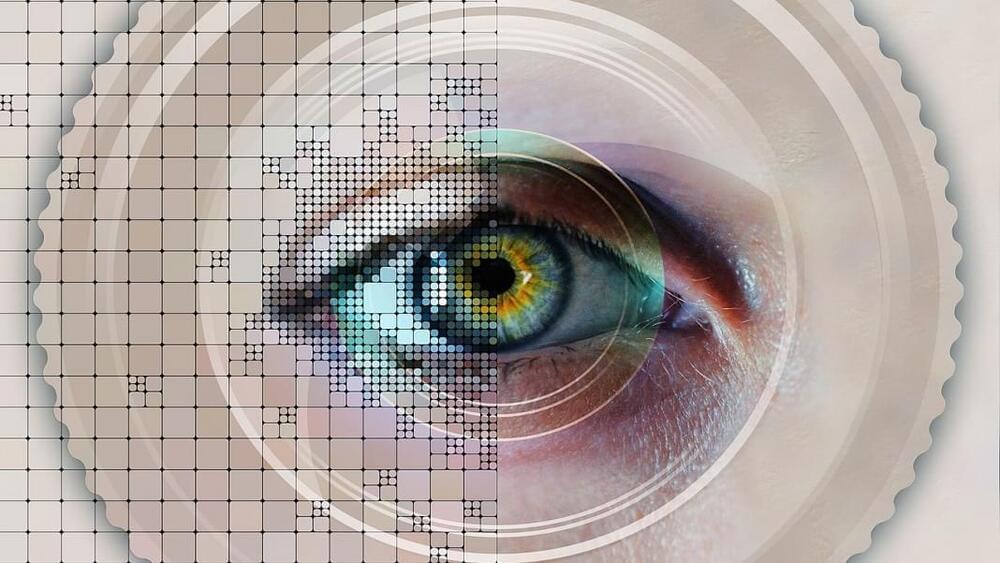
They then used QUARTZ to analyze retinal images from 7,411 more people, these aged 48 to 92, and combined this data with information about their health history (such as smoking, statin use, and previous heart attacks) to predict their risk of heart disease. Participants’ health was tracked for seven to nine years, and their outcomes were compared to Framingham risk score (FRS) predictions.
A common tool for estimating heart disease risk, the FRS looks at age, gender, total cholesterol, high density lipoprotein cholesterol, smoking habits, and systolic blood pressure to estimate the probability someone will develop heart disease within a given span of time, usually 10 to 30 years.
The QUARTZ team compared their data to 10-year FRS predictions and said the algorithm’s accuracy was on par with that of the conventional tool.