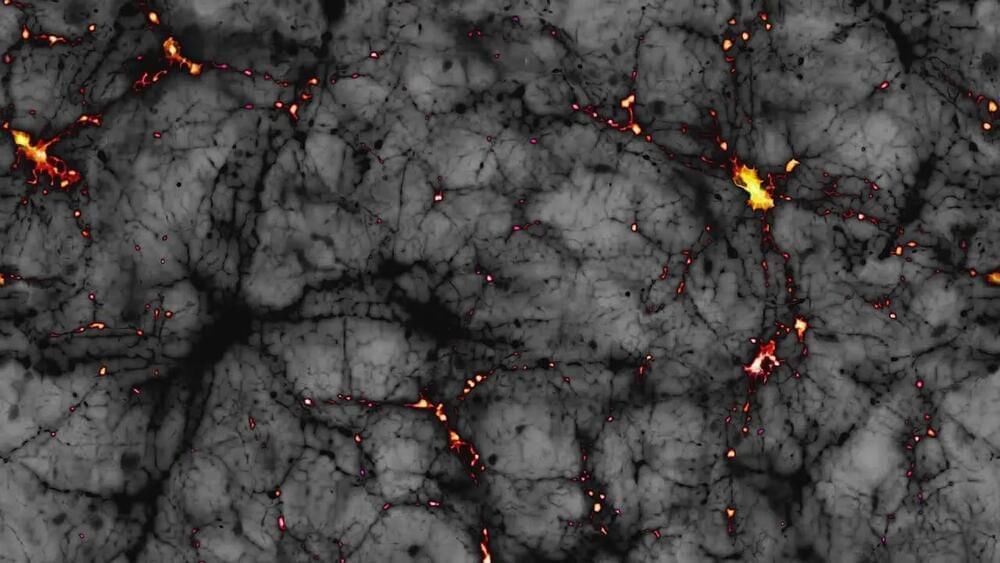
Researchers Capture First-ever ‘image’ Of A Dark Matter That Connects Galaxies
Researchers have created a composite image showing dark matter’s role in linking galaxies, using data from 23,000 galaxy pairs located 4.5 billion light-years away. This discovery, through weak gravitational lensing, offers direct evidence of the dark matter web predicted for decades, moving from theoretical assumptions to measurable proof. The finding helps confirm dark matter’s critical role in keeping galaxies intact, at a time when some scientists are questioning its existence. Though still largely invisible, this breakthrough brings us closer to truly understanding the unseen forces binding the universe together.
The idea of dark matter originated out of sheer necessity. Given the amount of matter we can observe, the universe shouldn’t be able to exist and function the way it does—this visible matter simply can’t produce the gravitational forces required to hold galaxies together. Dark matter offers scientists a solution to this problem. They suggest the universe must contain a type of matter that we are unable to detect, one that doesn’t absorb, reflect, or emit light—hence, a truly “dark” form of matter.
To maintain the accuracy of our scientific models, dark matter would need to make up more than a quarter of the universe’s total matter. However, what exactly constitutes dark matter remains a mystery, and attempting to find evidence for something invisible is a difficult endeavor. Until now, scientists have primarily relied on observing its gravitational influence as indirect proof of dark matter’s existence. But researchers from the University of Waterloo in Ontario, Canada, have gone a step further—they’ve produced a composite image that confirms galaxies are linked by dark matter.

See Without Being Seen: UCLA’s Unidirectional Imaging Breakthrough
UCLAs new unidirectional imaging technology enables image formation in a single direction, preventing image capture in the reverse direction.
This novel technology, which operates effectively under partially coherent light, offers significant advancements in optical communication and visual information processing by providing selective, high-quality imaging.
Unidirectional Imaging
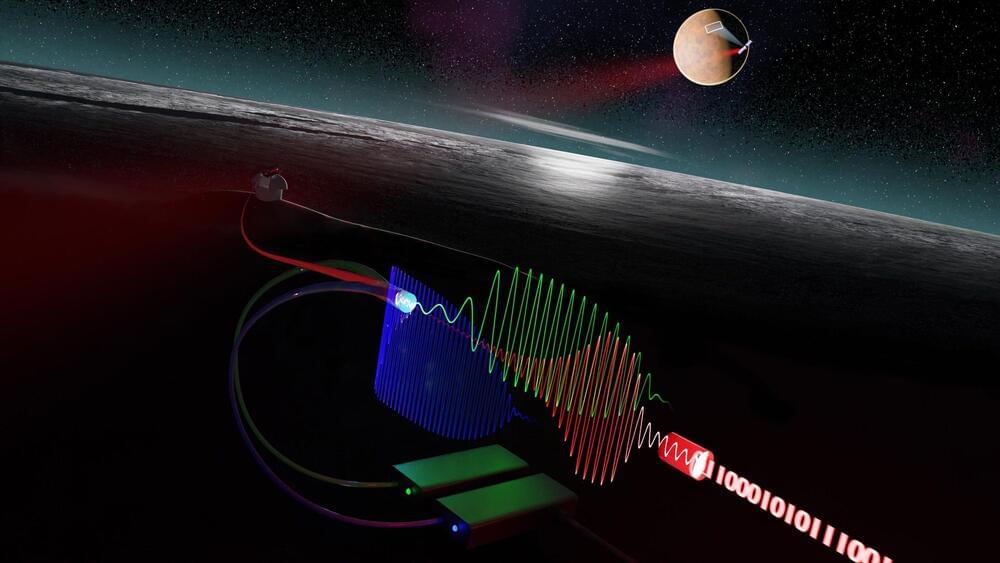

Silent Signals: The Breakthrough Technology Powering Faster Space Data
In space exploration, long-distance optical links now enable the transmission of images, videos, and data from space probes to Earth using light.
However, for these signals to travel the entire distance undisturbed, hypersensitive receivers and noise-free amplifiers are essential. Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden have now developed a system featuring a silent amplifier and an ultra-sensitive receiver, opening up possibilities for faster and more reliable space communication.
Space communication systems are increasingly relying on optical laser beams instead of traditional radio waves, as light experiences less signal loss over vast distances. However, even light-based signals weaken as they travel, meaning that optical systems need highly sensitive receivers to detect these faint signals by the time they reach Earth. Researchers at Chalmers have developed an innovative approach to optical space communication that could unlock new opportunities—and discoveries—in space.