
Category: innovation – Page 154

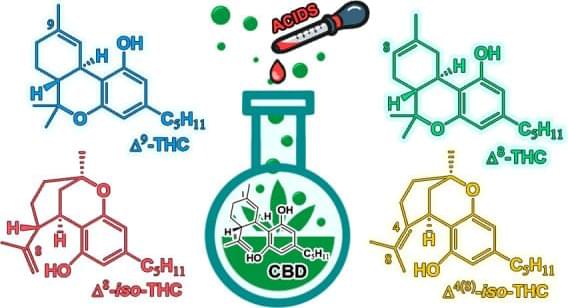
Cannabidiol as the Substrate in Acid-Catalyzed Intramolecular Cyclization
Circa 2020 Lewis acids such as in some candies can active thc in cannibidiol making a room temperature thc activation. Which has been unheard of until now leading to a breakthrough in thc activation at lower temperatures even room temperature through a lewis acid catalyst.
The chemical reactivity of cannabidiol is based on its ability to undergo intramolecular cyclization driven by the addition of a phenolic group to one of its two double bonds. The main products of this cyclization are Δ9-THC (trans-Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) and Δ8-THC (trans-Δ-8-tetrahydrocannabinol). These two cannabinoids are isomers, and the first one is a frequently investigated psychoactive compound and pharmaceutical agent. The isomers Δ8-iso-THC (trans-Δ-8-iso-tetrahydrocannabinol) and Δ4-iso-THC (trans-Δ-4,8-iso-tetrahydrocannabinol) have been identified as additional products of intramolecular cyclization. The use of Lewis and protic acids in different solvents has been studied to investigate the possible modulation of the reactivity of CBD (cannabidiol). The complete NMR spectroscopic characterizations of the four isomers are reported. High-performance liquid chromatography analysis and 1 H NMR spectra of the reaction mixture were used to assess the percentage ratio of the compounds formed.
Recent years have seen a dramatically increasing interest in phytocannabinoids. Isolated from Cannabis in 1940,1,2 cannabidiol (CBD) is one of the most abundant phytocannabinoids in the species of Cannabis for textile uses.3,4 Despite the structural similarity between CBD and Δ9-THC (trans-Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol) (Figure Figure1 1), CBD has a low agonistic effect for cannabinoid receptors; in particular, it is considered an allosteric negative modulator of CB1 and CB2 receptors (cannabinoid receptor types 1 and 2).5,6 Current evidence shows that CBD exerts pharmacological effects via specific molecular targets such as adenosine, glycine, opioid, serotonin, nonendocannabinoid G protein-coupled, nicotinic acetylcholine, and proliferator-activated receptors.7 Moreover, CBD shows anticonvulsant, antispasmodic, anxiolytic, antinausea, antirheumatoid arthritis, and neuroprotective properties.
A new computer cooling method enables a 740 percent increase in power per unit
We have all had the experience of one of our electronic devices overheating. Needless, to say that when that happens, it becomes dangerous both for the device and its surroundings. But considering the speed at which devices work, is overheating avoidable?
A 740 percent increase in power per unit.
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC) and the University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley) have recently devised an invention that could cool down electronics more efficiently than other alternative solutions and enable a 740 percent increase in power per unit, according to a press release by the institutions published Thursday.

General AI through scaling: Meta’s AI chief Yann LeCun speaks out
Does the breakthrough to general AI need more data and computing power above all else? Yann LeCun, Chief AI Scientist at Metaon the recent debate about scaling sparked by Deepmind’s Gato.
The recent successes of large AI models such as OpenAI’s DALL-E 2, Google’s PaLM and Deepmind’s Flamingo have sparked a debate about their significance for progress towards general AI. Deepmind’s Gato has recently given a particular boost to the debate, which has been conducted publicly, especially on Twitter.
Gato is a Transformer model trained with numerous data modalities, including images, text, proprioception or joint moments. All training data is processed by Gato in a token sequence similar to those of large language models. Thanks to the versatile training, Gato can text, describe images, play video games or control robotic arms. Deepmind tested the AI model with over 600 benchmarks.

Is DeepMind’s Gato AI really a human-level intelligence breakthrough?
😃
DeepMind has released what it calls a “generalist” AI called Gato, which can play Atari games, accurately caption images, chat naturally with a human and stack coloured blocks with a robot arm, among 600 other tasks. But is Gato truly intelligent – having artificial general intelligence – or is it just an AI model with a few extra tricks up its sleeve?
What is artificial general intelligence (AGI)?
Outside science fiction, AI is limited to niche tasks. It has seen plenty of success recently in solving a huge range of problems, from writing software to protein folding and even creating beer recipes, but individual AI models have limited, specific abilities. A model trained for one task is of little use for another.

Dell Technologies expands edge innovations for retailers
Dell Technologies announces the expansion of its edge solutions to help retailers quickly generate more value and deliver enhanced customer experiences from data generated in retail locations.
From grocery merchandising and curbside pickup to frictionless checkout and loss prevention, retailers have embraced edge technologies to keep pace with industry demands and create better customer experiences. A recent study conducted by 451 Research, part of S&P Global Market Intelligence, and commissioned by Dell found this growth will continue with 77% of retailers expecting to increase edge deployments significantly in the next two years1. However, without a holistic approach, new technologies across wide geographies and locations can lead to complex and siloed solutions that drive up a retailer’s IT management cost.
“Retailers are increasingly relying on IT technologies and data at the edge to offer more personalized and intelligent customer experiences that drive better business outcomes, dramatically accelerating the need for retailers to bring together siloed technologies,” said Gil Shneorson, senior vice president of edge solutions, Dell Technologies. “We’re helping retailers easily consolidate these technologies so they can analyze data where it’s created, make faster decisions and deliver positive experiences for in-store shoppers and employees.”

The supermassive black hole at the heart of our galaxy proves Einstein right
Here’s how over 300 astronomers captured the dazzling first image of Sagittarius A*, and why it matters.
Our team was part of the global Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) Collaboration, which has used observations from a worldwide network of eight radio telescopes on our planet — collectively forming a single, Earth-sized virtual telescope — to take the stunning image. The breakthrough follows the collaboration’s 2019 release of the first-ever image of a black hole, called M87*, at the center of the more distant Messier 87 galaxy.
Black holes: Looking into darkness
The team observed Sagittarius A* on multiple nights, collecting data for many hours in a row, similar to using a long exposure time on a camera. Although we cannot see the black hole itself, because it is completely dark, glowing gas around it reveals a tell-tale signature: a dark central region (called a “shadow”) surrounded by a bright ring-like structure. The new view captures light bent by the powerful gravity of the black hole, which is four million times more massive than our Sun. The discovery also yields valuable clues about the workings of black holes, which are thought to reside at the center of most galaxies.

How Israel used innovation to beat its water crisis
Israel is a desert, and water resources are scarce, but today it produces 20% more water than it needs. What can the world learn from Israel’s experience?
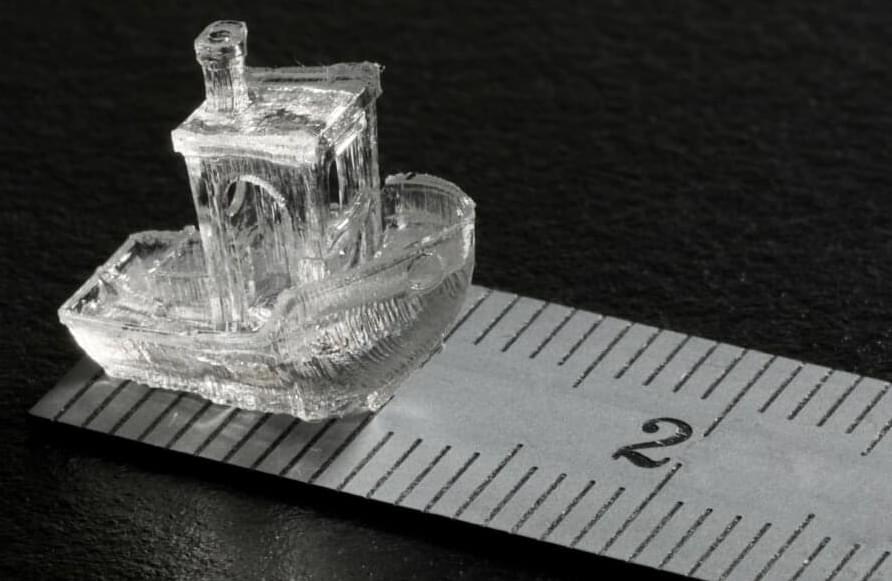

Light-based 3D printing technique prints full objects in just seconds
Circa 2020
Researchers have created a new 3D printing technique that could replace traditional 3D printers that take far to long to create desired objects.
The problem with traditional 3D printers is that they work in horizontal layers. This process is the bane of 3D printing, as it means that, depending on the size of the object, it will take time to construct. What if the printer could build the entire model all at once, instead of layer-by-layer? Researchers from Switzerland’s Ecole polytechnique federale de Lausanne (EPFL) have done just that with their new invention.