A CNS 2021 provided an incredible opportunity to learn more how the anatomy and integrity of brain networks impact higher-level cognition.
In the 19th and 20th century, cases of individuals with brain injury, such as Phineas Gage or Henry Molaison, have advanced our understanding of the relationship between the anatomy of the brain and its function. Back then, methods were limited to investigate whole-brain structure and function. Now, cognitive neuroscientists have some ability to visualize and measure activity of the whole brain at once, as well as the computational tools to investigate complex network-level relationships between brain structure, brain function, and behavior.
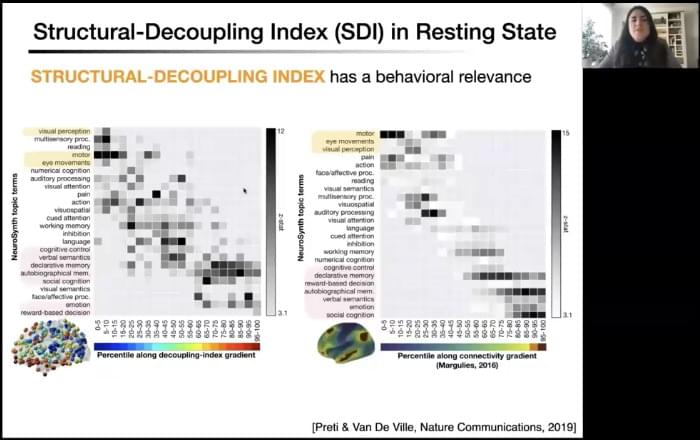
As a doctoral student working on stroke recovery, attending the CNS 2021 symposium led by Danielle Bassett was an incredible opportunity to learn more about some of the most recent methods that have been developed to understand how the anatomy and integrity of brain networks impact higher-level cognition. Strokes highly disrupt anatomical and functional connectivity, leading to cognitive and motor impairments. In individuals with post-stroke language impairments, namely aphasia, evidence shows that the more functional brain networks recover an organization similar to healthy individuals the better the recovery (Kiran et al., 2019). Understanding the relationship between brain structure and function in health and disease is therefore essential to develop appropriate treatments.
At this CNS symposium, the speakers showed how different models can help us better understand brain structural organization and how this particular organization constrains cognitive processes. They also showed direct relationships between alteration of anatomical networks, caused by disease or behavioral training, and changes in behavioral performance.