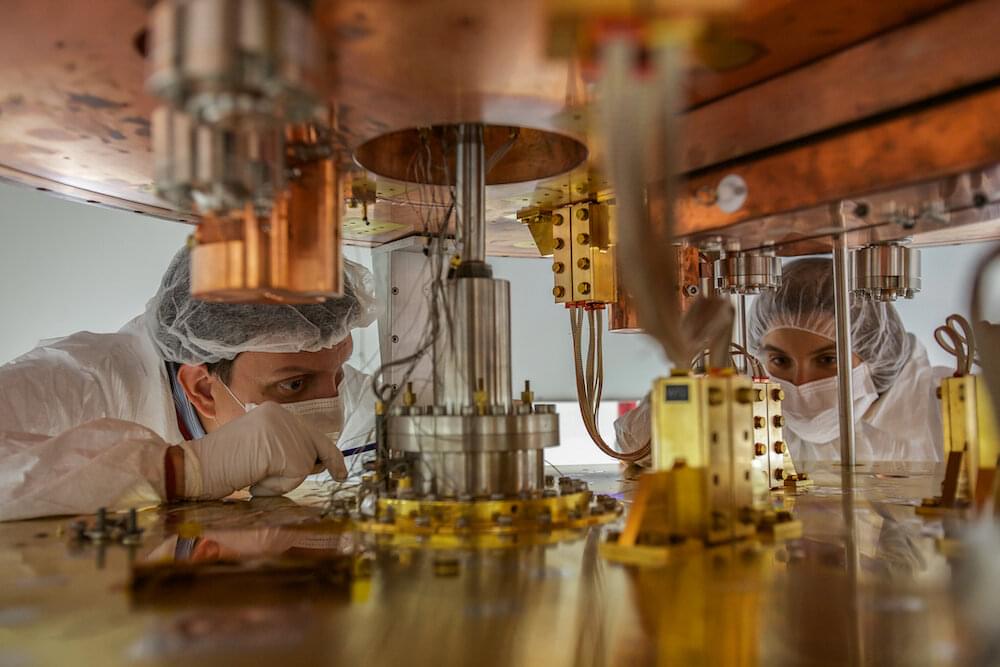
In a laboratory under a mountain, physicists are using crystals far colder than frozen air to study ghostly particles, hoping to learn secrets from the beginning of the universe. Researchers at the Cryogenic Underground Observatory for Rare Events (CUORE) announced this week that they had placed some of the most stringent limits yet on the strange possibility that the neutrino is its own antiparticle. Neutrinos are deeply unusual particles, so ethereal and so ubiquitous that they regularly pass through our bodies without us noticing. CUORE has spent the last three years patiently waiting to see evidence of a distinctive nuclear decay process, only possible if neutrinos and antineutrinos are the same particle. CUORE’s new data shows that this decay doesn’t happen for trillions of trillions of years, if it happens at all. CUORE’s limits on the behavior of these tiny phantoms are a crucial part of the search for the next breakthrough in particle and nuclear physics—and the search for our own origins.
“Ultimately, we are trying to understand matter creation,” said Carlo Bucci, researcher at the Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso (LNGS) in Italy and the spokesperson for CUORE. “We’re looking for a process that violates a fundamental symmetry of nature,” added Roger Huang, a postdoctoral researcher at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and one of the lead authors of the new study.
CUORE—Italian for “heart”—is among the most sensitive neutrino experiments in the world. The new results from CUORE are based on a data set ten times larger than any other high-resolution search, collected over the last three years. CUORE is operated by an international research collaboration, led by the Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN) in Italy and Berkeley Lab in the US. The CUORE detector itself is located under nearly a mile of solid rock at LNGS, a facility of the INFN. U.S. Department of Energy-supported nuclear physicists play a leading scientific and technical role in this experiment. CUORE’s new results were published today in Nature.