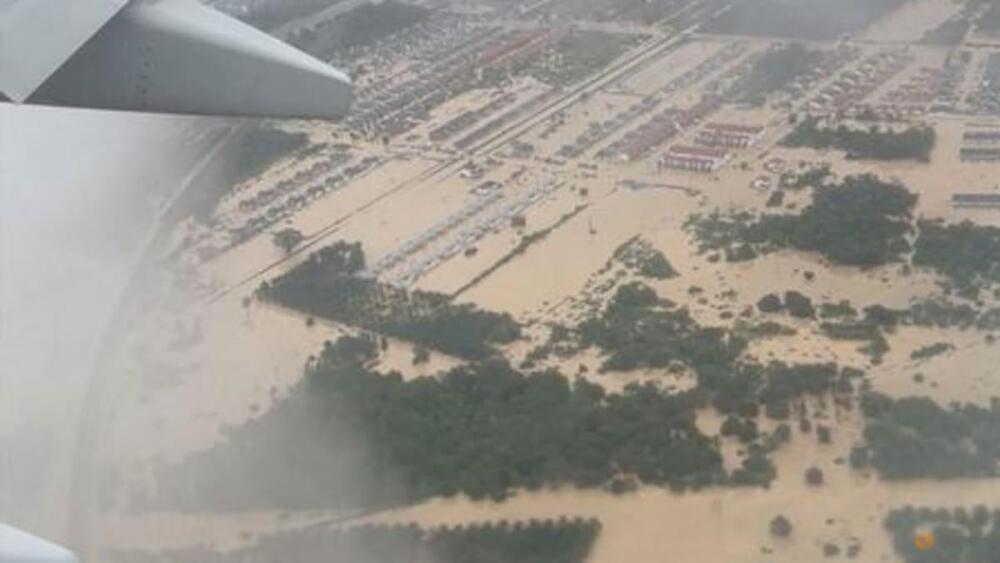
How far our safety regulations have come…
Dr Suzannah Lipscomb looks at the hidden dangers of the British post-war home. In the 1950s, people embraced modern design for the first time after years of austerity and self-denial. The modern home featured moulded plywood furniture, fibreglass, plastics and polyester — materials and technologies that were developed during World War II.
Content licensed from DRG. Any queries, please contact us at: [email protected]