High-intensity exercise induces brain-protective effects that have the potential to not just slow down but possibly reverse the neurodegeneration associated with Parkinson’s disease, a new pilot study suggests.
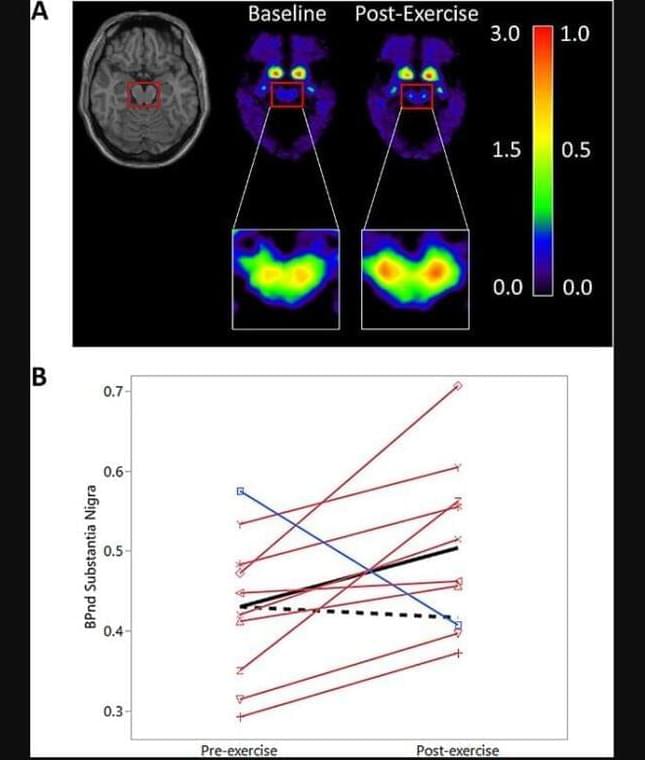
Prior research has shown that many forms of exercise are linked to improved symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. But there has been no evidence that hitting the gym could create changes at the brain level. Now, a small proof-of-concept study involving 10 patients showed that high-intensity aerobic exercise preserved dopamine-producing neurons, the brain cells that are most vulnerable to destruction in patients with the disease.
In fact, after six months of exercise, the neurons actually had grown healthier and produced stronger dopamine signals. Dopamine is a chemical that helps brain cells communicate with one another. The researchers published their findings in npj Parkinson’s Disease on February 9.