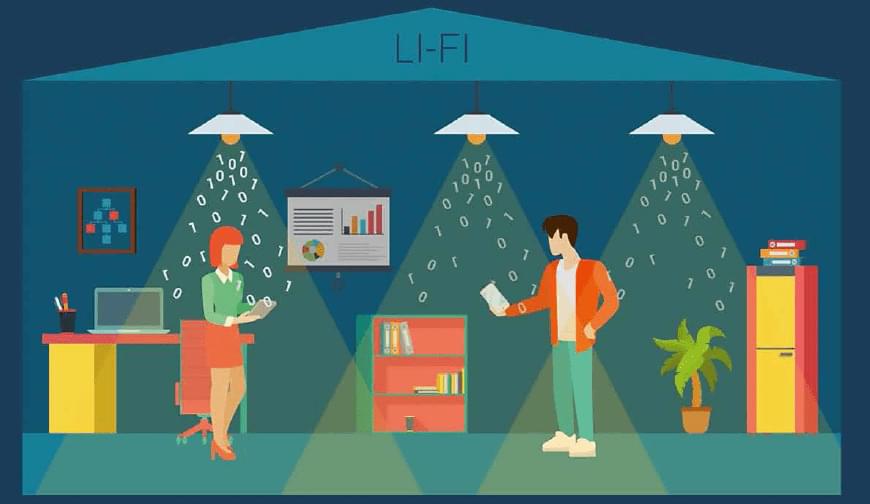
The recent ratification of the IEEE 802.11bb standard represents a seismic shift in wireless communication, offering a new frontier that goes beyond Wi-Fi: LiFi (Light Fidelity). Utilizing infrared light instead of radio waves, this standard brings LiFi technology closer to mainstream adoption. This article delves into what this innovative standard means for various applications, including smart homes, healthcare, retail, and more.
The Core of IEEE 802.11bb
The IEEE 802.11bb standard serves as a robust framework for secure, reliable, and high-speed wireless communication. Unlike traditional LiFi that used visible light, this new standard utilizes infrared (IR) lightwaves, invisible to the human eye but highly effective for transmitting data at lightning speeds.