Huawei has approached some Chinese tech companies about testing a new chip, called the Ascend 910D, which it hopes will be more powerful than Nvidia’s H100, The Wall Street Journal reported.
Category: innovation – Page 32
Battery in a battery: just one of CATL’s new EV tech announcements
Contemporary Amperex Technology Co., Limited (CATL), the largest battery manufacturer in the world with a 38% share of the global market, has just announced some fairly significant breakthroughs in battery tech that aren’t just theoretical; they’re already hitting the market.
Breakthrough! Quantum Droplets Shatter Like Rain—Here’s Why It Matters
Scientists have observed “quantum rain” for the first time—quantum droplets breaking up just like water in a storm! This discovery bridges classical fluid dy…

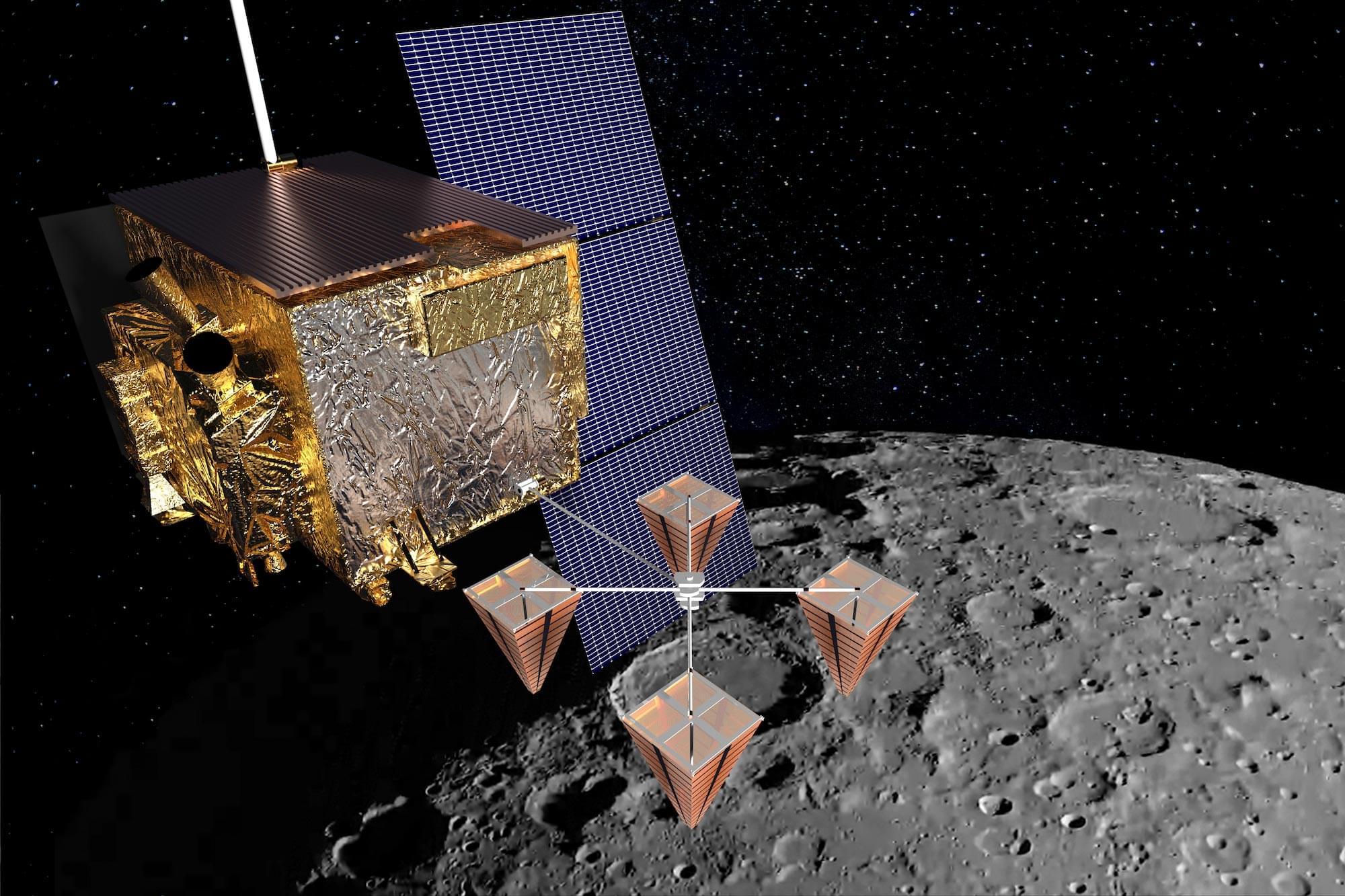
Secrets in the Shadows: ShadowCam and Cosmic Rays Uncover Moon’s Hidden Ice
Scientists are using cutting-edge techniques to track water ice on the Moon—an essential resource for future space missions.
A University of Hawai‘i team utilized ShadowCam to peer into the Moon’s perpetually dark craters, refining estimates of surface ice. Another team introduced a cosmic ray-based method to detect deeply buried ice, a breakthrough in lunar exploration. Both approaches could revolutionize how we locate usable water beyond Earth, with Hawai‘i emerging as a key player in the growing space frontier.
Unlocking lunar water: why ice on the moon matters.
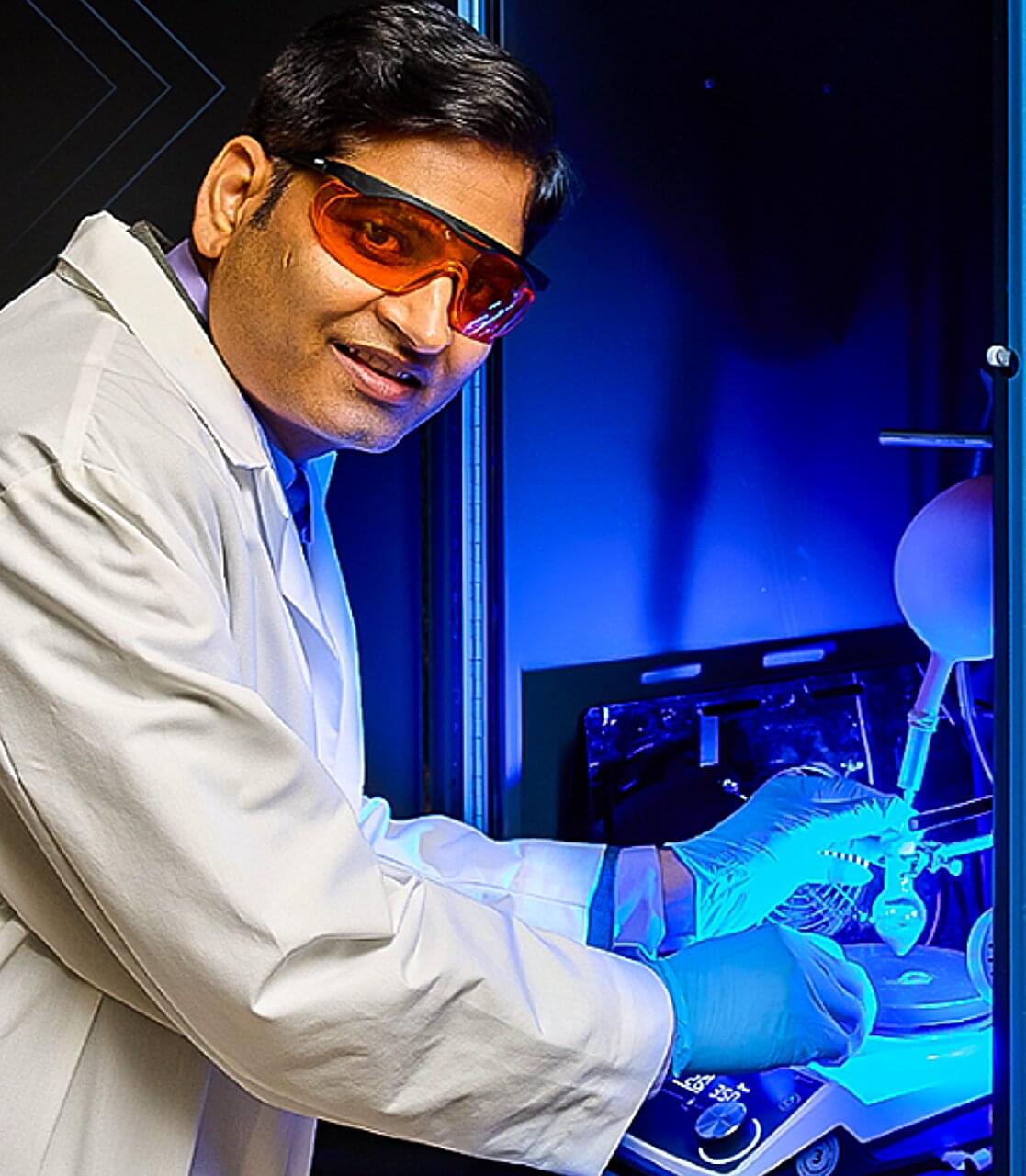



Iron and blue light enable rapid, low-toxicity creation of carbohydrates for new antibiotics
Researchers at the University of Oklahoma have made a discovery that could potentially revolutionize treatments for antibiotic-resistant infections, cancer and other challenging gram-negative pathogens without relying on precious metals.
Currently, precious metals like platinum and rhodium are used to create synthetic carbohydrates, which are vital components of many approved antibiotics used to combat gram-negative pathogens, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a notorious hospital-acquired infection responsible for the deaths of immunocompromised patients. However, these elements require harsh reaction conditions, are expensive to use and are harmful to the environment when mined.
In an innovative study published in the journal Nature Communications, an OU team led by Professor Indrajeet Sharma has replaced these precious metals with either blue light or iron, achieving similar results with significantly lower toxicity, reduced costs, and greater appeal for researchers and drug manufacturers.
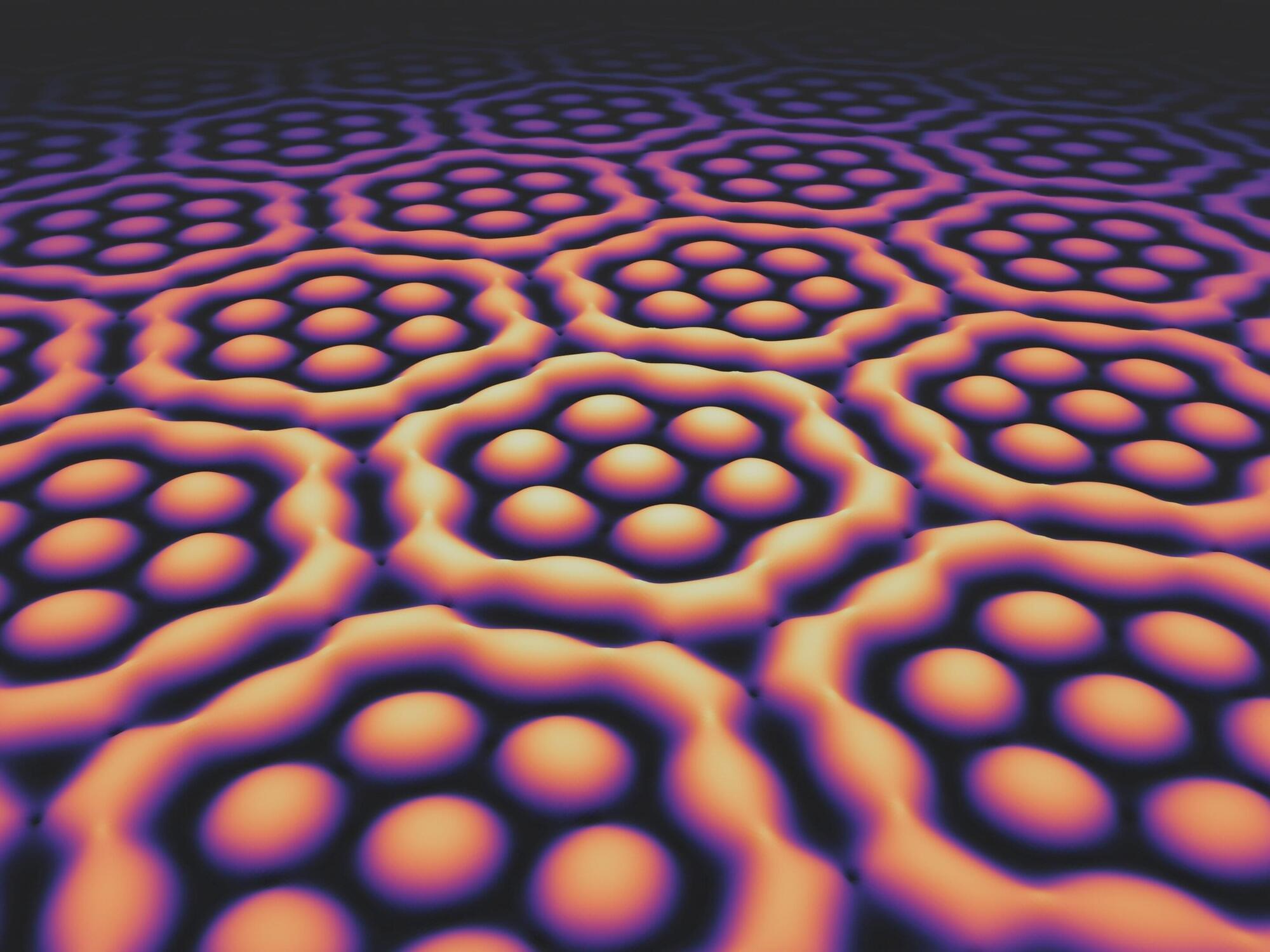
Light fields with extraordinary structure: Plasmonic skyrmion bags
A research group at the University of Stuttgart has manipulated light through its interaction with a metal surface so that it exhibits entirely new properties. The researchers have published their findings in Nature Physics.
“Our results add another chapter to the emerging field of skyrmion research,” proclaims Prof. Harald Giessen, head of the Fourth Physics Institute at the University of Stuttgart, whose group achieved this breakthrough. The team demonstrated the existence of “skyrmion bags” of light on the surface of a metal layer.
Scientists make incredible breakthrough that could help unleash limitless energy source: ‘Trying to make the design process as smooth as possible’
To address issues in stellarator reactors, Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory has developed its QUADCOIL computer code for optimizing and accelerating the design process.